Master Redox Balancing with Our Worksheet Guide

The chemical world is filled with intricate processes that often require a detailed understanding to master. Among these processes, redox reactions stand out due to their prevalence and significance in both industrial applications and everyday life. If you are an AP chemistry student or simply a chemistry enthusiast eager to grasp the nuances of redox reactions, then our Redox Balancing Worksheet Guide is here to assist you. Let's embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries of oxidation-reduction reactions together.
Understanding Redox Reactions

Before diving into how to balance redox reactions, it’s fundamental to understand what they are. Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between chemical species. Here’s a quick breakdown:
- Oxidation - The loss of electrons by an atom, molecule, or ion.
- Reduction - The gain of electrons by an atom, molecule, or ion.
These reactions are not happening in isolation; they go hand in hand. When one substance loses electrons (oxidation), another gains them (reduction). This electron transfer drives countless chemical transformations around us.

Identifying Oxidation and Reduction
To balance a redox reaction, you first need to identify which atoms are being oxidized and which are being reduced. Here are some steps to do that:
- Assign Oxidation Numbers - Determine the oxidation states of each element before and after the reaction.
- Identify Changes - Look for increases (oxidation) or decreases (reduction) in oxidation numbers.
- Trace Electron Transfer - Establish which element loses electrons and which gains them.
🧪 Note: For elements in their free or elemental state, the oxidation number is always zero. In ions, it's equal to the charge of the ion.
The Half-Reaction Method

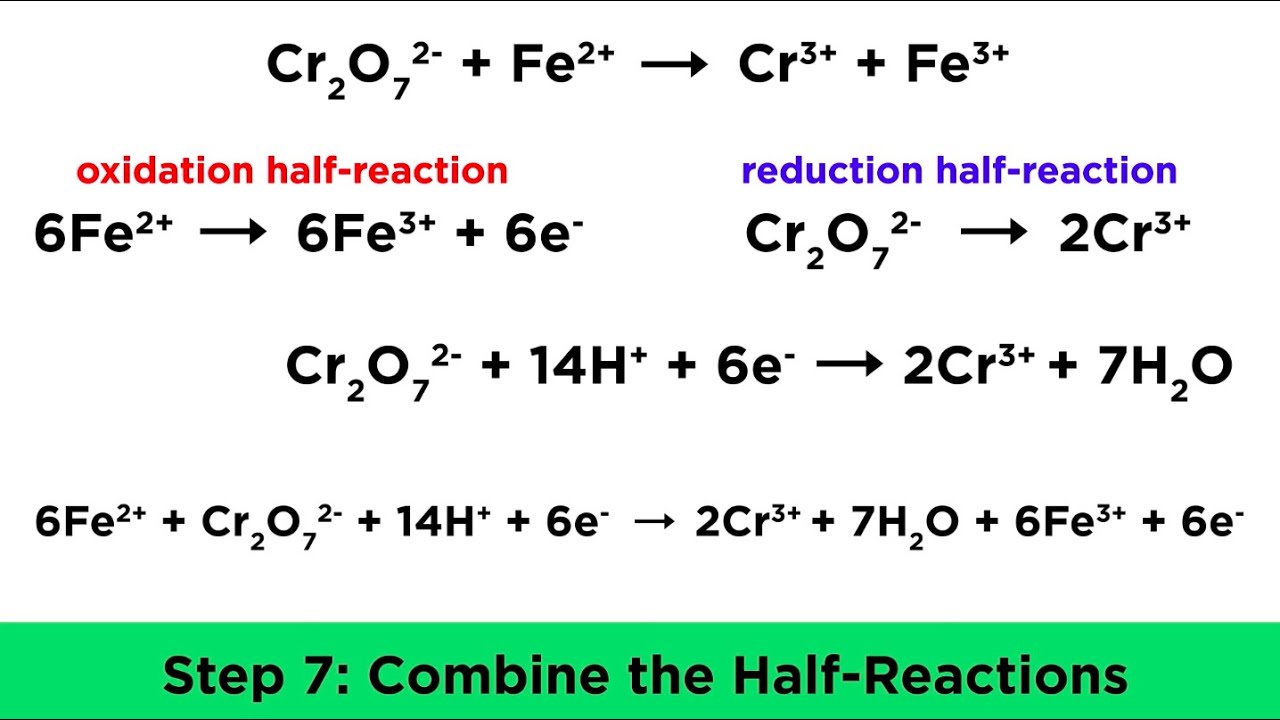
The half-reaction method is one of the most effective ways to balance redox reactions:
- Split the Reaction - Divide the overall equation into two half-reactions: one for oxidation and one for reduction.
- Balance Atoms - Balance atoms other than H and O in both half-reactions.
- Balance Oxygen - Use water molecules for any imbalanced oxygen atoms.
- Balance Hydrogen - Add H+ ions for imbalanced hydrogen atoms in acidic solutions, or OH- for basic ones.
- Balance Charge - Equalize the charge on both sides of each half-reaction with electrons.
- Combine Half-Reactions - Multiply by common factors to cancel out electrons and combine the reactions.
- Check and Balance - Ensure atoms and charges are balanced in the final equation.

