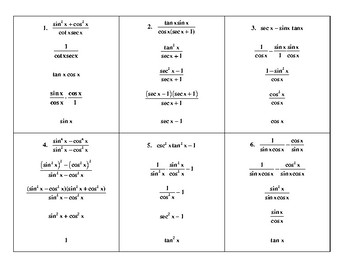
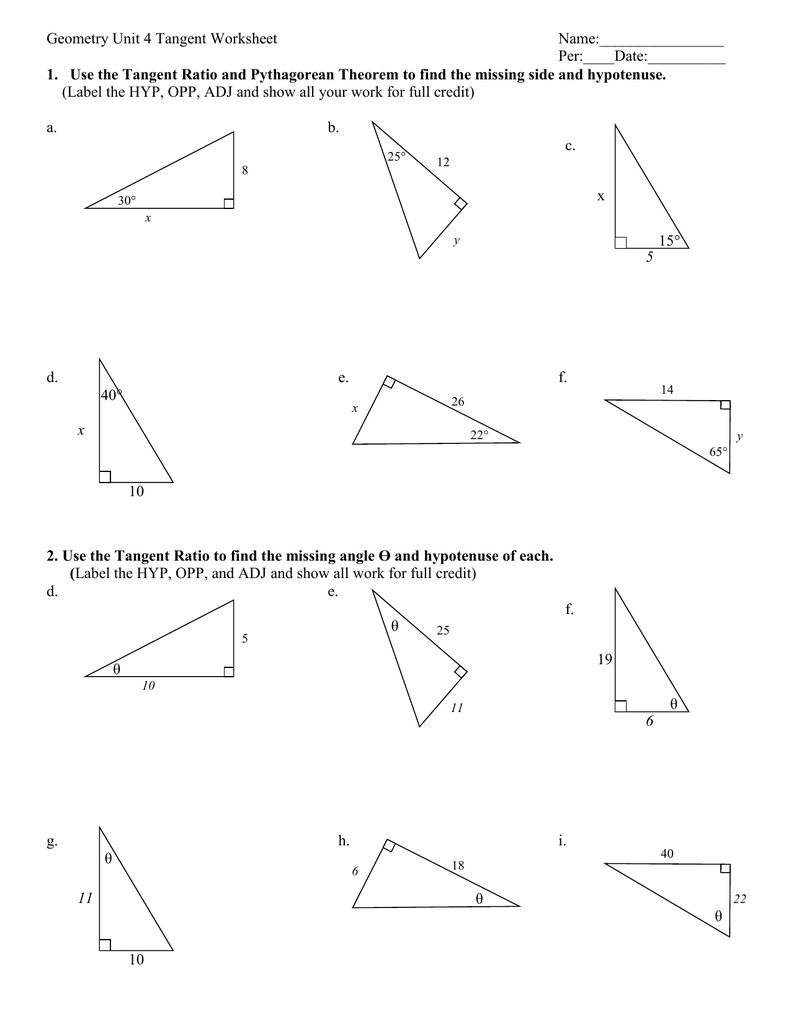
Dihybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key: Quick Guide

In the realm of genetics, understanding dihybrid crosses is crucial for students and enthusiasts alike. This guide serves as your comprehensive answer key to a standard dihybrid cross worksheet, providing a clear and easy-to-follow breakdown of the steps involved. Whether you're a student studying genetics, a teacher looking to aid students, or a curious learner, this guide aims to clarify the complexities of dihybrid inheritance through real-world examples.
What is a Dihybrid Cross?

A dihybrid cross involves the study of inheritance of two different traits at once. Unlike monohybrid crosses which focus on one trait, dihybrid crosses reveal the combinations of two different gene pairs, like seed color and seed shape in pea plants, the classic example used by Gregor Mendel. Here’s how we approach it:
- Traits Selection: Choose two traits you want to examine. For instance, in Mendel’s peas, one could select seed color (yellow or green) and seed shape (round or wrinkled).
- Parental Generation: Start with the parents, or P-generation, who are true-breeding for their traits (homozygous).
- Cross Pollination: Cross pollinate these parents to create the first filial (F1) generation.
- Analyze F1 Generation: Observe the phenotypes and genotypes in this generation.
- Self-Cross or Test Cross: Self-pollinate or perform a test cross with F1 to produce the second filial (F2) generation.
- Observe and Calculate: Use a Punnett square or a dihybrid cross calculator to predict the ratios of offspring’s traits.
Performing the Dihybrid Cross: A Step-by-Step Guide

Let’s perform a dihybrid cross between a plant with round, yellow seeds (RRYY) and one with wrinkled, green seeds (rryy).
Step 1: Determine the Parental Genotypes

