Chemistry Conversions Made Easy: Practice Worksheet

In the world of science, particularly in chemistry, understanding unit conversions is paramount. Whether you're measuring volume, mass, or moles, knowing how to convert between different units ensures accuracy and consistency in your calculations. This comprehensive guide will take you through various conversion practices, making chemistry conversions not only easier but also more intuitive for students, teachers, and enthusiasts alike.
The Basics of Chemistry Conversions
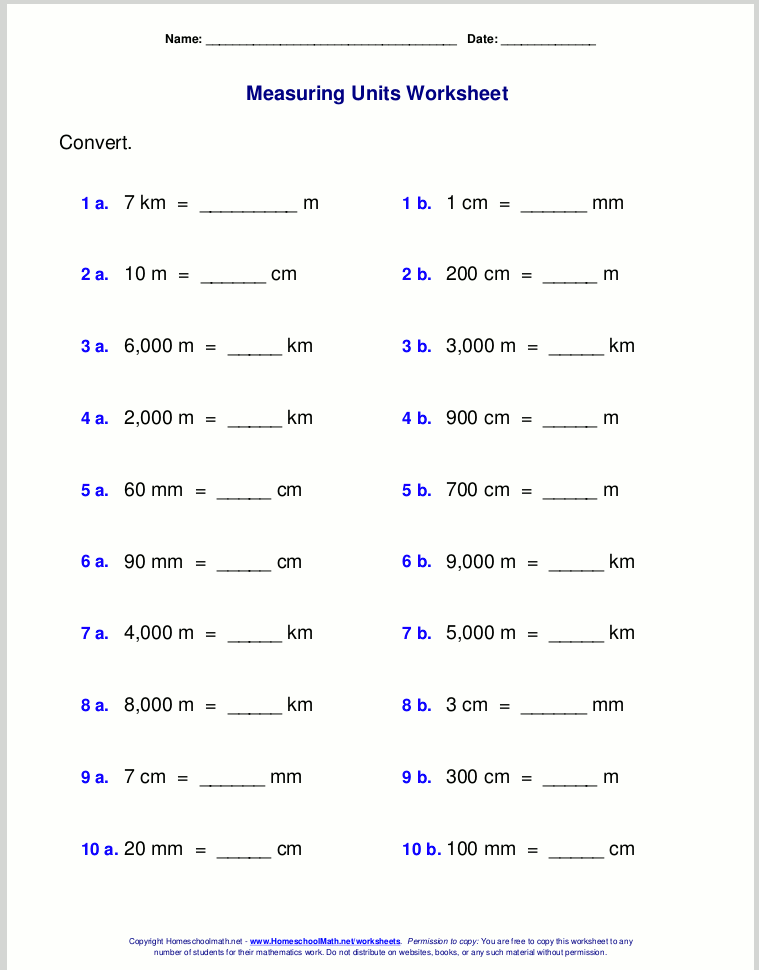
Converting units in chemistry often involves converting between the metric system units or between metric and imperial units. Here’s how to get started:
- Understand the Metric Prefixes: Familiarize yourself with prefixes like milli-, centi-, deci-, kilo-, etc.
- Dimensional Analysis: Use this method to convert units by setting up ratios that cancel out the units you don't need.
- Conversion Factors: Know common conversion factors, such as 1 meter = 100 centimeters or 1 gram = 1000 milligrams.
Converting Mass

One of the most common conversions in chemistry involves mass. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the initial unit and the target unit.
- Determine the conversion factor.
- Set up the equation so that units cancel out.
- Perform the calculation.
⚠️ Note: Always check if the conversion factor you're using is correct. A common mistake is to invert the conversion factor, leading to incorrect results.
Converting Volume

When dealing with liquids or gases, understanding volume conversion is crucial:
| Unit | Conversion |
|---|---|
| Liter (L) to Milliliter (mL) | 1 L = 1000 mL |
| Mililiter (mL) to Cubic Centimeter (cc or cm³) | 1 mL = 1 cc |