Balancing in Acidic and Basic Solutions

Redox reactions can occur in different environments, affecting the balancing process:
- Acidic Solutions - Use H+ ions to balance hydrogen atoms.
- Basic Solutions - Add OH- ions to balance hydrogen atoms, but remember to add OH- ions to both sides to keep the equation balanced.
🔬 Note: In basic solutions, you can cancel out H+ ions by adding OH- ions to convert them to H2O. Simplify the equation afterward.
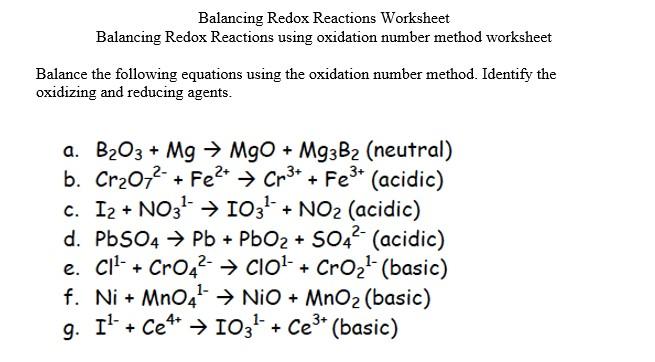
Worksheet Guide

Now, let’s explore some key elements of our Redox Balancing Worksheet Guide:
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | Overview of redox reactions, key terms, and principles. |
| 2. Identifying Oxidation and Reduction | Practice problems to identify which substances are oxidized or reduced. |
| 3. Half-Reaction Method | Step-by-step problems on balancing reactions using the half-reaction method. |
| 4. Balancing in Different Mediums | Balancing reactions in acidic, basic, or neutral solutions. |
| 5. Advanced Balancing | Tricks and tips for dealing with reactions involving complex molecules. |


By following this guide, you'll navigate through various redox balancing scenarios with confidence. The worksheet is structured to gradually increase in difficulty, ensuring you build your skills step by step.
This journey into the world of redox reactions not only strengthens your chemical knowledge but also empowers you to tackle complex problems in AP chemistry or beyond. Use our worksheet as a companion to your studies, and remember:
- Focus on understanding the process rather than rushing through the problem.
- Consider both the atoms and charges for a thorough balance.
- Keep practicing, as proficiency comes with repeated application of the methods learned.
As we wrap up our exploration of redox balancing, remember that these skills are essential for understanding larger chemical concepts. Whether you're interested in electrochemistry, biochemistry, or environmental chemistry, redox reactions are at the heart of many processes. Here's to mastering redox balancing with our guide, which we hope will become an indispensable tool in your chemical arsenal.
What are the differences between oxidation and reduction?
+
Oxidation involves the loss of electrons from an atom, molecule, or ion, while reduction is the gain of electrons. The oxidation state or number increases in oxidation and decreases in reduction.
Why is it important to balance redox reactions?

+
Balancing redox reactions ensures that mass and charge are conserved, which is fundamental to understanding the chemical process. An unbalanced reaction misrepresents the reality of chemical changes.
Can you balance redox reactions in any solution?

+
Redox reactions can indeed be balanced in various solutions, including acidic, basic, or neutral environments. Different balancing strategies are used depending on the medium, but the principles remain the same.
How does the half-reaction method differ in acidic and basic solutions?

+
In acidic solutions, H+ ions are used to balance hydrogen atoms. For basic solutions, OH- ions are added, but both sides of the equation must be treated equally to keep the equation balanced.
How can I practice balancing redox reactions?

+
Practice with our Redox Balancing Worksheet Guide, which offers problems ranging from basic to advanced. Regularly solving these problems will enhance your understanding and skill in redox balancing.