DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key Revealed!

Welcome to our exploration of the intricacies of DNA, the magnificent molecule of life! DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, holds the blueprint for all living organisms, and understanding its structure is fundamental for biology students. In this post, we delve into a guided worksheet designed to clarify the components of DNA, its structural forms, and how it functions in biology. This article will not only serve as an answer key but also enhance your understanding of DNA through interactive and educational content.
Understanding DNA: The Basics

Before we look into the worksheet answers, let’s cover some fundamentals:
- What is DNA? DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides.
- Structure: DNA adopts a double helix structure, resembling a twisted ladder.
- Components: The DNA ladder consists of sugars, phosphates, and four types of nitrogenous bases.
- Chargaff’s Rule: In DNA, the amount of adenine (A) equals thymine (T), and guanine (G) equals cytosine ©.

DNA Structure Worksheet: Answers

Let’s proceed to the worksheet answers:
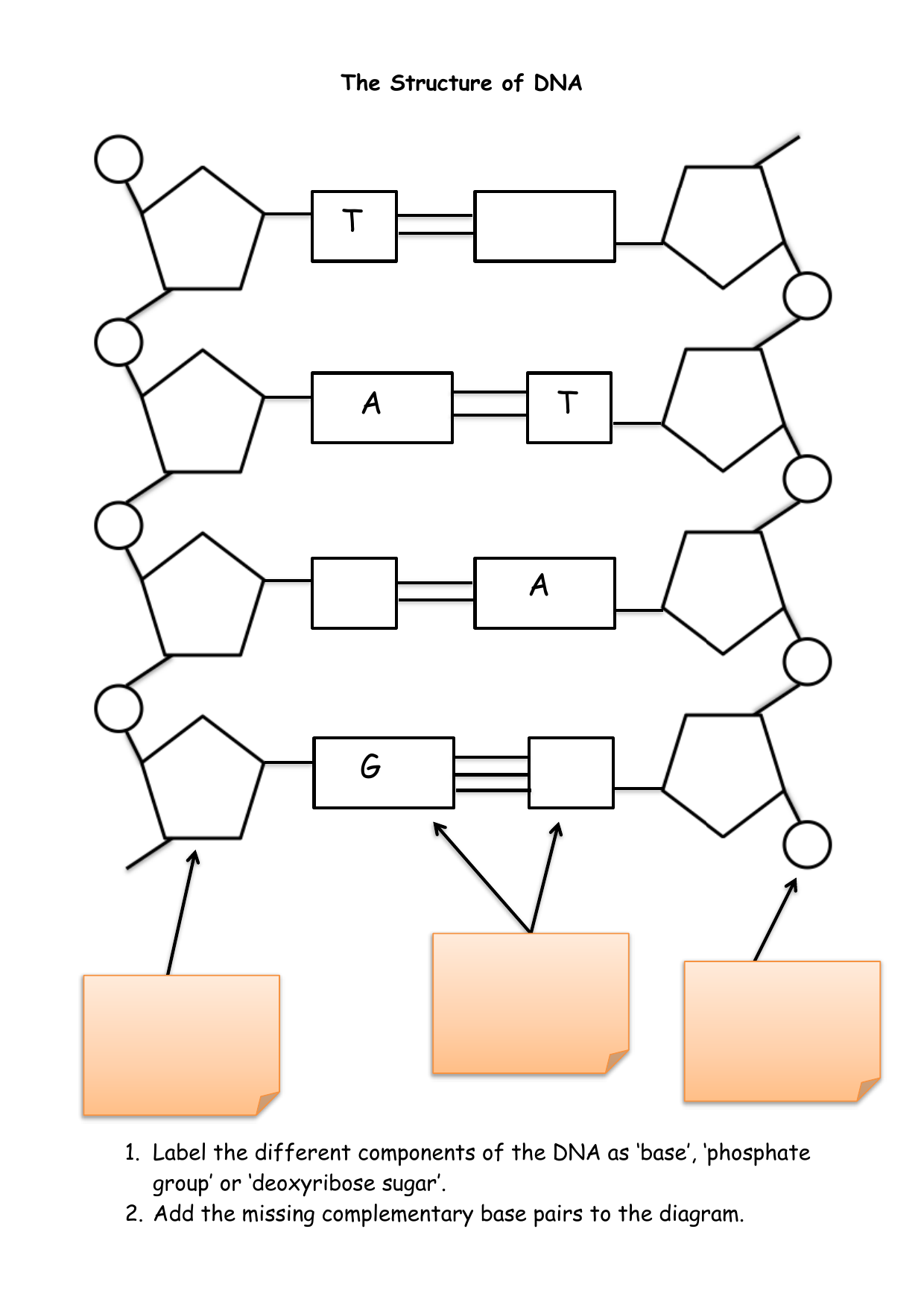
1. Nucleotides

Define what constitutes a nucleotide:
- A phosphate group
- A deoxyribose sugar
- One of four nitrogenous bases (A, T, C, or G)
2. Complementary Base Pairing

Explain the concept of complementary base pairing:
Each base pairs with another specific base through hydrogen bonds:
- Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T)
- Guanine (G) pairs with Cytosine ©
🌟 Note: The specific pairing is essential for the replication and function of DNA.
3. Helical Twist

Discuss how the DNA molecule twists into a helix:
- The sugar-phosphate backbones run in opposite directions (antiparallel)
- The double helix forms due to the twist and tilt of the base pairs.
4. DNA Replication

Provide an overview of DNA replication:
- Helicase unwinds the DNA helix.
- DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to form new strands.
- The new strands are complementary to the original template strands.
| Enzyme | Role in Replication |
|---|---|
| Helicase | Unwinds DNA |
| Primase | Adds RNA primer |
| DNA Polymerase | Synthesizes new strands |
In closing, understanding DNA’s structure is not only fascinating but also crucial for students and enthusiasts of biology. From the basic components to the replication process, the complexity of DNA offers endless insights into how life functions at its core. This worksheet and the answers provided herein serve as a foundational guide to navigate through the molecular architecture that makes life possible. We’ve touched upon various aspects of DNA, from the basics of its structure to its intricate replication process, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of this vital molecule.
What is the importance of DNA structure?

+
The structure of DNA is critical for its function in storing, copying, and transmitting genetic information. It allows for accurate replication, mutation prevention, and the packaging of genetic material in cells.
How does DNA replication ensure the genetic continuity?

+
Through semi-conservative replication, where each new DNA molecule has one strand from the original molecule, ensuring that genetic information is passed down accurately to daughter cells.
What happens if there are mistakes during DNA replication?
+
Mistakes in DNA replication can lead to mutations. These mutations can sometimes be beneficial, leading to evolution, but can also result in diseases or disorders if they affect critical gene functions.