6 Essential Answers for Geometry Worksheet 2.6
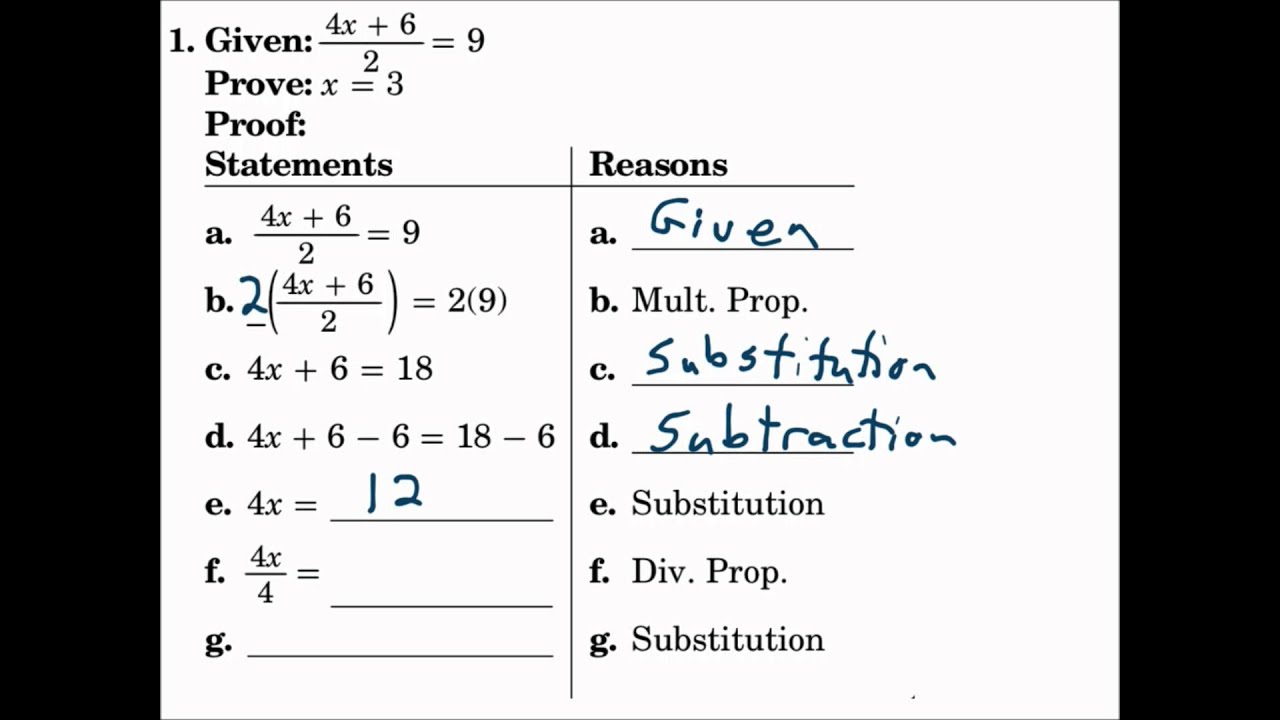
Geometry Worksheet 2.6, often an integral part of high school math curricula, challenges students with a variety of problems that push the boundaries of their understanding of geometric principles. This worksheet typically involves topics like parallel lines, transversals, angles, triangles, and congruent shapes. Let's delve into six essential answers and concepts that are commonly explored in such an assignment to better understand and tackle these geometric challenges.
Understanding Parallel Lines and Angles

One of the fundamental concepts in Geometry Worksheet 2.6 is understanding the relationships between angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal.
- Corresponding Angles: When two parallel lines are cut by a transversal, corresponding angles are congruent.
- Alternate Interior Angles: These angles are inside the parallel lines on opposite sides of the transversal and are also congruent.
- Consecutive Interior Angles: These are interior angles that lie on the same side of the transversal, and their sum equals 180 degrees.
✏️ Note: Use the properties of parallel lines to simplify solving these problems without needing to calculate each angle individually.
Triangle Congruence

