Hess's Law Worksheet: Simplify Enthalpy Calculations Easily

When dealing with chemical reactions, understanding how heat is exchanged between reactants and products can be crucial for predicting behavior and efficiency. Hess's Law provides a straightforward approach to calculating enthalpy changes, which are essentially the heat content of a system. By applying this principle, scientists and students alike can predict the heat exchanged in reactions without physically conducting every possible experiment. Here's a comprehensive guide to mastering Hess's Law with a worksheet designed to enhance your understanding.
Understanding Hess’s Law

Hess’s Law states that the total enthalpy change for a reaction is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or several steps. This principle is based on the fact that enthalpy is a state function, which means the enthalpy change depends only on the initial and final states of the system, not on the path taken to reach that state.
The Basics
- State Function: Enthalpy (ΔH) is a property that depends only on the state of the system, not on how the system reached that state.
- Path Independence: The sum of enthalpy changes for a series of individual steps that make up an overall reaction will equal the enthalpy change of the overall reaction.
Why Use Hess’s Law?
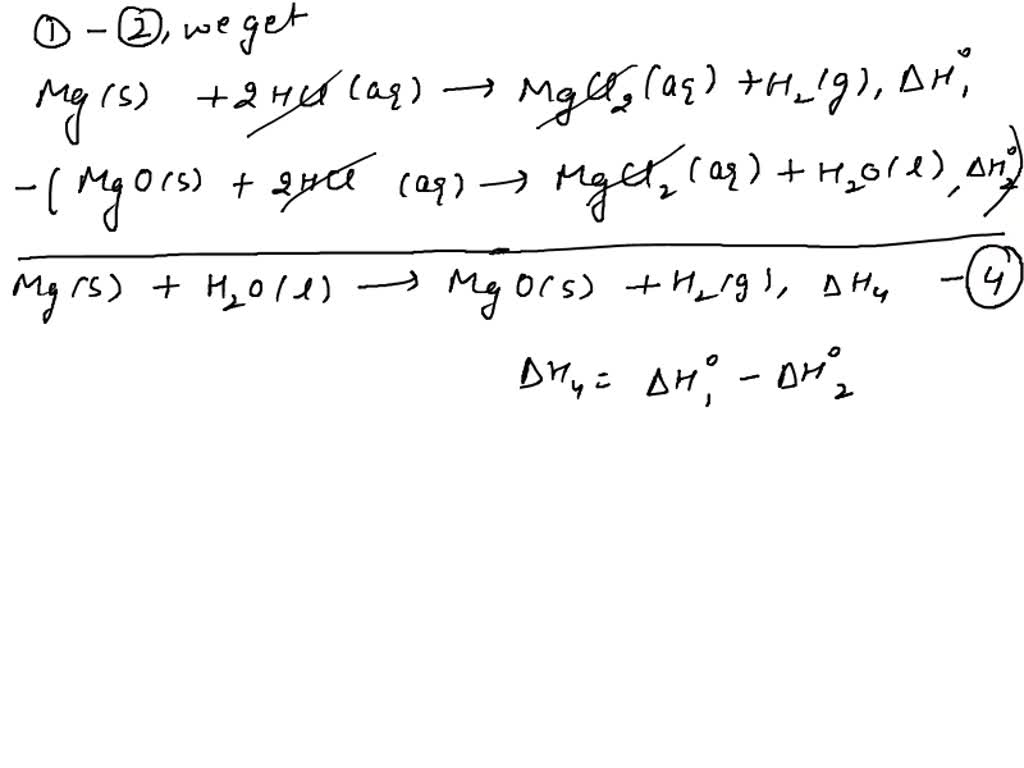
Hess’s Law allows us to:
- Calculate the enthalpy change for reactions that are difficult or impossible to measure directly.
- Use known enthalpy changes to find unknowns.
- Save time and resources in experimental setups.
Application: Constructing an Energy Cycle
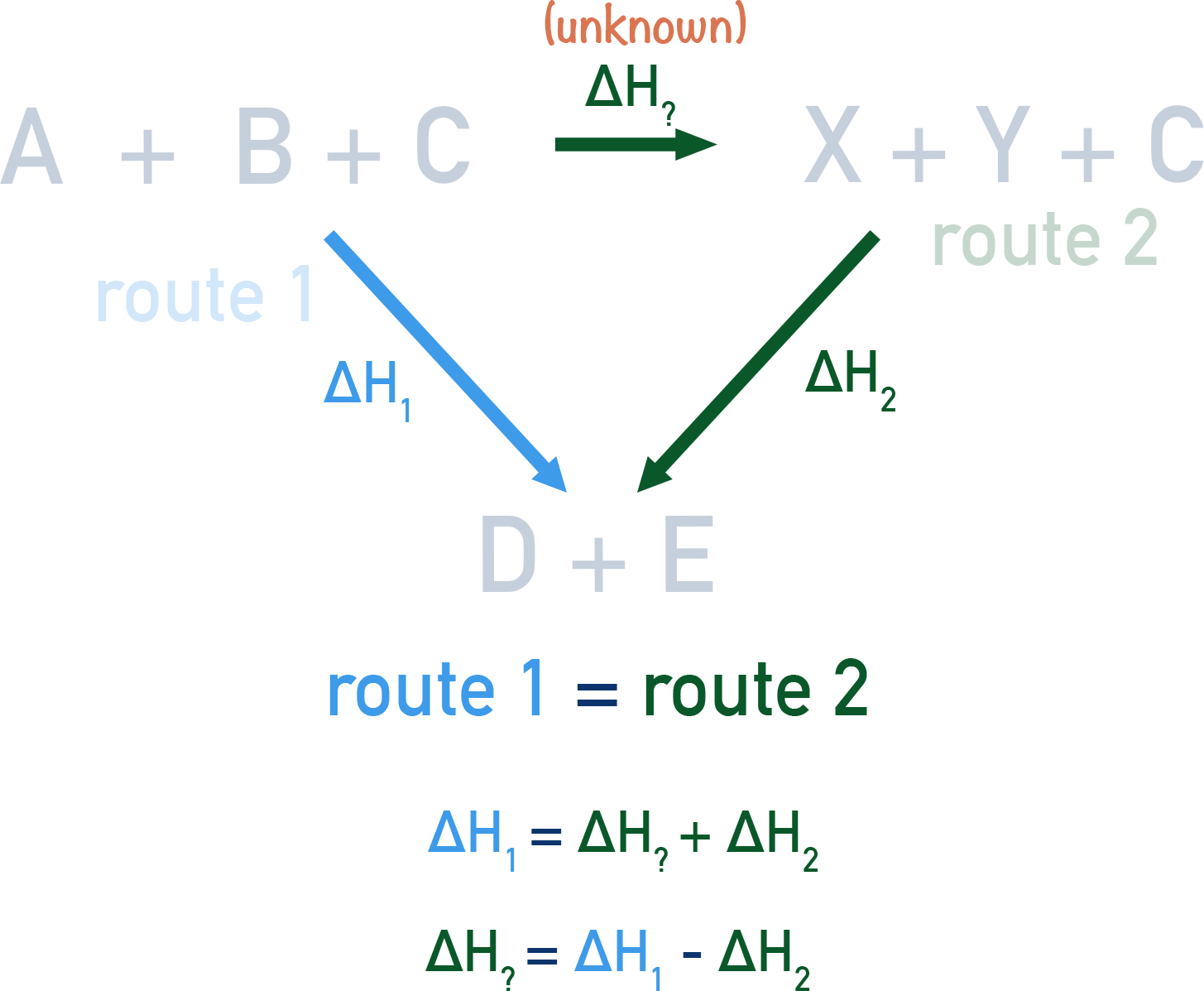
An energy cycle or Hess’s cycle is a visual representation of the enthalpy changes involved in a series of chemical reactions. Here’s how to construct one:
Steps to Constructing an Energy Cycle

