Ecological Pyramids Answer Key: 5 Quick Insights

Ecological pyramids offer a visual representation of the structure of ecosystems, highlighting the relationships between different levels of biological organization. These diagrams provide insights into energy flow, biomass, and the number of organisms at various trophic levels. Here are five quick insights to understand the significance of ecological pyramids better.
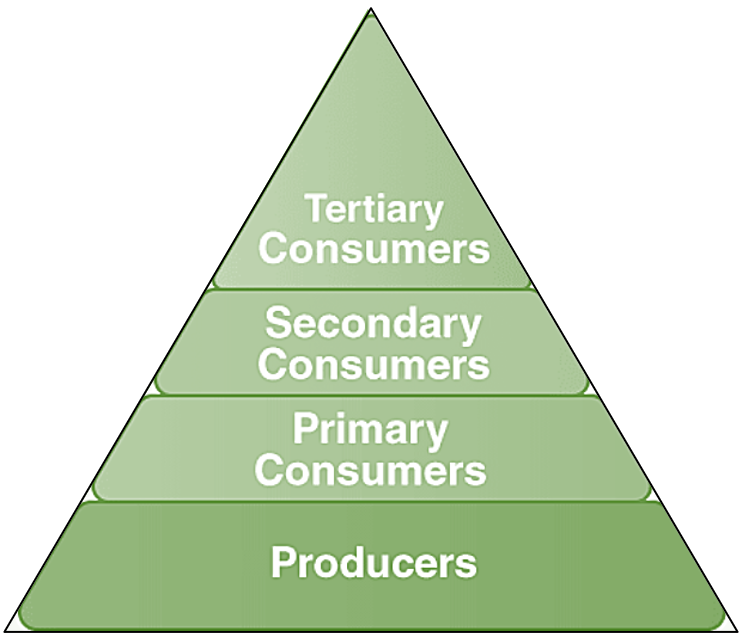
Understanding the Three Types of Ecological Pyramids

