Mastering Division: 2-Digit Divisors Worksheet Guide

Understanding and mastering the art of division with 2-digit divisors is essential not only for academic success but also for everyday problem-solving. This comprehensive guide offers a structured approach to navigating through worksheets focused on 2-digit divisors. Whether you're a student looking to enhance your mathematical skills or a tutor helping others, the strategies and insights provided here will prove invaluable.
Understanding 2-Digit Division
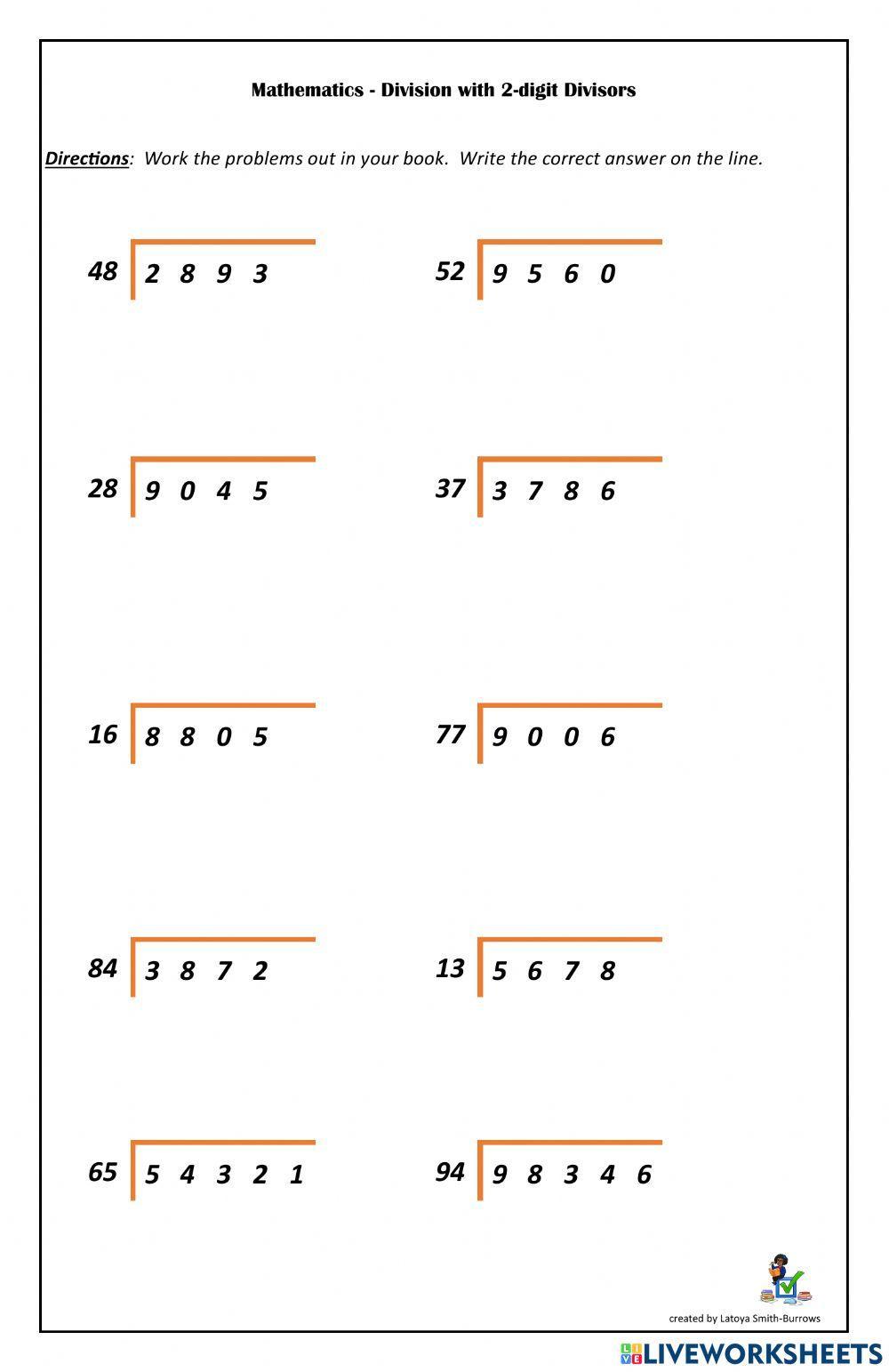
Before tackling the worksheets, it's crucial to understand what division by 2-digit numbers entails. Here are key points to grasp:
- Division Terminology: Recognize terms like divisor, dividend, quotient, and remainder. Understanding these will make your learning journey smoother.
- Estimating: Estimating the result can be a helpful strategy. Look at the numbers involved and make educated guesses on where to start your calculations.
- Place Value: Knowing the place value of digits aids in performing long division more effectively. It helps in aligning numbers correctly during division steps.
Steps to Solve Division Problems