- Identify the main reaction: Write down the balanced chemical equation for the reaction you’re interested in.
- Find reactions that can be combined: Look for reactions where products from one reaction are reactants in another.
- Draw the cycle: Use arrows to depict energy flows, ensuring that:
- The arrows indicate the direction of heat flow (exothermic or endothermic).
- All intermediates are accounted for.
- Add known ΔH values: Assign enthalpy changes to each step, taking care with signs.
- Sum to get the net enthalpy change: Add or subtract the ΔH values according to the direction of the reactions.
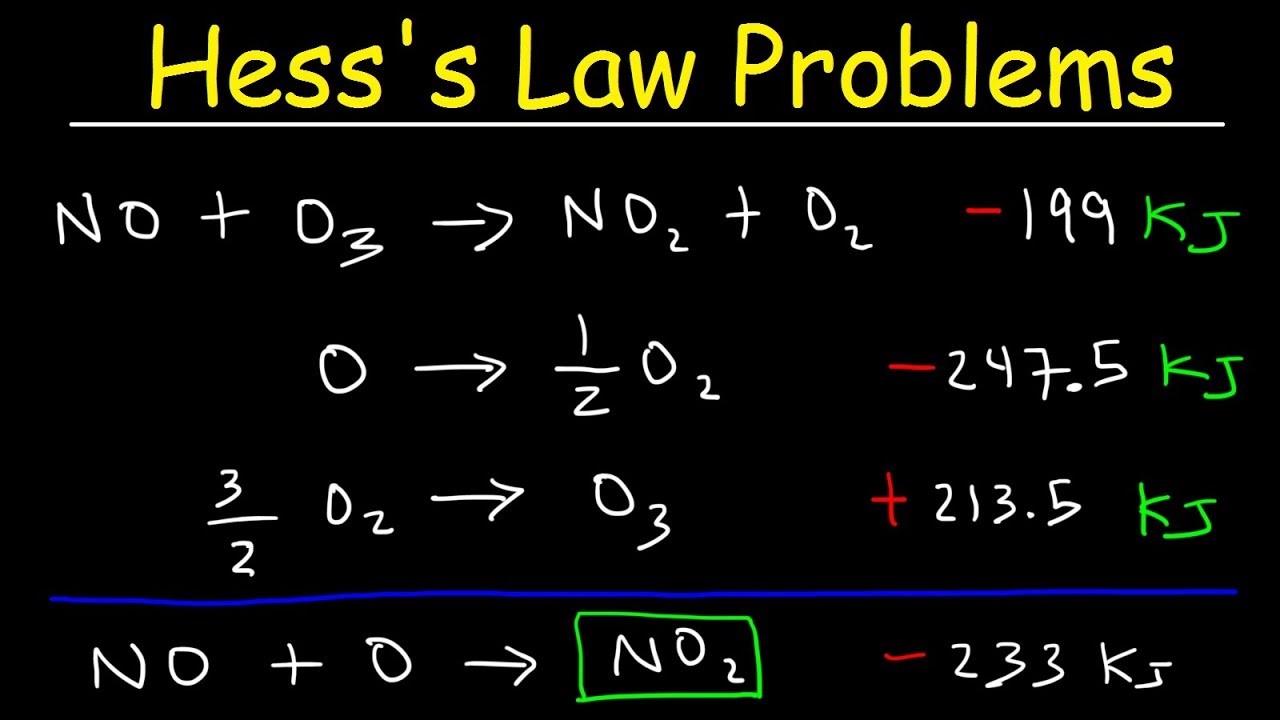
Hess’s Law Worksheet: Practice Scenarios

Let’s apply what we’ve learned with some example problems:
| Scenario | Reactions | ΔH (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1 | A + B → C C → D + E |
-72 95 |
| Scenario 2 | F + G → H + I H + J → K |
40 -150 |
| Scenario 3 | L + M → N N → O + P P → Q + R |
12 -35 20 |