There are primarily three types of ecological pyramids that elucidate different aspects of an ecosystem:
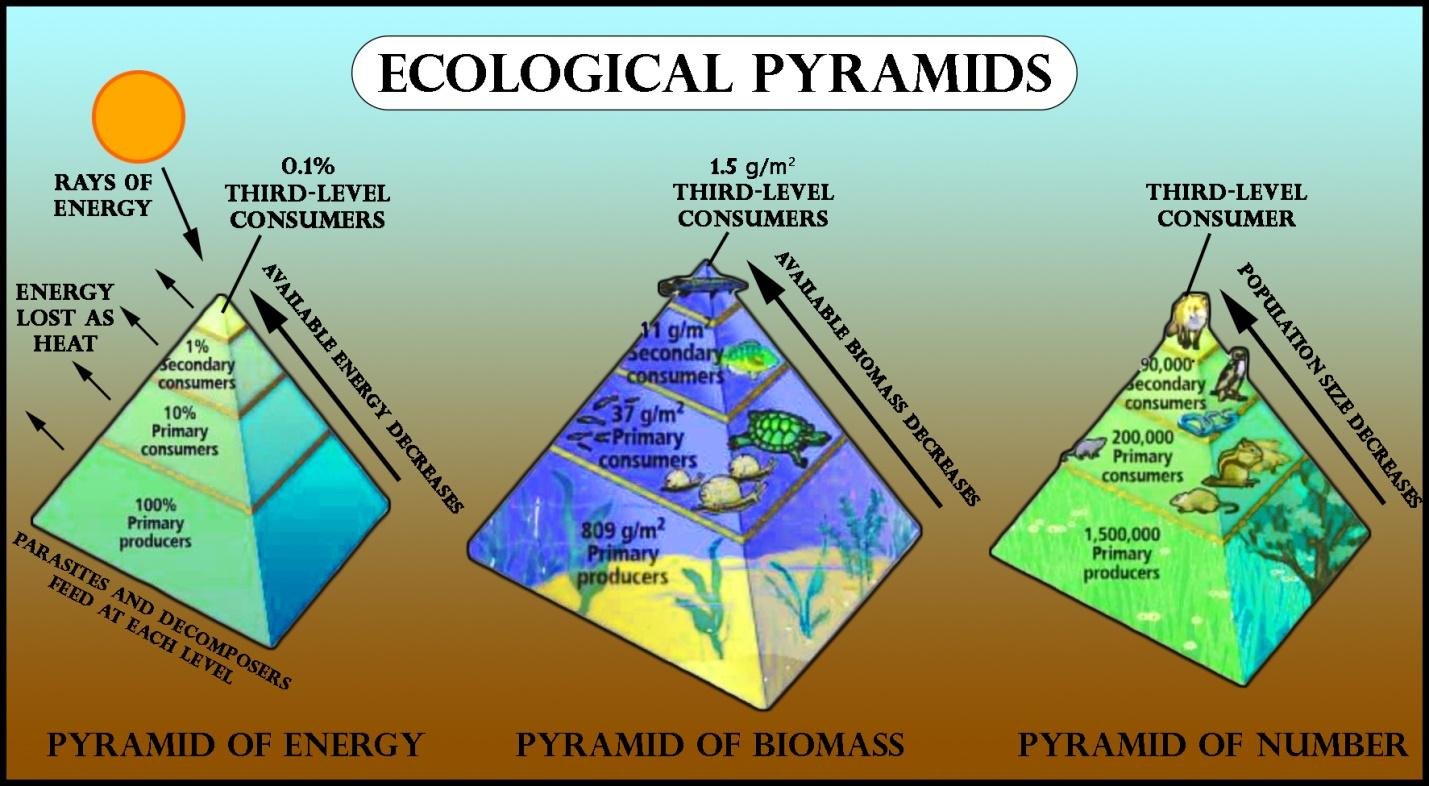
- Pyramid of Numbers - This pyramid illustrates the number of organisms at each trophic level. It often has a broad base, representing a large number of primary producers, narrowing towards the apex where fewer organisms exist at higher trophic levels.
- Pyramid of Biomass - Depicting the total mass of living organisms within each trophic level, this pyramid shows how the total biomass decreases as you move up the food chain, except in certain aquatic ecosystems where this pattern can invert.
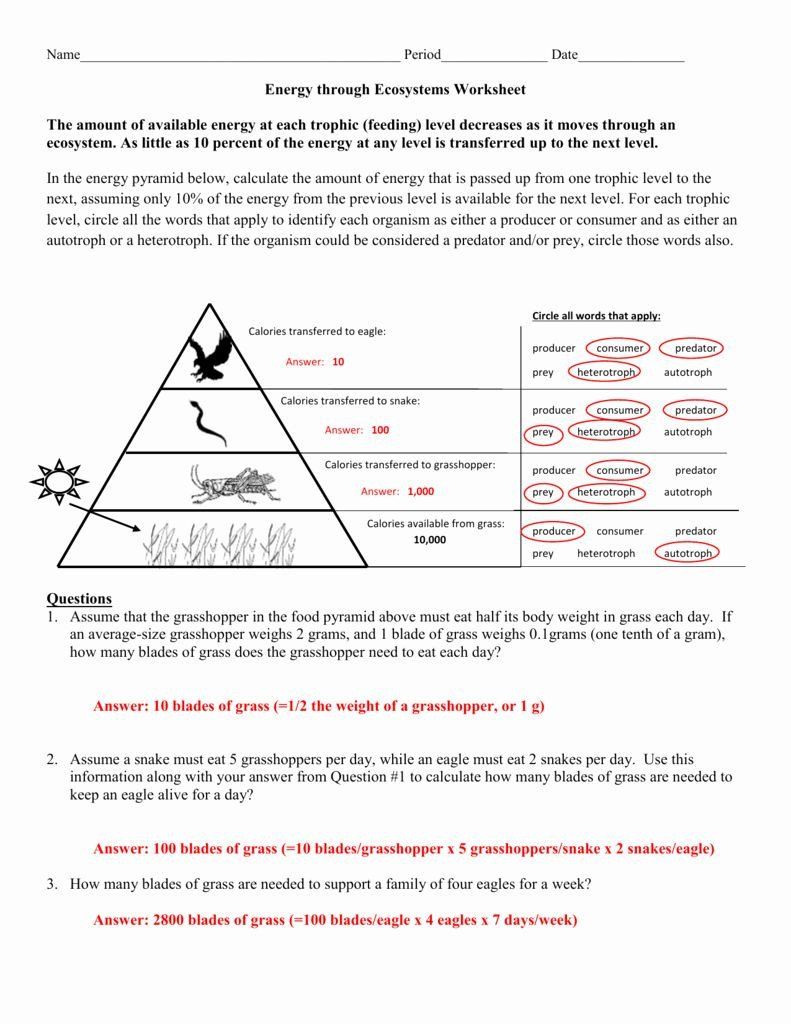
- Pyramid of Energy - Demonstrating the flow of energy through the ecosystem, the pyramid of energy quantifies the energy transfer efficiency, which is generally quite low (around 10%), highlighting why ecosystems can support only a limited number of top-level consumers.
Why Do Pyramids Matter?

