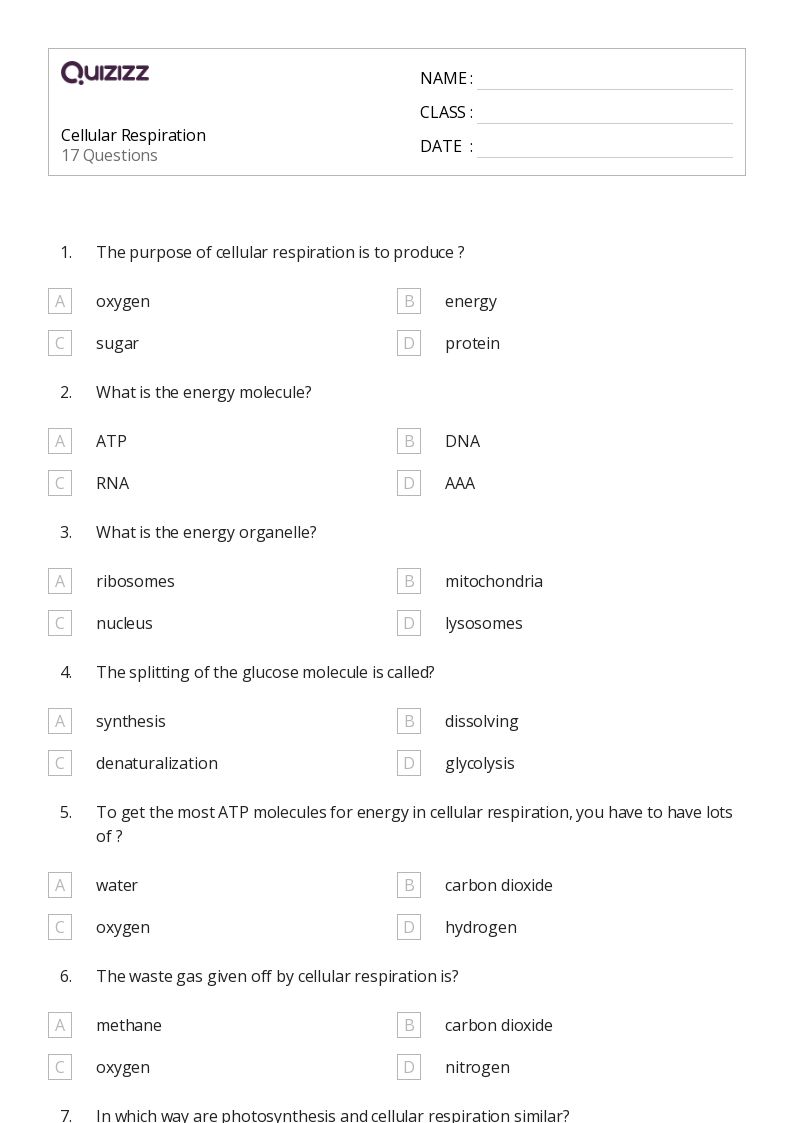
5 Essential Answers to Cellular Respiration Worksheets

Understanding cellular respiration is fundamental for students exploring biology, chemistry, and health sciences. It's the process through which cells convert food into energy, a vital function for life. To help you master this topic, here are five essential answers to common questions found in cellular respiration worksheets:
What is Cellular Respiration?


Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. Here’s a breakdown:
- Glycolysis: Splits glucose into two molecules of pyruvate, occurring in the cytoplasm.
- Citric Acid Cycle (Krebs Cycle): Occurs in the mitochondria, producing ATP, NADH, and FADH2.
- Oxidative Phosphorylation: Electron Transport Chain (ETC) and Chemiosmosis generate the bulk of ATP in mitochondria.
💡 Note: Remember, cellular respiration is aerobic, meaning it requires oxygen for complete oxidation of glucose.
How Does Cellular Respiration Differ from Photosynthesis?

While photosynthesis captures sunlight to produce glucose, cellular respiration uses that glucose to generate ATP. Here are the key differences:
| Cellular Respiration | Photosynthesis |
|---|---|
| Breaks down glucose | Synthesizes glucose |
| Produces ATP | Uses ATP in synthesis |
| Occurs in all living organisms | Occurs only in plants, algae, and some bacteria |
| Releases CO₂ as a byproduct | Uses CO₂ as a reactant |

What are the Energy Yields from Cellular Respiration?
The process of cellular respiration produces energy, but how much? Here’s a brief summary:
- Glycolysis: Produces 2 ATP
- Citric Acid Cycle: Yields 2 ATP
- Oxidative Phosphorylation: Generates around 32-34 ATP through the electron transport chain.
🔋 Note: The total energy yield varies slightly depending on the efficiency of the ETC and proton motive force.
What Factors Affect the Rate of Cellular Respiration?

Several environmental and physiological factors can impact cellular respiration rates:
- Temperature: Optimal range for most enzymes is around 37°C.
- Oxygen Concentration: Lower oxygen levels can slow down aerobic respiration.
- Substrate Availability: More glucose or other substrates can increase the rate.
- pH: Enzymes work best within a certain pH range.
How Can Cellular Respiration be Regulated?

Cells need to adjust their energy production based on need:
- Feedback Inhibition: High ATP concentrations inhibit enzymes like phosphofructokinase in glycolysis.
- Hormonal Regulation: Hormones like insulin and glucagon regulate glucose levels, which impacts respiration.
- Enzyme Control: Allosteric regulation of enzymes involved in different steps of respiration.
🧬 Note: Regulation ensures energy is produced only when needed, preventing waste.
In summary, cellular respiration is an intricate process that’s crucial for all life forms. Whether you’re dissecting it in a worksheet or understanding its real-world applications, knowing the differences from photosynthesis, the energy yields, rate-influencing factors, and regulation mechanisms provides a comprehensive view of how life sustains itself.
Why is cellular respiration considered an aerobic process?

+
Cellular respiration is considered aerobic because it requires oxygen to function most efficiently, particularly during oxidative phosphorylation where the electron transport chain uses oxygen as the final electron acceptor.
What happens if there’s no oxygen available for cellular respiration?

+
In the absence of oxygen, cells can still produce ATP through anaerobic respiration or fermentation, but the yield is significantly lower, with processes like lactic acid fermentation or alcohol fermentation taking over.
Can human cells perform photosynthesis?

+
No, human cells do not have the organelles or enzymes necessary to perform photosynthesis. This process is unique to plants, algae, and some bacteria that contain chloroplasts.
What is the role of ATP in cellular respiration?

+
ATP serves as the primary energy currency of the cell, providing the energy needed for various cellular processes from muscle contraction to protein synthesis. Cellular respiration produces ATP to replenish these energy demands.
How does temperature affect cellular respiration?

+
Temperature affects the rate of enzymatic reactions in cellular respiration. At lower temperatures, enzymes slow down, reducing the rate of respiration. Too high, and enzymes might denature, also hindering the process.