7 Essential Tips for Enzyme Activity Worksheet Answers

In the dynamic world of biological sciences, understanding enzyme activity is crucial for students and researchers alike. Enzymes, the biological catalysts, are fundamental to nearly all processes that sustain life. An enzyme activity worksheet not only tests your understanding of these proteins but also enhances your skills in experimental design, data analysis, and interpretation. Here are seven essential tips to effectively tackle an enzyme activity worksheet and maximize your learning outcome:
1. Understand the Basics of Enzyme Function


Before diving into the specifics of an enzyme activity worksheet, ensure you have a firm grasp on the fundamentals:
- Enzyme-Substrate Complex: Enzymes bind to substrates at active sites to form enzyme-substrate complexes. The fit between the enzyme and its substrate can be explained by the “lock and key” model or the more dynamic “induced fit” model.
- Catalysis: Enzymes lower the activation energy of reactions, speeding up biological processes.
- Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity: Temperature, pH, substrate concentration, enzyme concentration, and inhibitors can all influence enzyme activity.
2. Review the Experimental Setup

Every enzyme activity worksheet will typically require you to interpret data from an experiment. Here’s how to approach this:
- Identify the variables (dependent, independent, and controlled).
- Understand the method used for measuring enzyme activity, like colorimetry, spectroscopy, or product detection.
- Check if there are any controls or inhibitors present in the setup.
🧐 Note: Always ensure you understand the purpose of each part of the experimental setup, including how the enzyme activity is measured.
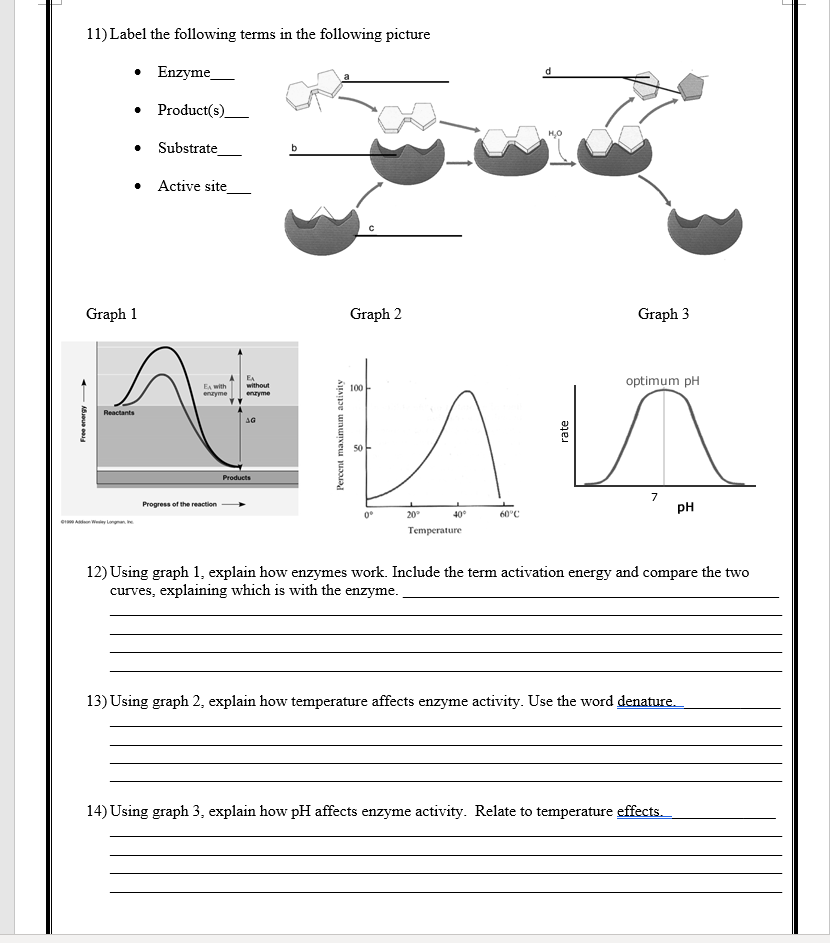
3. Analyze Enzyme Kinetics

The Michaelis-Menten equation is central to understanding enzyme kinetics:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Vmax | The maximum rate of reaction when the enzyme is fully saturated with substrate. |
| Km | The substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax. |

When analyzing data from your worksheet, consider:
- The initial rate of reaction at different substrate concentrations.
- The effect of changing conditions on Vmax and Km.
4. Interpret Graphs and Data Correctly

Graphs are pivotal in visualizing enzyme activity data:
- Lineweaver-Burk Plot: Useful for determining Km and Vmax through linear regression.
- Effect of Inhibitors: Study how competitive, non-competitive, and uncompetitive inhibitors affect the shape and position of enzyme activity graphs.
- Plotting: Ensure you’re plotting the correct variables on the x and y axes (e.g., substrate concentration vs. rate of reaction).
5. Deal with Inhibition and Enzyme Control

Enzyme inhibitors are a common focus in worksheets. Here’s what to look for:
- Competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme’s active site, reducing its activity.
- Non-competitive inhibitors bind elsewhere on the enzyme, affecting its ability to catalyze the reaction.
- Uncompetitive inhibitors only bind to the enzyme-substrate complex, altering the kinetics.
Ensure you understand the different types of inhibition and how they change the enzyme’s behavior.
6. Experiment Design and Optimization

Worksheets might ask you to design experiments or optimize conditions for enzyme activity:
- Consider the enzyme’s optimal conditions for temperature and pH.
- Think about how to measure the enzyme activity accurately.
- Assess potential confounding variables and how to control for them.
🔬 Note: Designing an experiment means not just setting up conditions but also anticipating potential issues and how to resolve them.
7. Application of Concepts to Real-life Scenarios
Connecting theory to practice:
- Enzyme inhibitors in medicine as drugs or toxins.
- Industrial applications where enzymes are optimized for efficiency.
- Use of enzymes in food production, biotechnology, and environmental applications.
Summing up, mastering enzyme activity worksheets involves understanding the basics, carefully analyzing data, interpreting results correctly, and applying these concepts to real-life scenarios. This process not only hones your scientific skills but also deepens your appreciation for how enzymes drive the metabolic engine of life.
What is the significance of Vmax in enzyme kinetics?

+
Vmax represents the maximum rate of enzyme-catalyzed reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate. It indicates the enzyme’s efficiency at high substrate concentrations.
How do enzyme inhibitors affect enzyme function?

+
Enzyme inhibitors can reduce or block the catalytic activity of enzymes by binding to them in different ways, thus altering the rate of reaction. Competitive inhibitors compete with the substrate for the active site, while non-competitive inhibitors bind elsewhere, changing the enzyme’s shape.
Can enzymes work indefinitely without degradation?

+
No, enzymes are subject to degradation and can lose their catalytic activity over time. This can happen due to extreme pH, high temperature, or proteolytic enzymes breaking them down.