5 Essential Tips for Mastering Triangle Interior Angles
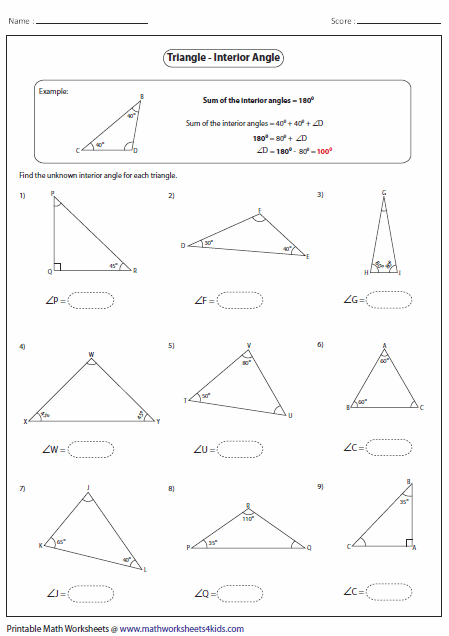
Understanding the interior angles of triangles is fundamental in geometry. Mastery of these angles can enhance your ability to solve complex geometric problems, create accurate diagrams, and understand spatial relationships. Here are five essential tips to help you excel in this area:
Understand the Basics

Before delving into more complex aspects, let’s revisit the basics:
- The sum of the interior angles in any triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Each triangle has three interior angles, and the sum of these angles can be used to find unknown angles.
- The angles opposite to equal sides in an isosceles triangle are equal.
- In an equilateral triangle, all angles are 60 degrees.
📘 Note: These basic principles form the foundation for understanding more advanced triangle concepts.
Use Geometry Theorems

Geometry theorems offer shortcuts to understanding triangle angles:
- Angle Sum Property: The sum of the angles in any triangle is 180 degrees. This can be directly applied to find missing angles.
- Exterior Angle Theorem: The measure of an exterior angle equals the sum of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
- Triangle Inequality Theorem: The sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle must be greater than the length of the third side, which indirectly affects the angles.
Here’s an example:
If you know two angles of a triangle are 40° and 60°, you can find the third angle by subtracting the sum of these two angles from 180°: 180° - (40° + 60°) = 80°
Visualize Angles with Diagrams

Visualization is key:
- Draw the triangle and mark the angles you know. This visual aid can help in solving for unknown angles.
- Use colored pens or markers to differentiate between known and unknown angles.
- Create an exterior angle and apply the Exterior Angle Theorem to find interior angles.
By visualizing the relationships, you can better understand how changes in one angle affect the others.
Practice with Various Types of Triangles

Mastery comes from practice:
- Isosceles and equilateral triangles have special angle properties that you should practice often.
- Right triangles have one 90-degree angle, making angle calculations straightforward due to the known angle.
- Oblique triangles (neither right nor isosceles/equilateral) require you to apply general triangle properties and theorems.
- Practice with real-world applications like roof pitches or architectural designs can make learning more practical.
Try solving problems where you must find all angles of a triangle given various conditions.
Apply Trigonometric Concepts

Advanced mastery involves integrating trigonometry:
- Sine, Cosine, and Tangent: Use these trigonometric functions to find angles when side lengths are known.
- Law of Sines and Law of Cosines: These laws allow you to solve triangles that are not right-angled by using angles and lengths.
- Angle-side relationships: Apply trigonometric identities to find angles or sides when only certain measurements are given.
For instance, if you know the side lengths and one angle, you can use the Law of Cosines to find the other angles:
In a triangle ABC with sides a, b, and c, and angle C, you can find angle B using: cos(B) = (a2 + c2 - b2) / (2ac)
🔬 Note: Trigonometry provides an elegant way to deal with angles in complex triangles, especially when traditional geometric methods fall short.
By following these five tips, you can gain a deeper understanding and mastery of triangle interior angles. From basic principles to advanced trigonometric applications, each step builds upon the last to solidify your geometric knowledge. Remember, practice is key, and the more you engage with these concepts through problem-solving and practical applications, the more naturally these principles will become to you. Whether you're working on school assignments, preparing for standardized tests, or exploring geometry for personal enrichment, these strategies will undoubtedly enhance your geometric prowess.
Why do triangles always have angles summing to 180 degrees?
+
The sum of the interior angles of any triangle equalling 180 degrees is a result of the Triangle Postulate, which states that the three interior angles of a plane triangle sum up to a straight line, which is always 180 degrees.
What is the practical use of knowing triangle angles?
+
Understanding triangle angles is crucial in fields like architecture, engineering, and surveying, where it’s necessary to ensure stability, balance, and accurate measurements. They also help in navigation, computer graphics, and designing structural components.
Can the same triangle have different angle measurements?

+
While the measurements of the angles in a specific triangle remain constant, different triangles with different side lengths can have different angle measurements. However, the sum of these angles will always be 180 degrees for planar triangles.



