Mastering Trigonometry: Simplify Trig Expressions Worksheet
In the realm of mathematics, trigonometry stands as a pivotal branch, offering the tools to model a plethora of phenomena from the movement of celestial bodies to the vibrations in sound waves. One of the cornerstones of mastering trigonometry lies in simplifying trigonometric expressions. This skill not only streamlines calculations but also deepens one's understanding of trigonometric identities and their applications. In this detailed guide, we'll embark on a journey through the intricacies of simplifying trig expressions, equipping you with the skills to tackle any trig problem with confidence.
The Basics of Trigonometric Functions

Before delving into simplification, a quick recap of the primary trigonometric functions is beneficial:
- Sine (sin) - Measures the angle’s opposite side over the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
- Cosine (cos) - Measures the adjacent side over the hypotenuse.
- Tangent (tan) - The ratio of sine to cosine; tan(θ) = sin(θ) / cos(θ).
- Secant (sec), Cosecant (csc), and Cotangent (cot) - The reciprocals of cos, sin, and tan respectively.
Understanding Trigonometric Identities

Trigonometric identities serve as the backbone for simplifying expressions. Here are some fundamental identities:
- Pythagorean Identity: sin²(θ) + cos²(θ) = 1.
- Angle Addition and Subtraction Identities: sin(A ± B), cos(A ± B), etc.
- Double Angle Formulas: 2sin(A)cos(A) = sin(2A), 1 - 2sin²(A) = cos(2A), etc.
- Power Reduction Formulas: sin²(θ) = ½(1 - cos(2θ)), cos²(θ) = ½(1 + cos(2θ)).
Steps to Simplify Trigonometric Expressions

- Recognize the Function: Determine the trigonometric function involved.
- Identify the Identities: Look for applicable trigonometric identities that can simplify the expression.
- Apply Identities: Substitute the identified identities into the expression.
- Combine Like Terms: Simplify by combining like terms where possible.
- Convert to Preferred Form: If needed, convert expressions to a form that is easier to handle or recognize, such as changing sec to 1/cos.
Example Problem: Simplify sin(θ)cos(θ)tan(θ)

Let’s simplify the expression sin(θ)cos(θ)tan(θ):
- Using the Pythagorean Identity and the definition of tangent, we get:
- sin(θ)cos(θ) * (sin(θ)/cos(θ)) = sin²(θ)
✅ Note: Always ensure your approach aligns with the fundamental definitions and identities for accuracy.
Advanced Techniques

Using Substitution

Substitution can be particularly useful when dealing with multiple trigonometric functions:
- If sin(θ) + cos(θ) is part of your expression, let u = sin(θ) + cos(θ). Then, (sin(θ) + cos(θ))² = u².
Partial Fractions

For more complex expressions, partial fraction decomposition might simplify things:
- Expressions like 1/(sin(θ)cos(θ)) can be broken down using identities into simpler forms like (tan(θ)/2 + cot(θ)/2).
💡 Note: Advanced techniques like these often require a strong foundation in algebra and a deep understanding of trigonometric identities.
Common Pitfalls in Simplification

When simplifying trigonometric expressions, here are some common errors to watch out for:
- Sign errors - Misinterpreting the sign of trigonometric functions or identities.
- Misidentifying identities - Using the wrong identity or form can lead to incorrect results.
- Over-simplifying - Sometimes, expressions look deceptively simple but need careful manipulation.
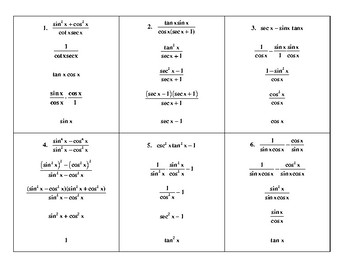
Now that we've covered the basics, techniques, and common pitfalls, it's time to put this knowledge to practice. Here's a simple worksheet designed to hone your skills in simplifying trigonometric expressions:
| Expression | Simplification |
|---|---|
| sin(θ)cos(θ) + cos²(θ) | cos(θ)sin(θ) + cos²(θ) = cos(θ)(sin(θ) + cos(θ)) |
| (1 - sin²(θ))/tan(θ) | cos²(θ)/tan(θ) = (cos(θ) / sin(θ))cos(θ) = cos²(θ) / sin(θ) |
| (1 + cot²(θ))cot(θ) | (1 + (1 / tan²(θ)))(1 / tan(θ)) = (1 + (1 / sin²(θ))(cos²(θ))) / tan(θ) |

By tackling these problems, you'll solidify your ability to recognize and apply trigonometric identities, enhancing your problem-solving skills in trigonometry.
Wrapping Up

Mastering the art of simplifying trigonometric expressions is more than just an academic pursuit; it’s a key step in understanding the fundamental principles of trigonometry. Through consistent practice, an understanding of trigonometric identities, and careful application of algebraic techniques, you can significantly improve your proficiency in this subject. This comprehensive guide has outlined the steps, provided examples, and highlighted common pitfalls, ensuring that you’re well-prepared to tackle any trigonometric challenge. Remember, every complex expression can be broken down into simpler components, revealing the beauty and logic behind trigonometry.
Why do we simplify trigonometric expressions?

+
Simplification helps in understanding the underlying relationships between trigonometric functions, reduces the complexity of equations, and makes solving problems more manageable.
How do trigonometric identities help in simplification?

+
Trigonometric identities provide a way to rewrite expressions in different forms that might be easier to work with or more directly reveal a solution.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when simplifying trig expressions?

+
Avoid misusing or misinterpreting identities, overlooking sign changes, and over-simplifying expressions which could lead to incorrect simplifications.