Here's a step-by-step guide to solving division problems with 2-digit divisors:
1. Choose a Divisor

First, select a 2-digit number you wish to divide by. For example, let's take 23.
2. Set Up the Division

Write the dividend (the number being divided) and the divisor (in our example, 23) like this:
456 ÷ 23
3. Estimate Quotient

Estimate how many times 23 can fit into 45. Since 23 is roughly 20, and 45 is slightly more than twice 20, we'll start with an estimated quotient of 2.
4. Multiply and Subtract

Multiply the divisor (23) by the estimated quotient (2):
23 × 2 = 46This is more than 45, so the estimate was too high. Adjust:
- Try 1 as the quotient:
23 × 1 = 23
- Subtract this from 45:
45 - 23 = 22
5. Bring Down Next Digit

Bring down the next digit of the dividend (which is 6), making it 226.
6. Repeat Process

Estimate how many times 23 fits into 226. Since 23 is roughly 20, and 226 is a bit over 10 times 20, start with 10 as the next digit in the quotient.
- Multiply 23 by 10:
23 × 10 = 230
- Subtract this from 226:
226 - 230 = -4
This gives a remainder of -4, indicating we need to decrease our estimation.
7. Finalize Calculation

Correct the multiplication to 9:
- Multiply 23 by 9:
23 × 9 = 207
- Subtract:
226 - 207 = 19
The final quotient is 19, with a remainder of 19. This means:
456 ÷ 23 = 19 r19
📝 Note: If the remainder exceeds the divisor, keep dividing to reduce it to a smaller number.
Worksheet Exercises

Let's look at typical exercises found in division worksheets:
- Simple 2-digit divisions where the quotient is a whole number.
- Problems where remainders are involved.
- Word problems requiring division by 2-digit numbers.
Examples of Worksheets

Here's a table with some 2-digit divisor problems for practice:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| 36 ÷ 12 | 3 |
| 96 ÷ 24 | 4 |
| 144 ÷ 36 | 4 |

💡 Note: Regularly practicing different types of problems will strengthen your understanding and speed in division.
Tips for Efficiency

Here are some practical tips to improve your efficiency in division:
- Use Shortcuts: Learn shortcuts like using the double-up method or recognizing patterns in numbers.
- Mental Math: Develop mental math skills for quick estimates, reducing the need for complex calculations.
- Practice: Regular practice ensures familiarity with the process, reducing errors and increasing speed.
Understanding Remainders

Remainders often confuse learners. Here are key points about remainders:
- Remainders are always less than the divisor.
- They represent an unutilized part of the dividend left after division.
📊 Note: In everyday applications, remainders might be ignored or have different interpretations based on the context.
Wrapping Up

Division by 2-digit numbers can seem daunting initially, but with the right approach, it becomes manageable and even intuitive. This guide has walked you through the essential concepts, steps, and practice needed to master division with 2-digit divisors. Regular practice, understanding the logic behind each step, and employing shortcuts will undoubtedly boost your mathematical prowess. With these skills, you'll approach division problems with confidence and efficiency.
Why is division with 2-digit divisors more complex than with 1-digit?

+
With 2-digit divisors, you’re dealing with larger numbers, making estimation and calculation more intricate due to the need for aligning digits and managing remainders effectively.
Can you give an example of a real-life division problem with a 2-digit divisor?

+
Here’s one: If a group of 56 people needs to be divided into teams of 12 players each, how many teams can you form?
What’s the best way to practice division with 2-digit divisors?
+Start with simple problems and gradually increase complexity. Use worksheets, online tools, and real-life examples. Consistent practice is key to mastery.