The parents are homozygous for their traits:
- RRYY (round, yellow seeds) - A true-breeding plant for round and yellow.
- rryy (wrinkled, green seeds) - A true-breeding plant for wrinkled and green.
Step 2: Cross the Parental Generation

When crossed, all F1 offspring will be:
| RR | Rr |
———————
Y | RY |
y | Ry |
All the F1 seeds will be RrYy, meaning they will be heterozygous for both seed shape and color, resulting in round and yellow seeds due to dominance.
Step 3: F1 Self-Cross
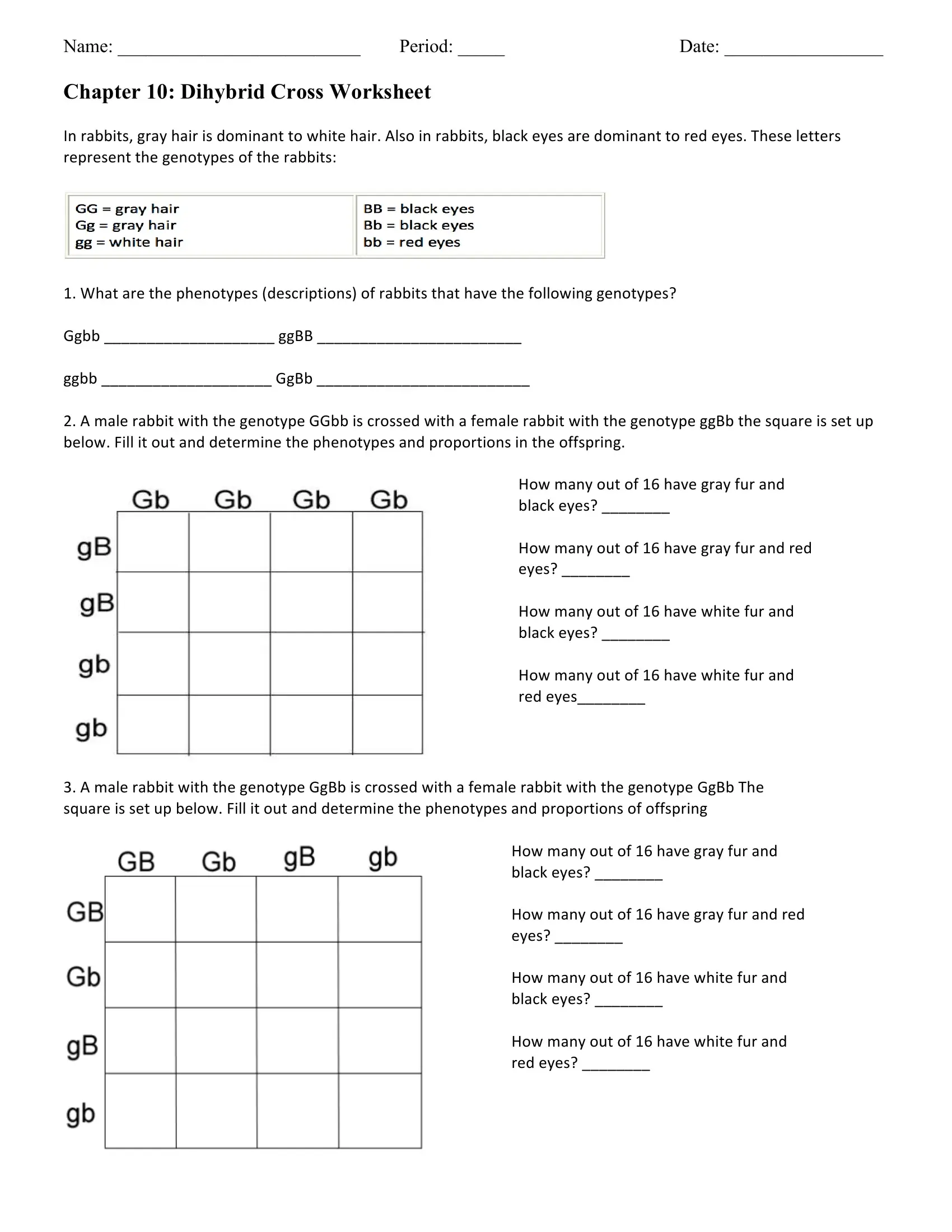
Now, self-pollinate these F1 plants:
| RY | Ry | rY | ry |
—————————–
RY |RRYY| RRYy| RrYY| RrYy|
Ry |RRYy| RRyy| RrYy| Rryy|
rY |RrYY| RrYy| rrYY| rrYy|
ry |RrYy| Rryy| rrYy| rryy|
This Punnett square represents a 16-cell matrix that predicts all possible genotypes and phenotypes in the F2 generation.
Step 4: Analyze the Results

