Calorimetry Problems Worksheet Answers Explained

In the study of thermodynamics, calorimetry plays an essential role in understanding how heat is transferred during chemical and physical processes. Whether you're an undergrad student grappling with concepts of heat capacity, specific heat, or an avid scientist working on calorimetric experiments, this long-form blog post aims to provide clarity on the most common types of calorimetry problems, their solutions, and underlying principles. Here, we delve into the intricacies of calorimetry, guiding you through various problems, offering solutions, and sharing insights to solidify your grasp on this vital subject.
The Basics of Calorimetry


Calorimetry involves measuring the heat exchanged in chemical reactions, or between substances with different temperatures. Here are the key concepts:
- Heat Capacity: The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of an object by one degree Celsius. This is measured in joules per degree Celsius (J/°C).
- Specific Heat: Denoted as c, this is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. Units are J/g·°C.
- Calorimeter: A device used to measure the heat of reaction or physical changes as well as heat capacity.
Solving Calorimetry Problems
Example Problem 1: Temperature Change

Consider a problem where 50 grams of water at 20°C is mixed with 100 grams of water at 90°C. What will be the final temperature?
| Substance | Mass (g) | Initial Temperature (°C) | Specific Heat (J/g·°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water (cold) | 50 | 20 | 4.18 |
| Water (hot) | 100 | 90 | 4.18 |

Here is how we solve it:
- Heat lost by the hot water = Heat gained by the cold water
- Heat gained = (mass x specific heat x temperature change)
- Let T be the final temperature:
- Heat lost by hot water: 100 x 4.18 x (90 - T)
- Heat gained by cold water: 50 x 4.18 x (T - 20)
- Set the equations equal and solve for T:
100 x 4.18 x (90 - T) = 50 x 4.18 x (T - 20)
Upon solving, we find T = 60°C.
🔥 Note: The final temperature reached in a calorimeter represents thermal equilibrium, where there is no net exchange of heat between substances.
Example Problem 2: Heat of Reaction

When 1 mole of NaOH reacts with HCl, the heat released is measured in a coffee cup calorimeter:
- Initial temperature of water = 25.0°C
- Final temperature = 30.2°C
- Volume of water = 100 mL
Here’s the calculation:
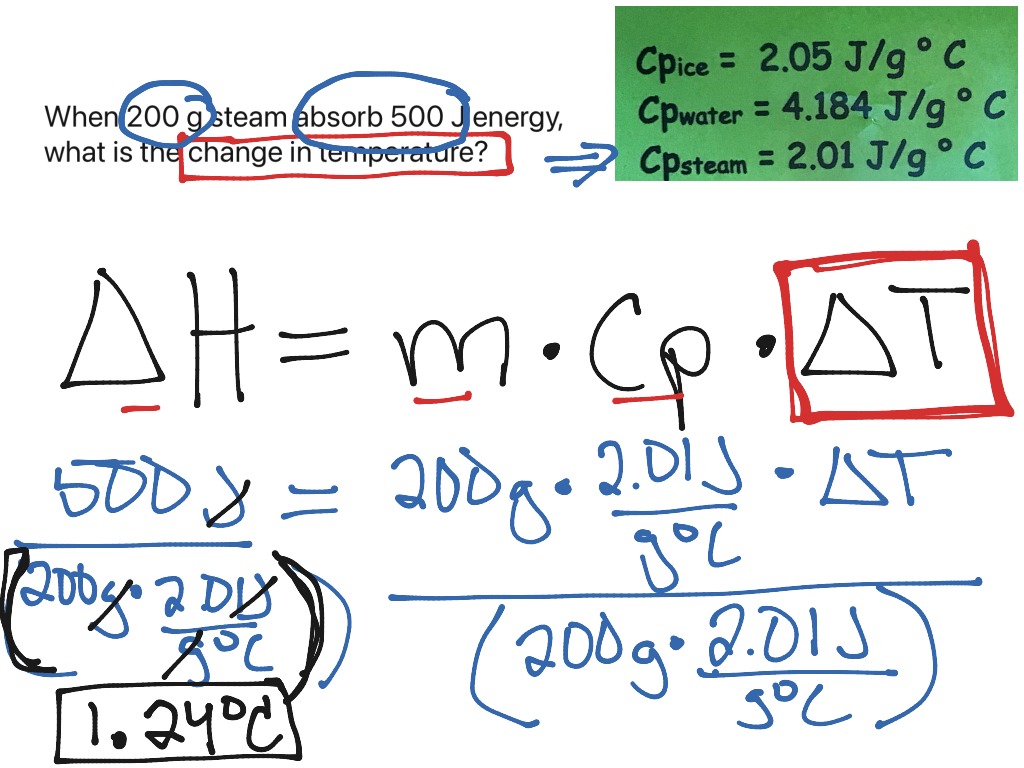
- Heat released, Q = m x c x ΔT
- m (mass of water) = 100 g (since density of water is approximately 1 g/mL)
- c (specific heat of water) = 4.18 J/g·°C
- ΔT = 30.2°C - 25.0°C = 5.2°C
- Q = 100 x 4.18 x 5.2 = 2173.6 J or 2.17 kJ
💡 Note: The above calculations assume the heat capacity of the calorimeter itself is negligible compared to the water's heat capacity. This is generally true for simple coffee cup calorimeters.
Advanced Calorimetry: Bomb Calorimetry


