Cell Membrane Worksheet: Structure, Function, and Answers

The cell membrane, often called the plasma membrane, plays an indispensable role in the life of every cell, acting as a selective barrier that orchestrates a multitude of cellular processes. Understanding the structure, function, and interactions of the cell membrane isn't just fascinating but essential for anyone interested in the biological sciences or health-related fields. In this detailed guide, we'll delve into what makes up this extraordinary structure, how it functions, and how we can engage with this knowledge through a cell membrane worksheet.
What is the Cell Membrane?

The cell membrane is a bilayer of lipids and proteins which forms the outer boundary of the cell. Here are some key points:
- Composition: Primarily made of phospholipids, with cholesterol for stability and proteins for various functions.
- Fluid Mosaic Model: This model describes the cell membrane as a fluid structure with proteins embedded within the lipid bilayer, moving in a 'sea' of lipids.
- Selective Permeability: The membrane allows certain substances to pass through while blocking others, maintaining cell integrity and functionality.
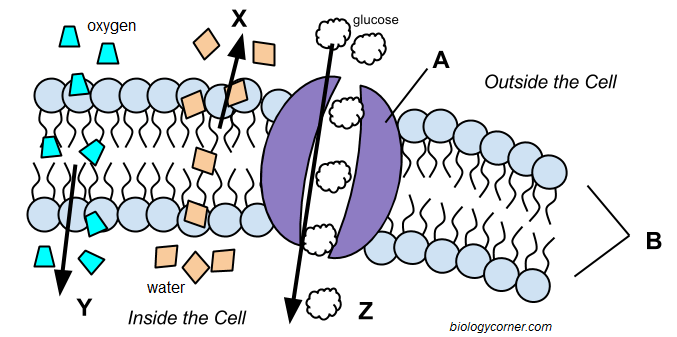
Structure of the Cell Membrane

Let's break down the structure further:
Phospholipid Bilayer

The foundation of the cell membrane consists of:
- Hydrophilic Heads: Polar phosphate groups face outwards, interacting with the aqueous environment.
- Hydrophobic Tails: Non-polar fatty acid tails face inwards, avoiding water.
Embedded Proteins

Proteins within the membrane serve various roles:
- Integral Proteins: Span the membrane, often involved in transport.
- Peripheral Proteins: Attached to the surface, they provide structural support or catalytic functions.
Cholesterol

Cholesterol regulates fluidity by:
- Reducing membrane fluidity at high temperatures.
- Increasing membrane fluidity at low temperatures.
Carbohydrate Chains

Glycoproteins and glycolipids have carbohydrate chains that:
- Provide cell identification.
- Participate in cell adhesion.
Functions of the Cell Membrane

The cell membrane performs several vital functions:
1. Protection and Structural Support

- Separates the cell from its environment, shielding it from toxins.
- Maintains cell shape and provides structure.
2. Selective Permeability

- Allows passage of nutrients and necessary molecules via:
- Passive Transport: Facilitated diffusion, osmosis.
- Active Transport: Pumps, endocytosis, exocytosis.
3. Cell Signaling

- Receptors on the membrane surface bind to signaling molecules.
- Initiates intracellular signaling pathways.
4. Cell Adhesion and Communication

- Facilitates cell-to-cell adhesion through proteins like cadherins.
- Allows cells to communicate via gap junctions or synapses.
A Cell Membrane Worksheet for Hands-On Learning
To solidify your understanding, here's a worksheet that covers these concepts:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What are the main components of a cell membrane? | Phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, carbohydrates |
| How does cholesterol affect the fluidity of the cell membrane? | Cholesterol reduces fluidity at high temperatures and increases it at low temperatures, acting as a buffer. |
| What is selective permeability and why is it important? | Selective permeability allows the membrane to control what enters and exits the cell, ensuring the cell's survival and function. |
| What roles do peripheral proteins play? | Provide structural support, serve as enzymes, or act as receptors for signaling molecules. |

🔍 Note: For further understanding, consider watching animations or using interactive 3D models of the cell membrane to visualize these structures and functions.
Wrapping up our exploration, we've delved into the intricate world of the cell membrane, from its composition to its vital roles in maintaining life. By engaging with this knowledge through exercises and interactive learning tools, we not only enhance our understanding but also appreciate the remarkable complexity of life at the cellular level. This fundamental knowledge empowers us to explore further, innovate, and even discover potential treatments for various cellular dysfunctions.
What are the main functions of the cell membrane?

+
The cell membrane has several key functions including protection, selective permeability, cell signaling, and adhesion and communication.
How do the components of the cell membrane work together to maintain fluidity?

+
Phospholipids form a flexible bilayer with hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions. Cholesterol modulates fluidity by regulating the interactions between lipid tails, while proteins can also influence fluidity by affecting the membrane’s structure.
Why is the Fluid Mosaic Model significant?
+The Fluid Mosaic Model describes the dynamic nature of the cell membrane, showing how components are mobile within the lipid bilayer, which is crucial for functions like transport, signaling, and repair.