- Genotypes: From this cross, we get nine different genotypes.
- Phenotypes: The phenotypic ratio is 9:3:3:1, meaning:
- 9 (round, yellow) : Round and yellow seeds are dominant.
- 3 (round, green) : Only round seeds, but green in color.
- 3 (wrinkled, yellow) : Wrinkled shape but yellow seeds.
- 1 (wrinkled, green) : Recessive traits expressed.
🚨 Note: In actual plant breeding, environmental factors can influence the expression of traits, deviating from these expected ratios.
Step 5: Verification through Data
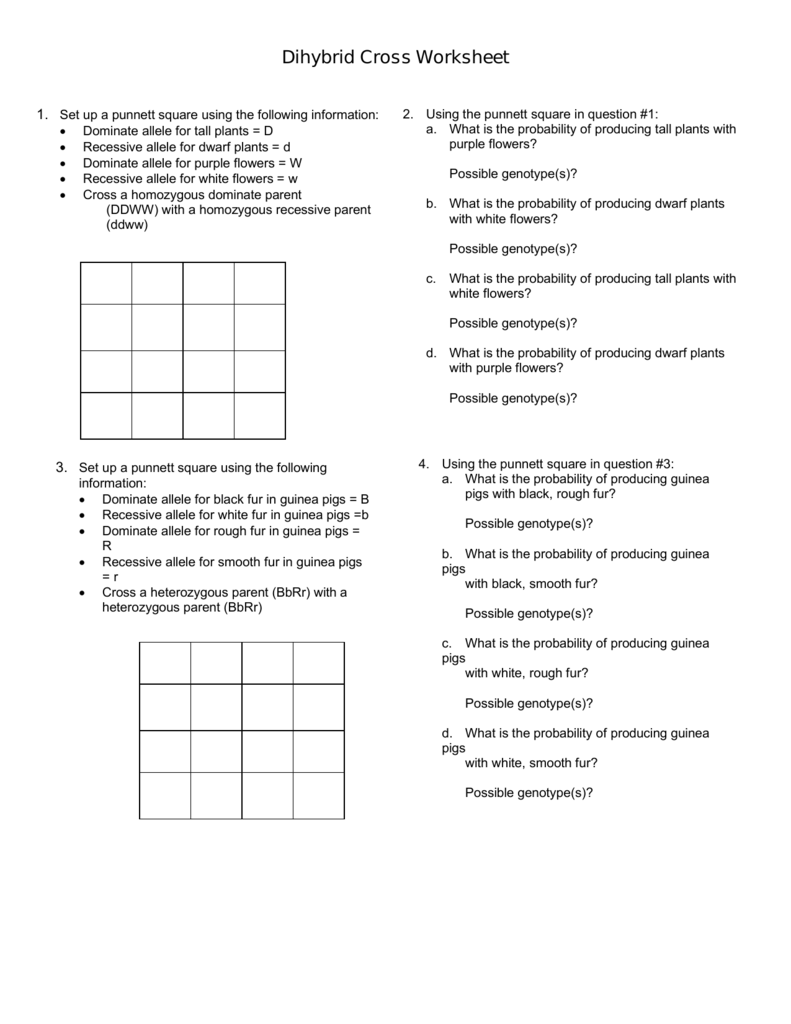
If you have actual counts from an experiment, compare them to the expected ratios to validate your understanding of inheritance.
| Phenotype | Expected Ratio | Your Data |
|---|---|---|
| Round, Yellow | 9 | [Enter your count here] |
| Round, Green | 3 | [Enter your count here] |
| Wrinkled, Yellow | 3 | [Enter your count here] |
| Wrinkled, Green | 1 | [Enter your count here] |

Wrap-up

This guide covers the essentials of dihybrid crosses, from understanding the process to analyzing the results. By following these steps, you’ll be able to predict and understand the inheritance of two traits simultaneously. Remember, genetics is not just about Mendel’s laws; it’s a field where exceptions can teach us as much as the rules. Whether you’re solving dihybrid cross problems for homework or conducting your own genetic experiments, this guide provides a foundation for exploring the fascinating world of heredity.
What is the difference between a monohybrid and dihybrid cross?

+
A monohybrid cross focuses on the inheritance of one trait, while a dihybrid cross looks at two traits simultaneously. A dihybrid cross reveals how these traits are inherited together.
How do I know if my F2 generation follows Mendelian ratios?

+
Your F2 generation should follow the 9:3:3:1 ratio if the traits are independently assorted as per Mendel’s law. You can perform a chi-square test to check if your observed results match the expected ratios.
What are the limitations of Mendelian inheritance?

+
Mendelian inheritance doesn’t account for polygenic traits, genetic linkage, or the impact of environmental factors on gene expression. Also, exceptions like codominance, incomplete dominance, and sex-linkage can occur.