Master Map Scale with Our Answer Key Guide

In the world of geography, understanding how to read and interpret maps is crucial. Whether you're an avid hiker, a city planner, or simply someone who loves exploring the intricacies of our planet, map scale is a fundamental concept you need to grasp. With this guide, we'll dive deep into the art of reading map scales and unlock the secrets to navigating with precision, all with the help of an Answer Key.
What is Map Scale?


Map scale refers to the relationship or ratio between the distance on a map and the corresponding distance on the ground. Understanding map scale is akin to learning the language of maps. It’s your translator from a flat, 2D representation to the 3D world we inhabit. Here are the three primary types of map scales:
- Graphic Scale: A line divided into segments representing various distances.
- Representative Fraction (RF): A numerical ratio, e.g., 1:100,000, where 1 unit on the map equals 100,000 units on the ground.
- Verbal Scale: A simple statement like “1 inch represents 1 mile.”
The Importance of Map Scale
Imagine planning a route or deciding on a camping spot without knowing the actual distances. A map without a properly understood scale is like a recipe without measurements. Here’s why map scale matters:
- Accurate Navigation: Knowing the scale ensures you’re prepared for the journey ahead.
- Detailed Analysis: For professionals, scale is key for land-use planning, resource management, and more.
- Comparing Features: It allows you to compare the size of geographic features accurately.
Reading Map Scale: A Step-by-Step Guide

To read and interpret a map scale effectively:
- Identify the Scale Type: Check if it’s graphic, RF, or verbal. Each type has its method of reading.
- Understand the Proportions: For RF, the first number is map distance; the second number is the real-world distance.
- Use Reference Objects: Some maps use objects like rulers or pen caps as a quick visual reference.
- Convert Scale Units: Sometimes, you need to convert the units into your preferred measuring system (e.g., from feet to meters).
- Apply the Scale: Measure the distance on the map and multiply by the scale ratio to find the real-world distance.
Answer Key to Map Scale Practice Problems

| Problem | Scale Type | Steps | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| If a map has a scale of 1:24,000 and the distance between two points is 3 cm, what is the real-world distance? | RF | Multiply map distance (3 cm) by the scale ratio (24,000). | 72,000 cm or 720 meters |
| A map shows that 1 inch equals 4 miles. What’s the real-world distance if a line on the map is 5 inches long? | Verbal | Multiply the map distance (5 inches) by the verbal scale ratio (4 miles per inch). | 20 miles |
| On a map with a graphic scale where 1 segment equals 50 km, how long is a 6-segment line? | Graphic | Multiply the number of segments (6) by the distance per segment (50 km). | 300 km |

By understanding and solving such problems, you get a practical grasp of map scales, enhancing your ability to interpret geographic data.
📌 Note: Practice with different map scales to familiarize yourself with conversions between units and real-world distances.
Understanding Map Scale in Different Contexts

Maps serve various purposes, and each type of map often requires a different approach to scale interpretation:
- Topographic Maps: These maps need precise measurements for elevation and distance.
- Nautical Charts: With safety being paramount, scale accuracy is vital for marine navigation.
- Road Maps: General road maps might have larger scales, while detailed route maps require smaller scales.
- City Planning Maps: These involve scales that allow for city block measurements, traffic analysis, and infrastructure planning.
Key Takeaways for Enhancing Your Map Scale Skills
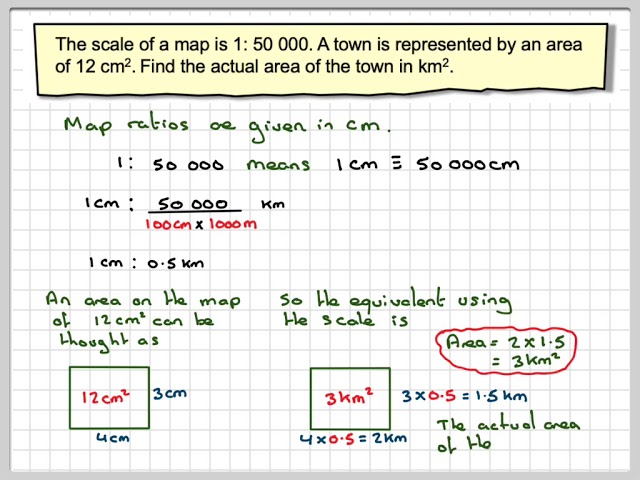
Here are a few tips to improve your understanding and utilization of map scales:
- Always verify the scale type when starting with a new map.
- Practice regularly with real maps and solve example problems.
- Familiarize yourself with scale conversion tools or tables.
- Learn the common scales used in different types of maps for quick reference.
Now that we've covered how to master map scales, you're equipped to explore our vast world with more precision and confidence. From the backcountry trails to city planning and beyond, map scale is your gateway to understanding the spatial relationships in any environment.
Remember, maps are not just drawings; they are a bridge between cartography and reality. With this guide, the answer key to map scale problems, and these key takeaways, you'll be navigating like a pro in no time.
What does “1:50,000” mean on a map?

