Mastering Molarity and Molality: Your Essential Guide

Understanding Molarity

At the core of chemistry is the concept of concentration, and when it comes to solutions, two primary measurements stand out: molarity and molality. Let's dive into molarity, a measure used frequently in chemical laboratories for its convenience.
- Definition: Molarity, symbolized as M, is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. The formula for molarity is: \[ \text{Molarity (M)} = \frac{\text{Moles of Solute}}{\text{Liters of Solution}} \]
How to Calculate Molarity

Here's a step-by-step guide to calculating molarity:
- Identify the Solute and Solvent: Determine what substance you're dissolving (solute) and the liquid you're using to dissolve it in (solvent).
- Calculate the Moles of Solute: Use the mass of the solute divided by its molar mass to find the number of moles.
- Measure the Volume of Solution: Ensure you're measuring the total volume of the solution, including both solute and solvent.
- Apply the Formula: Divide moles of solute by the volume of the solution in liters.
💡 Note: Always use the total volume of the solution, not just the volume of the solvent added.
Understanding Molality
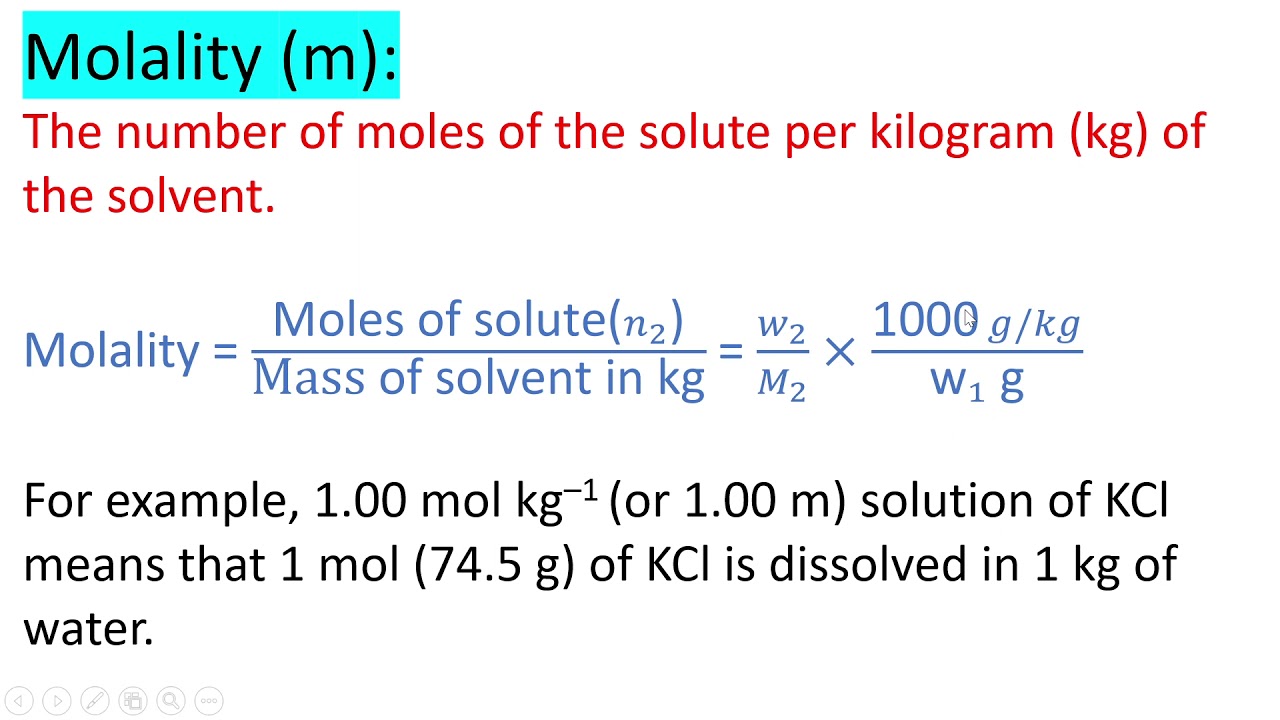
Molality, on the other hand, is less commonly used but essential in scenarios where temperature variation matters, as it is not dependent on solution volume.
- Definition: Molality, symbolized as m or mol/kg, is defined as the number of moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. The formula for molality is: \[ \text{Molality (m)} = \frac{\text{Moles of Solute}}{\text{Kilograms of Solvent}} \]
How to Calculate Molality