Another common topic in Geometry Worksheet 2.6 is proving triangle congruence, which involves different methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| SSS (Side-Side-Side) | All three sides of triangles are equal. |
| SAS (Side-Angle-Side) | Two sides and the included angle between them are equal. |
| ASA (Angle-Side-Angle) | Two angles and the included side between them are equal. |
| AAS (Angle-Angle-Side) | Two angles and a non-included side are equal. |

Understanding these methods can help students in various geometric proofs and applications.
The Sum of Interior Angles of a Triangle
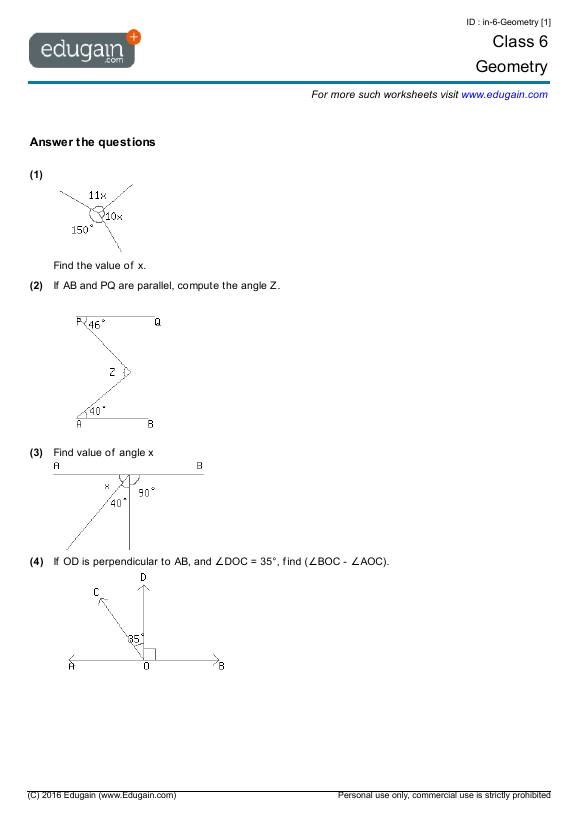
One of the key facts in geometry is that the sum of the interior angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees. This principle is crucial for solving problems related to angles and triangles in Worksheet 2.6.
Isosceles and Equilateral Triangles

When dealing with isosceles and equilateral triangles, students often need to apply the following concepts:
- In an isosceles triangle, the base angles are equal, and the altitude from the vertex angle splits the base into two equal segments.
- In an equilateral triangle, all sides and angles are equal, with each angle measuring 60 degrees.
Pythagorean Theorem

The Pythagorean theorem is a pivotal tool for students to calculate the sides of right triangles, which frequently appear in Geometry Worksheet 2.6:
- Formulation: a^2 + b^2 = c^2 where c is the hypotenuse.
- It's used not only to find the hypotenuse but also to verify if three sides can form a right triangle.
Using Coordinates in Geometry

Geometry isn't just about shapes on paper; coordinates play a significant role:
- Distance Formula: Calculate the distance between two points.
- Midpoint Formula: Find the center point between two given points.
- Slope Formula: Determine the gradient of a line or the properties of a triangle.
These formulas help bridge the gap between algebra and geometry, providing tools to analyze geometric figures in a coordinate plane.
In the exploration of Geometry Worksheet 2.6, students encounter these key concepts and more, which not only test their understanding of geometric principles but also their ability to apply these principles to solve problems. Each answer or solution contributes to a deeper understanding of the subject, enhancing logical thinking and mathematical skills. The key to mastering these questions lies in recognizing patterns, remembering theorems, and applying them methodically.
How do you determine if lines are parallel?

+
To determine if lines are parallel, check if the corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, or consecutive interior angles are congruent when a transversal cuts through them.
What is the significance of proving triangles congruent?

+
Proving triangles congruent is significant because it ensures that properties (like angles, sides, or perimeters) are identical, which is essential for solving many geometric problems and proofs.
Why is the sum of interior angles in a triangle always 180 degrees?

+
The sum of interior angles in a triangle is always 180 degrees because if you draw a straight line through one vertex, it forms two supplementary angles with the third angle, summing up to 180 degrees.