When analyzing substances that might undergo pressure changes, like combustion reactions, a bomb calorimeter is used. Here, the reaction container is sealed to contain pressure, and heat exchange is measured indirectly through the temperature change of water surrounding it.
- A known mass of the substance is burned in an oxygen-rich environment.
- Heat released from the reaction warms the bomb and surrounding water.
- The temperature change is used to calculate the heat of combustion.
Example Problem 3: Combustion Calorimetry

Suppose we combust 1.00 g of benzoic acid in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 9.93 kJ/°C. If the temperature rises from 25.00°C to 29.67°C, determine the heat of combustion.
- Change in temperature = 29.67°C - 25.00°C = 4.67°C
- Heat of combustion = Heat capacity of calorimeter x ΔT
- Q = 9.93 kJ/°C x 4.67°C = 46.34 kJ/g
Analyzing the Data

In all calorimetry experiments, accuracy and precision are crucial. Here’s what you need to consider:
- Measurement accuracy for temperature, mass, and specific heat.
- Calorimeter’s heat capacity, which can impact the final calculations, especially in advanced setups like bomb calorimetry.
- Heat loss to the surroundings, often minimized in well-designed experiments.
❗ Note: For accurate results, it's vital to calibrate the calorimeter, often using a substance with known heat of combustion or reaction, like benzoic acid.
In summary, this blog post has navigated through the fundamental principles of calorimetry, explaining how to solve typical problems related to heat exchange, thermal equilibrium, and reaction enthalpies. We've covered basic calorimetry, advanced techniques like bomb calorimetry, and provided practical examples for better understanding. Calorimetry is not just a set of procedures but a gateway to understanding energy transfer in various scientific and industrial applications. Keeping in mind the detailed explanation of solutions, and ensuring precision in your calorimetry experiments will significantly enhance your grasp on thermodynamics and energy science.
Why do we use different types of calorimeters?

+
Different calorimeters are used for various purposes. Simple coffee cup calorimeters measure heat changes in solutions, while bomb calorimeters are used for combustion reactions under high pressure. This allows for the study of reactions where the pressure changes or where gases are produced.
How accurate are calorimetry measurements?

+
The accuracy of calorimetry depends on several factors, including the precision of the equipment, the insulation of the calorimeter, and the calibration of the device with known standards. Errors can occur due to heat losses to the environment, improper sealing, or inaccuracies in temperature measurement.
Can calorimetry help in real-world applications?

+
Yes, calorimetry has numerous applications from nutrition (determining caloric content of food) to industrial processes (efficiency of fuel combustion), material science (specific heat capacity), and even in environmental science to study heat exchange in ecosystems.