Here are the steps to calculate molality:
- Identify the Solute and Solvent: Similar to molarity, identify which substance you're dissolving and what liquid you're using.
- Calculate the Moles of Solute: Find the number of moles of solute using the formula above.
- Weigh the Solvent: Use a balance to find the mass of the solvent in kilograms.
- Apply the Formula: Divide the moles of solute by the kilograms of solvent.
📌 Note: Molality does not change with temperature, making it a better choice for physical property calculations.
When to Use Molarity vs. Molality
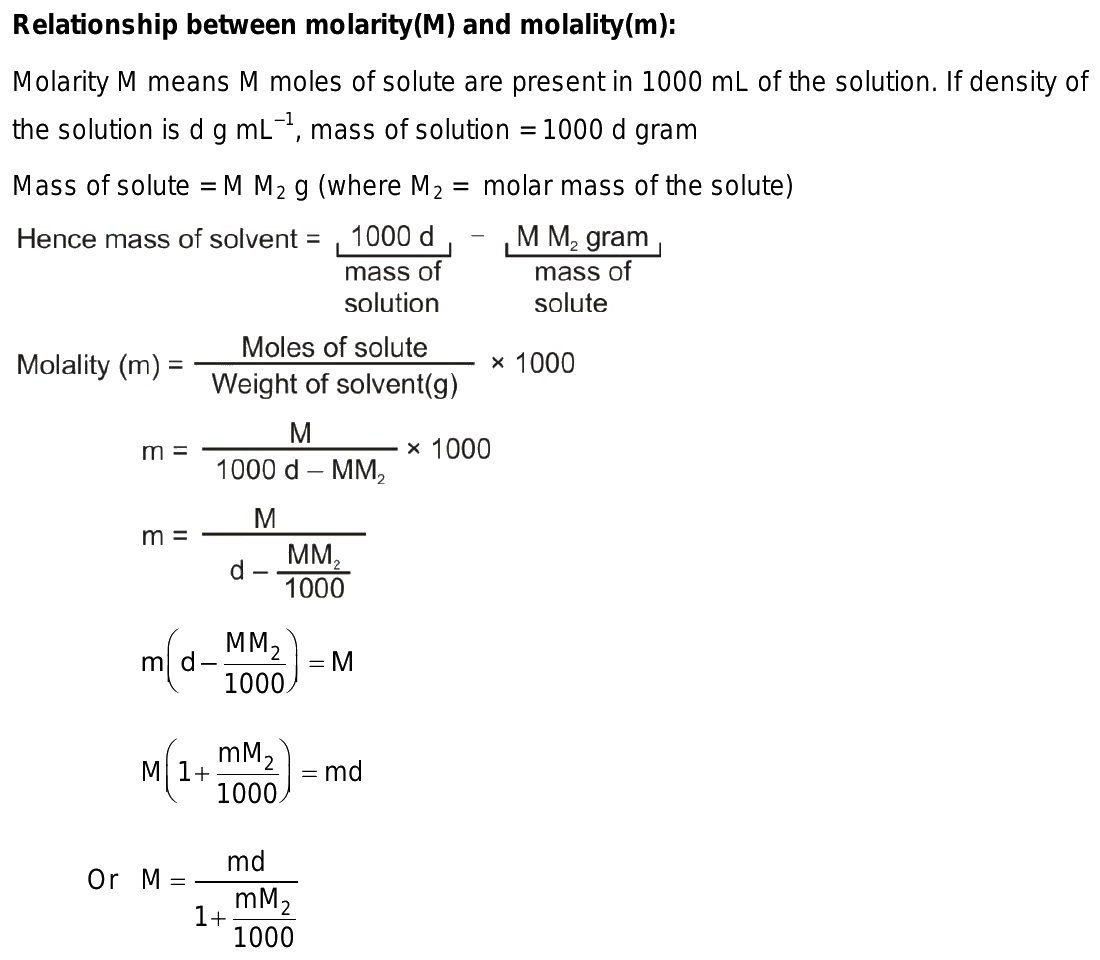
Choosing between molarity and molality often depends on:
- Volume vs. Mass: Use molarity if you're dealing with volume changes, especially in dilute solutions. Opt for molality when mass is more relevant, especially with concentrated solutions or when temperature changes are significant.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Molality remains constant with temperature changes, whereas molarity can change as the solution's volume expands or contracts.
- Precision in Measurement: For more precise work, where volume measurement can introduce errors, molality is preferred.
| Property | Molarity (M) | Molality (m) |
|---|---|---|
| Unit | mol/L | mol/kg |
| Temperature Dependency | Changes with temperature | Independent of temperature |
| Precision | Can be affected by volume measurement errors | Precision not affected by volume measurement |
| Use Cases | Lab work, reactions | Colligative property studies, industrial processes |

In summary, we've explored molarity and molality in detail, providing an understanding of their definitions, calculation, and appropriate use cases. Molarity is more common for volume-based reactions in labs, while molality ensures precision and is invaluable when dealing with changes in solution properties due to temperature. By mastering both, chemists can choose the most appropriate measure for their specific needs, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of their work. This understanding is not just theoretical but has practical implications in various fields from pharmaceuticals to environmental science, highlighting the importance of grasping these fundamental concepts.
Why is molality preferred for colligative properties?

+
Molality is used because it is independent of temperature, ensuring that the calculations for freezing point depression, boiling point elevation, osmotic pressure, and vapor pressure lowering remain accurate regardless of changes in volume due to temperature.
How do you convert molarity to molality?

+
To convert molarity to molality, you need to know the density of the solution. Using the formula: molality = molarity / (density of solution - molarity * molar mass of solute). This conversion accounts for the change in solution volume due to the addition of solute.
Can molarity and molality be the same?

+
Yes, they can be equal if the solute has a negligible effect on the solution’s volume or if the density of the solution is 1 kg/L, which is rare in practice but can happen with very dilute solutions.