Each scenario above outlines reactions and their respective enthalpy changes. To solve for the net enthalpy change, follow the steps outlined:
Step-by-Step Solutions
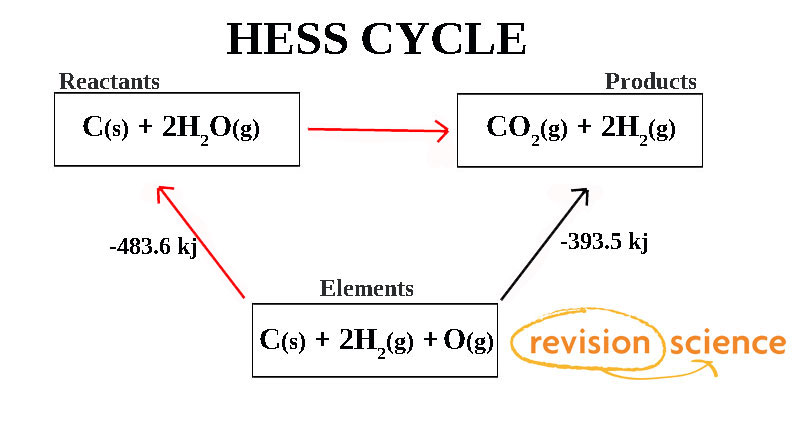
Scenario 1
- Identify the main reaction: A + B → D + E
- Set up the cycle:
- A + B → C (ΔH = -72 kJ/mol)
- C → D + E (ΔH = 95 kJ/mol)
- Add the ΔH values (since both reactions are in the direction of the main reaction):
- ΔHtotal = -72 + 95 = 23 kJ/mol
Scenario 2
Follow similar steps to calculate the enthalpy change for the desired reaction.
Scenario 3
Using the same method, you can determine the net enthalpy change for this sequence of reactions.
🔧 Note: When adding or subtracting enthalpy changes, be mindful of the reaction's direction and ensure the cycle accurately represents all steps of the process.
Understanding and practicing Hess's Law not only enhances your problem-solving skills in chemistry but also provides a deeper insight into the nature of energy in chemical systems. By completing these worksheets, you'll gain confidence in handling complex enthalpy calculations, improving your ability to predict and explain the outcomes of chemical reactions without the need for direct measurement.
Mastering Hess's Law requires both theoretical knowledge and practical application. This worksheet provides a structured approach to learning, ensuring that each step in the process is clear and logical. With continuous practice, the principles of Hess's Law will become second nature, allowing you to navigate through the world of enthalpy changes with ease.
What is Hess’s Law used for in chemistry?

+
Hess’s Law is used to calculate the standard enthalpy of a reaction without needing to perform the reaction itself. It’s particularly useful for predicting the enthalpy change of reactions that are difficult or impossible to measure directly, by using known enthalpy changes of other reactions.
Why is it important that enthalpy is a state function?

+
Enthalpy being a state function means that its value depends only on the initial and final states of the system, not on the path taken. This property allows for the application of Hess’s Law, where you can add or subtract the enthalpy changes of intermediate steps to get the total change for the overall reaction.
Can you explain how to know when to add or subtract enthalpy changes in a Hess cycle?
+
When constructing a Hess cycle, you add enthalpy changes if the reactions are in the direction that helps reach the final state of your main reaction. Conversely, if a reaction needs to be reversed to contribute to the cycle, you subtract its ΔH value. This can be tricky, so always ensure the cycle represents the reaction path correctly.
How can I check my calculations for accuracy?
+
To verify your calculations:
- Ensure all intermediate steps are accounted for.
- Check if the signs of the enthalpy changes are correct based on the direction of the reactions in your cycle.
- Sum up the enthalpy changes correctly and make sure they align with the expected outcome of the reaction.