Circles, Arcs, and Angles Worksheet Solutions: Geometry Mastery

The Basics of Circles, Arcs, and Angles

Understanding circles, arcs, and angles is a fundamental part of geometry, which opens the door to more advanced mathematical concepts and applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and design. Whether you're tackling complex math problems or just trying to grasp the basic principles, knowing how these geometric elements interact can significantly enhance your mathematical literacy. Let's dive into the key concepts, examine common worksheet problems, and provide solutions for mastering these aspects of geometry.
What Are Circles?

A circle is defined as the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed center point. Here's how different parts of the circle work:
- Center: The central point from which all points on the circle are equidistant.
- Radius (r): The distance from the center to any point on the circle.
- Diameter (d): Twice the radius, passing through the center, which divides the circle into two equal parts.
- Circumference (C): The total length of the perimeter of the circle, calculated by C = 2πr.
- Area (A): The space inside the circle, determined by A = πr².

Understanding Arcs
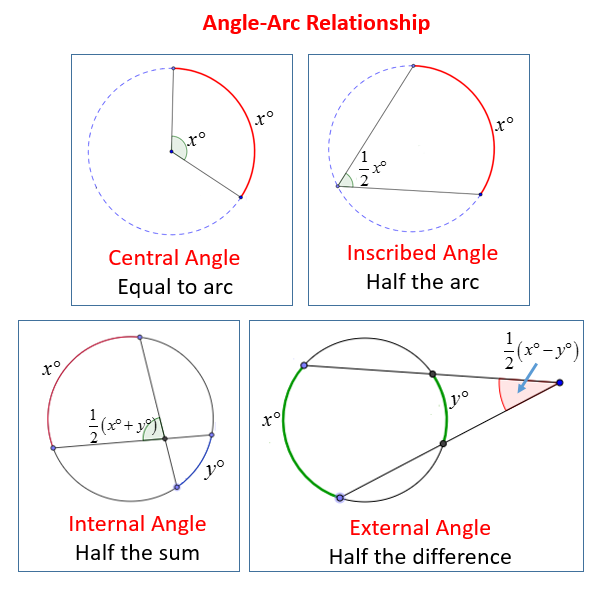
An arc is a portion of the circle's circumference. There are two types of arcs:
- Major Arc: An arc longer than a semicircle.
- Minor Arc: An arc shorter than or equal to a semicircle.
Arcs are typically named using their endpoints and sometimes the center of the circle. For instance, if points A and B are endpoints on the circumference, and C is the center, you might refer to the arc as Arc AB or Arc AC.
Angles Inscribed by Arcs

Angles associated with arcs can be:
- Central Angle: The angle whose vertex is at the circle's center.
- Inscribed Angle: An angle whose vertex is on the circumference of the circle and whose sides intercept the circle at two points.
- Inscribed Right Angle: An inscribed angle that measures 90 degrees, formed by a diameter subtending an arc.
Here's a handy formula to remember:
- The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of the arc it intercepts.
Worksheet Solutions for Circles, Arcs, and Angles

Now, let's delve into typical problems you might find in a circles, arcs, and angles worksheet and solve them step-by-step:
Example 1: Calculate the Arc Length
Given a circle with a radius of 5 units and a central angle of 54°:
To find the arc length:
- Convert the angle measure from degrees to radians: 54° * (π/180) ≈ 0.9425 radians
- Use the formula for arc length: Arc Length = r * θ, where r is the radius and θ is the angle in radians.
- Arc Length = 5 * 0.9425 ≈ 4.7125 units
⚠️ Note: When calculating arc length, always ensure that you use the angle in radians rather than degrees for accurate results.
Example 2: Inscribed Angle

If an inscribed angle measures 40°, find the measure of the intercepted arc:
- An inscribed angle is half the measure of its intercepted arc:
- Arc measure = 2 * inscribed angle = 2 * 40° = 80°
Example 3: Area of a Sector

Given a circle with a radius of 8 units and a central angle of 72°:
- Convert the angle to radians: 72° * (π/180) ≈ 1.257 radians
- Area of the sector = (θ/2π) * (πr²) = (1.257/2π) * (π * 8²) ≈ 32 square units
📚 Note: The fraction (θ/2π) is the ratio of the sector's angle to the full angle of the circle, 360° or 2π radians.
Advanced Applications

While the basics are important, mastering circles, arcs, and angles also means understanding their applications in various fields:
- Engineering: Calculating the curvature of gears, circular motions, and cam profiles.
- Architecture: Designing arches, domes, and circular rooms.
- Astronomy: Understanding orbital paths and celestial body motions.
- Art and Design: Creating visually pleasing circular compositions and radial symmetry.
Let's look at how these concepts play out in real-world scenarios:
Example Application: Architecture

Consider an architect designing a circular room with a radius of 10 meters. Here are some measurements they might need:
| Measurement | Calculation | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | d = 2r | 20 meters |
| Circumference | C = 2πr | ~62.8 meters |
| Area | A = πr² | ~314.16 square meters |
| Sector Angle (e.g., for an arch) | If an arch covers 60° | Arc length = r * θ = 10 * (π/180 * 60) ≈ 10.47 meters |

🔧 Note: Architects need to consider the structural integrity, materials, and aesthetics when incorporating circular features.
So, as we've explored, circles, arcs, and angles are not just abstract mathematical concepts; they are tools that shape our physical world. Through the examination of worksheets and real-world applications, we've gained a deeper appreciation for geometry's role in our environment and daily life.
How do you find the measure of an inscribed angle?

+
The measure of an inscribed angle is half the measure of the arc it intercepts.
What is the difference between a major and minor arc?

+
A major arc is an arc longer than a semicircle (more than 180°), while a minor arc is an arc shorter than or equal to a semicircle (less than or equal to 180°).
How can understanding circles, arcs, and angles help in design?

+
Understanding these geometric principles allows for creating aesthetically pleasing compositions, efficient use of space, and structural integrity in architecture and product design.
Can you calculate the circumference of a circle without knowing the radius?
+Yes, if you know the diameter or any other sufficient information that relates to the circle’s size, you can calculate its circumference. The diameter can be used with the formula C = πd.