Just like with mass:
- Identify your units.
- Choose the correct conversion factor.
- Set up the equation.
- Calculate the volume.
Converting Molarity and Concentration

Molarity (M) and concentration in chemistry are often expressed in moles per liter (mol/L). Here's how to convert these measurements:
- Molarity: M = moles of solute / volume of solution (in liters).
- Concentration: For percent by mass, volume, or molarity, use specific formulas to convert.
The key is to isolate and solve for the unit you need. For instance:
- To convert molarity to mass percent, use: mass percent = (moles of solute / total mass of solution) * 100%
Temperature Conversion

Converting between Celsius (°C), Fahrenheit (°F), and Kelvin (K) is common in chemistry:
- Celsius to Fahrenheit: F = (C × 9/5) + 32
- Fahrenheit to Celsius: C = (F - 32) × 5/9
- Celsius to Kelvin: K = C + 273.15
🌡 Note: Always round temperature conversion results appropriately, as excessive precision can lead to confusion and errors in real-world applications.
Practice and Application

Here are some exercises to solidify your understanding:
- Convert 2.5 grams to milligrams.
- Convert 45.3 mL to liters.
- Convert a solution of 0.5 mol/L NaOH to mass percent, given its density is 1.04 g/mL.
- What temperature in Kelvin corresponds to 25°C?
By practicing these conversions, you not only become adept at them but also gain confidence in handling various chemistry-related problems.
Converting units in chemistry might seem daunting at first, but with practice and understanding of basic principles, it becomes second nature. Whether it's adjusting measurements for a reaction or interpreting experimental results, conversions are a cornerstone of chemical calculations. We've explored the importance of knowing metric prefixes, employing dimensional analysis, and applying conversion factors for mass, volume, molarity, and temperature. By following these guidelines, you can navigate the world of chemistry with ease.
Why are conversions important in chemistry?

+
Conversions allow chemists to communicate measurements in consistent units, ensuring accuracy in experiments, data analysis, and theoretical calculations.
How can I practice unit conversions in chemistry?

+
Engage in regular problem-solving, use online conversion tools for verification, and try to apply conversions in real-life situations like cooking or measuring medication dosages.
What are common mistakes in chemistry conversions?

+
Frequent errors include inverting conversion factors, neglecting units when setting up equations, and using the wrong conversion factor for the units in question.
How does understanding metric prefixes help?
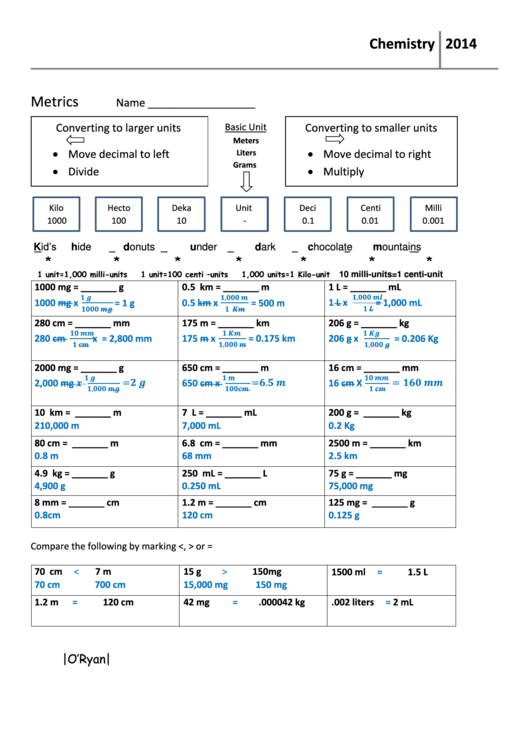
+
Understanding metric prefixes allows for quick mental calculations and conversions between units, making it easier to interpret and report scientific data.