+
“1:50,000” is a Representative Fraction (RF) scale, meaning that 1 unit of distance on the map represents 50,000 units on the ground. For example, 1 cm on the map equals 50,000 cm (or 500 meters) on the ground.
How can I determine the scale of a map that lacks a clear scale?
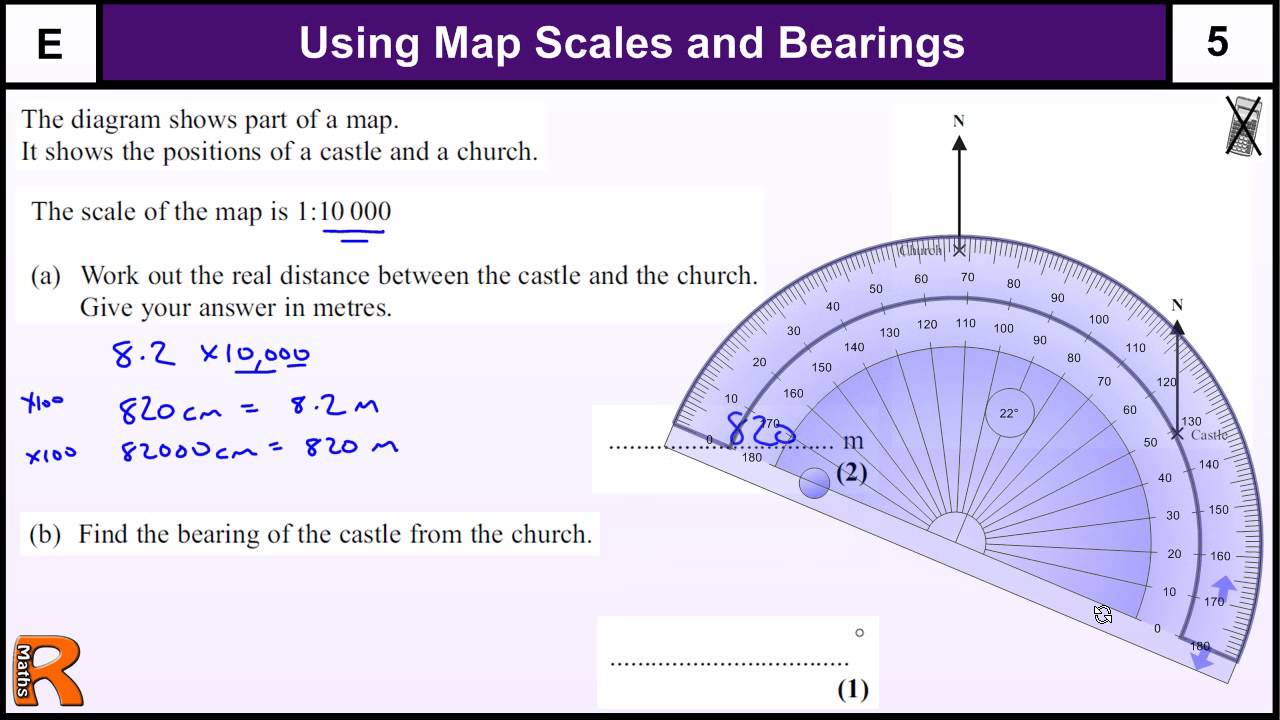
+
If there’s no scale provided, look for known landmarks or features on the map. Measure their known distance using outside sources (like Google Maps) and estimate a scale by comparing this distance to the corresponding map distance.
Why do some maps have multiple scales?
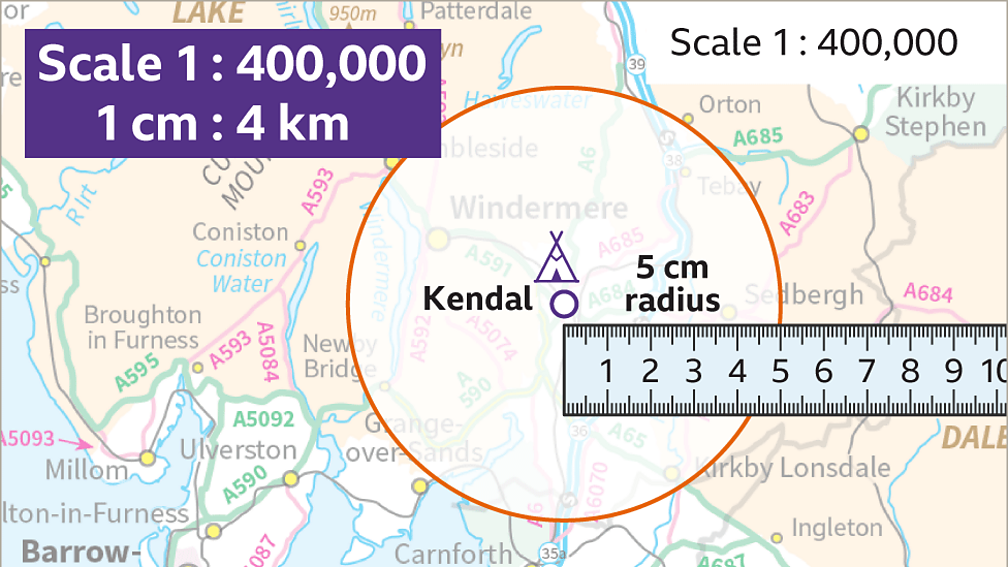
+
Maps might show multiple scales for different parts, especially in thematic maps, to emphasize certain features or to provide zoom-in views of areas within a larger context.