Ecological pyramids are more than just charts; they:
- Reflect Ecosystem Health: The shape and structure of pyramids can indicate the health and stability of an ecosystem. Irregular or inverted pyramids might signal underlying issues like pollution or ecological imbalance.
- Help Understand Energy Transfer: They graphically show how energy decreases with each successive trophic level, aiding in understanding the inefficiencies in energy conversion.
- Guide Conservation Efforts: By revealing the relationships between species and their ecological roles, pyramids can inform conservation strategies, such as protecting species at critical trophic levels to maintain ecosystem functionality.
Common Misconceptions
Here are some common misconceptions about ecological pyramids:
- They Are Always Upright: While this is often true, especially for energy pyramids, biomass pyramids in aquatic ecosystems can sometimes be inverted due to the long-lived biomass of phytoplankton supporting larger fish.
- They Show Exact Numbers: Pyramids are a generalization. Actual numbers can fluctuate due to environmental changes, seasons, or predation patterns.
The Role of Decomposition in Pyramids

Decomposers play a crucial role in ecosystems, yet they are often omitted from pyramid diagrams:
- The Detritus Pathway - Energy not captured through primary producers often flows through the detritus food chain, where decomposers recycle organic material back into the ecosystem, influencing the pyramid’s base indirectly.
🔍 Note: Even though decomposers aren't depicted in traditional pyramid diagrams, they significantly impact ecosystem functioning by recycling nutrients and breaking down organic matter.
Pyramids and Sustainability
Understanding ecological pyramids can drive sustainable practices:
- Resource Management: Knowing the limits of energy transfer informs sustainable harvesting and management of resources to prevent depletion of lower trophic levels.
- Promoting Biodiversity: Protecting species across all levels of the pyramid can enhance biodiversity, making ecosystems more resilient and adaptive to changes.
In summary, ecological pyramids provide a snapshot of ecosystem structure and dynamics. They shed light on energy transfer, biomass distribution, and species interactions, guiding not just ecological studies but also conservation efforts and sustainable management practices. By understanding these insights, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of nature and our role in maintaining it.
Why are some pyramids inverted?

+
In aquatic ecosystems, primary producers like phytoplankton might have a lower biomass than the consumers they support due to rapid reproduction rates and low individual biomass.
Can ecological pyramids be used to assess pollution?
+
Yes, changes in the shape or efficiency of energy transfer in pyramids can reflect ecosystem disruptions, including pollution, which can alter species populations and interactions.
How do you ensure the accuracy of ecological pyramids?

+
Accuracy depends on extensive field studies, counting organisms, measuring biomass, and assessing energy flows through various trophic levels, often involving multiple data points and comparisons.



