Free Area and Perimeter Worksheets for All Grades

Understanding area and perimeter is fundamental to mastering geometry and spatial reasoning, essential skills for students across all grade levels. These concepts not only aid in problem-solving but also pave the way for advanced mathematical understanding. In this extensive blog post, we delve into the importance of area and perimeter, explore the educational approaches to teaching these topics, provide free resources for all grades, and discuss how these concepts are applied in real-world scenarios.
Why Area and Perimeter Matter

Area and perimeter are cornerstones in mathematics education for several reasons:
- Foundation for Geometry: They introduce students to the basic principles of shapes, spatial relationships, and measurements.
- Real-Life Application: From measuring the living space in a home to calculating materials needed for a garden or craft project, understanding area and perimeter is practical.
- Conceptual Understanding: Students learn about formulas, why they work, and how to derive them, fostering a deeper mathematical understanding.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Calculating area and perimeter challenges students to use logical reasoning and mathematical formulas in various contexts.
Teaching Area and Perimeter

Educational strategies for teaching area and perimeter can be adapted based on students' age and developmental stage:
For Early Learners

- Introduce basic shapes using tangible objects like blocks, tiles, or cut-out shapes.
- Emphasize understanding the concept of counting units to find the area and the length of the edges for perimeter.
- Use interactive activities where students physically measure perimeters with string or outline shapes with their fingers.
Elementary and Middle School
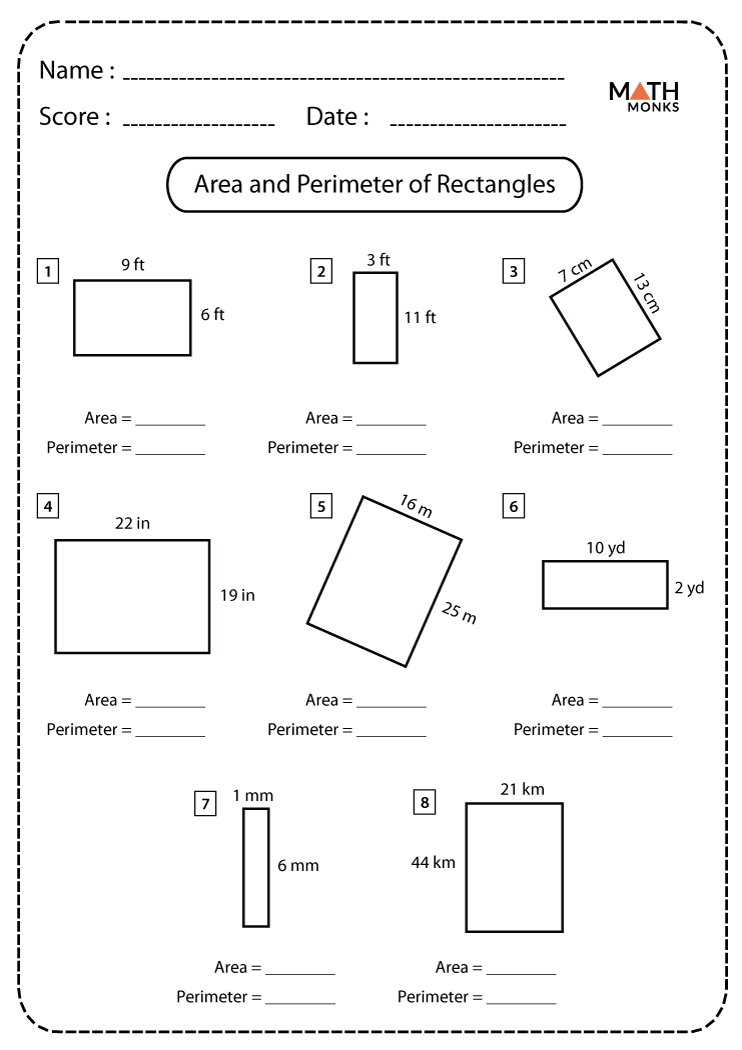
- Formula-based learning: Introduce formulas for different shapes, starting with simple ones like rectangles (A = l x w, P = 2l + 2w).
- Engage students with puzzles and games that require them to calculate areas and perimeters.
- Project-based learning where students design or construct shapes from given dimensions, enhancing their understanding of how area and perimeter relate.
High School and Beyond

- Advanced geometry and calculus: Students explore area and volume of complex shapes and surfaces.
- Real-world applications: Case studies or scenarios that require mathematical analysis, like calculating land area for zoning purposes or optimizing packaging.
- Mathematical proofs: Encourage students to prove area and perimeter formulas, promoting deeper comprehension.
Free Area and Perimeter Worksheets

To help educators and students explore these concepts, we provide free downloadable worksheets designed for different grade levels:
| Grade Level | Skills Covered |
|---|---|
| K-1 | Basic counting, identifying shapes, and simple measurements. |
| 2-3 | Calculating perimeter, introduction to area using unit squares. |
| 4-5 | Perimeter and area of rectangles, squares, and simple composite shapes. |
| 6-8 | Perimeter and area for triangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and more complex shapes. |
| 9-12 | Advanced problems, real-world applications, and geometry proofs. |

📚 Note: While these worksheets are useful, they should complement, not replace, hands-on learning and interactive discussions in class.
Integrating Technology

Modern educational tools can make learning about area and perimeter more engaging:
- Virtual Manipulatives: Apps and interactive websites allow students to dynamically change shapes and observe changes in area and perimeter.
- Mathematical Software: Tools like GeoGebra offer interactive geometry lessons, where students can calculate, experiment, and visualize area and perimeter concepts.
- Game-Based Learning: Educational games that integrate math can make practice sessions fun and educational.
Practical Applications in Everyday Life

Students often wonder why they need to know about area and perimeter. Here are some real-life applications:
- Home Improvement: Calculating the amount of paint, wallpaper, or flooring needed for home projects.
- Gardening: Determining the amount of soil, mulch, or seed required for different garden bed shapes.
- Construction: Architects and builders use area and perimeter calculations to design and estimate project materials.
- Manufacturing: Cutting materials to fit into containers or packaging in the most space-efficient way.
🚧 Note: These applications not only highlight the relevance of geometry but also stimulate problem-solving skills in everyday scenarios.
In essence, the journey through understanding area and perimeter is one that combines theoretical knowledge with practical application, enriching both the educational experience and real-world problem-solving skills. By providing tailored resources, integrating technology, and fostering real-world applications, educators can empower students to excel in geometry and beyond.
What’s the difference between area and perimeter?

+
Perimeter refers to the total distance around the outside of a shape, while area is the measure of the space inside a shape, typically expressed in square units.
How can I make learning about area and perimeter fun for my kids?

+
Incorporate games, puzzles, and real-world scenarios into learning. Use interactive tools like apps or virtual manipulatives where kids can experiment with shapes and see immediate changes in area and perimeter.
Why is understanding area and perimeter important for daily life?

+
These concepts are crucial for tasks like home decorating, gardening, construction, and even everyday decision-making like choosing the best packing options. Understanding spatial measurements aids in efficient planning and use of resources.