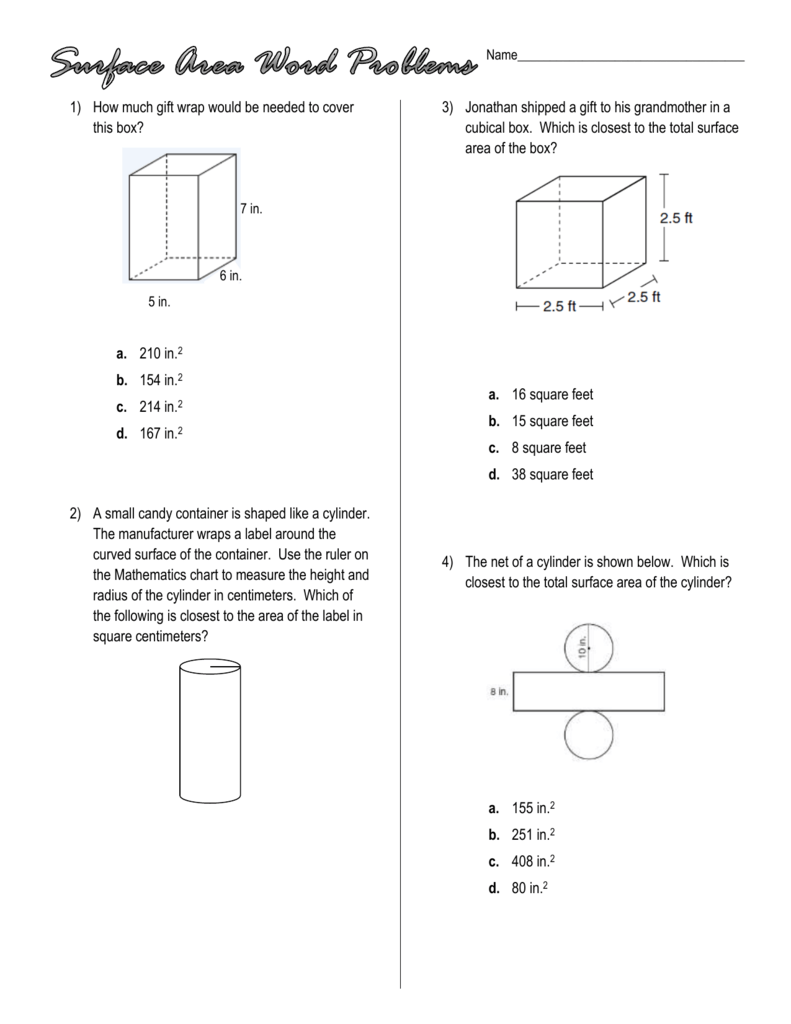
5 Essential Tips for Mastering Chemical Names and Formulas

Mastering the names and formulas of chemicals can be a daunting task for students stepping into the world of chemistry. This subject is fundamental in understanding the reactions, properties, and interactions of various substances, which are key to unlocking the secrets of the physical world. Here, we outline five crucial tips that can help you navigate the intricate labyrinth of chemical nomenclature with confidence and ease.
1. Understand the Basic Nomenclature Rules


Chemistry has its own language, with rules that govern how compounds are named. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) provides standardized naming rules:
- Binary Ionic Compounds: Start with the metal, followed by the non-metal with an “-ide” suffix. For example, NaCl is sodium chloride.
- Covalent Compounds: Use prefixes like ‘mono-’, ‘di-’, ‘tri-’, etc., to denote the number of atoms, followed by the non-metal with an “-ide” suffix. E.g., PCl3 is phosphorus trichloride.
- Polyatomic Ions: These ions have unique names and often complex structures. For instance, NH4+ is the ammonium ion.
- Acids: Naming acids depends on whether they’re in aqueous solution or not. Hydrochloric acid, HCl in solution, has a different naming convention than non-aqueous forms.
🧪 Note: Learning the IUPAC rules isn’t just about memorization; it’s about understanding the logic behind chemical names.
2. Utilize Flashcards for Memorization

Chemical memorization can be daunting due to the vast array of elements and compounds you need to know. Using flashcards can significantly enhance your retention:
- Create a card deck for each category of compounds like metals, non-metals, acids, bases, etc.
- Use the compound name on one side and the formula on the other, or vice versa.
- Incorporate the charge of ions to understand how they’ll interact in reactions.
Remember, consistency is key. Regularly revisiting these flashcards helps in cementing this information into long-term memory.
💡 Note: Digital flashcard apps can offer spaced repetition systems to optimize learning.
3. Practice Naming Conventions with Chemical Equations

Chemistry is not just about naming; it’s also about seeing how names translate into real-world reactions. Here are ways to integrate naming into practical chemical processes:
- Write out equations in words and then in symbols to reinforce naming.
- Solve chemical equations where you name the reactants and products.
- Engage in activities where you must name substances from a given reaction.
This method helps in understanding the interplay between chemical structures and their functional roles in reactions.
4. Use Mnemonics and Visual Associations

Memory aids like mnemonics can be a fun and effective way to remember chemical names and formulas:
- HONC: “HOCN,” which stands for hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon, indicating their usual number of covalent bonds (1, 2, 3, 4).
- Periodic Table Association: Visualize elements by their group and properties, helping you remember their common charges and bonding preferences.
- Color Coding: Use colors for different chemical groups or ions in your notes to visually categorize them.
5. Explore the Origin and Applications of Chemical Names

Understanding why chemicals are named as they are can provide context that makes memorization easier:
- Learn about the historical discovery of elements and compounds.
- Research the practical applications of chemicals in various industries.
- Understand the etymology of chemical names; for instance, “sodium” comes from the Latin “natrium,” which is why its symbol is “Na.”
This knowledge not only enriches your understanding but also makes the learning process more engaging.
In summary, mastering chemical names and formulas involves a combination of understanding basic rules, using effective memorization techniques like flashcards, practicing with real chemical reactions, employing mnemonics for recall, and delving into the origins and applications of chemicals. Each tip interlocks to form a strong foundation in chemistry, making it easier for you to grasp complex compounds and their roles in both academic and applied settings.
Why are some chemical compounds named with prefixes?

+
Covalent compounds use prefixes like mono-, di-, tri-, etc., to denote the number of atoms involved in the compound, which is necessary because covalent bonding doesn’t involve ions or fixed charges.
How can I remember which element comes first in a compound name?

+
Generally, in ionic compounds, the metal comes first, followed by the non-metal. For covalent compounds, the less electronegative element is listed first. It can help to remember the periodic table trends and electronegativity values.
What’s the best way to learn complex polyatomic ion names and formulas?
+
Flashcards, mnemonic devices, and understanding the common polyatomic ions’ structures can help. Associating them with common chemical reactions or familiar compounds where they are prevalent can also solidify your learning.