Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers: Essential Nutrition Guide for Fitness Enthusiasts

Understanding Carbohydrates for Optimal Fitness

Carbohydrates are a critical component of any fitness enthusiast's diet. They serve as the primary source of energy for physical activities, fuel workouts, and aid in recovery. If you're working out regularly, understanding how to balance carbohydrate intake can be the key to enhancing your performance, achieving your fitness goals, and maintaining your health. This guide will explore what carbohydrates are, why they are essential, how to optimize them for different types of workouts, and provide answers to common carbohydrate-related questions in fitness.
What Are Carbohydrates?

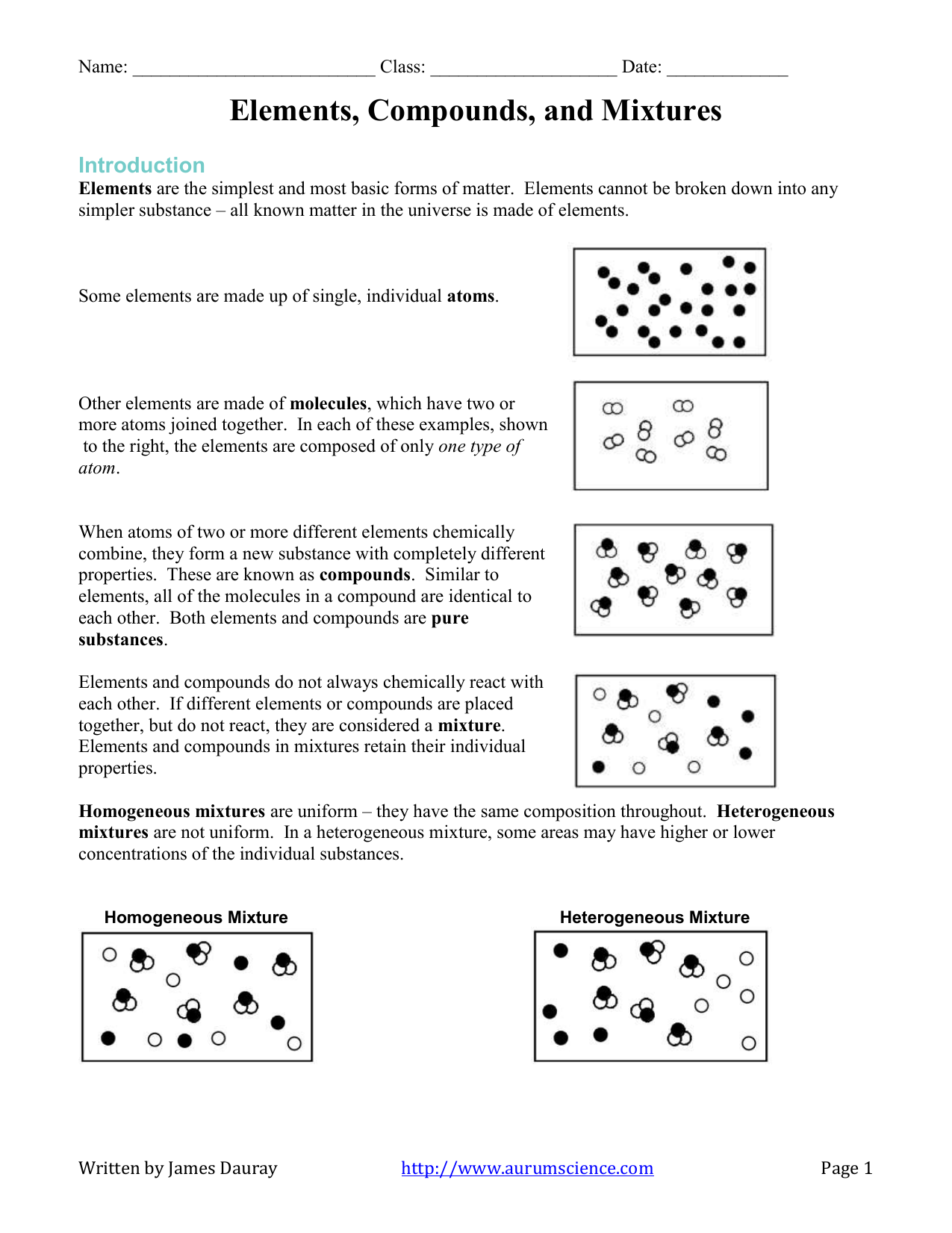
Carbohydrates are one of the three macronutrients (alongside protein and fat) that are needed in relatively large amounts for good health. They are molecules made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Here's a brief overview:
- Simple Carbohydrates: Known as simple sugars, these are quickly digested and provide rapid energy. Examples include glucose, fructose (fruit sugar), and sucrose (table sugar).
- Complex Carbohydrates: These include starches and fiber. They have longer molecular chains, which take longer to break down, providing sustained energy. Examples are whole grains, vegetables, and legumes.
🔍 Note: The classification of carbohydrates as 'simple' or 'complex' is based on their chemical structure, not necessarily their nutritional quality. Some simple carbs can be beneficial (like in fruits) while some complex carbs might be refined and less nutritious (like white bread).
Why Are Carbohydrates Essential for Fitness?

Carbohydrates play several key roles in supporting fitness activities:
- Energy Supply: Carbs are converted into glucose, which is used by muscles for contraction during exercise. Glycogen, a stored form of carbohydrate, is particularly important for prolonged, high-intensity activities.
- Brain Function: Your brain prefers glucose over other fuels. Maintaining carbohydrate levels can help with focus and cognitive performance during workouts.
- Recovery: Post-workout, carbohydrates help replenish glycogen stores and support muscle repair when combined with proteins.
- Hormonal Balance: Carbs influence insulin and glucagon levels, which regulate blood sugar and can impact fat storage and energy usage.
Optimizing Carbohydrates for Different Workouts

Your carbohydrate needs vary depending on your type of exercise:
Endurance Sports

Endurance athletes like marathon runners or cyclists need high carbohydrate diets:
- Load up with complex carbs before the event to maximize glycogen stores.
- Ingest carbohydrates during prolonged events to maintain energy levels.
- Post-event, focus on recovery with a combination of protein and carbs.
Strength Training

Strength or resistance training sessions require:
- Adequate carbs before a workout to fuel the session, particularly for high-volume or heavy lifting.
- Carbohydrate intake post-workout to replenish glycogen and aid in protein synthesis for muscle repair.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)

HIIT requires:
- Pre-workout carbs to ensure energy for the intense bursts of activity.
- Quick-digesting carbs like sports drinks or gels during long sessions to prevent bonking.
- Recovery carbs immediately after the workout to support glycogen resynthesis.
Carbohydrate Timing: When to Eat Carbs?

Timing is critical when it comes to carbohydrate consumption for fitness:
- Pre-Workout: Eat carbs 1-4 hours before exercising to top up glycogen stores. This time frame allows digestion and avoids discomfort during workouts.
- During Workout: For sessions lasting longer than 60 minutes, consuming carbs can help maintain performance. This includes gels, sports drinks, or other forms of simple sugars.
- Post-Workout: The recovery window is key. Within 30 minutes to an hour post-exercise, consuming carbs aids in glycogen replenishment.
⏰ Note: Don't forget hydration. Carbs and hydration go hand-in-hand to maintain optimal performance, particularly in endurance sports.
Quality of Carbohydrates

Not all carbohydrates are created equal. Here's what to consider:
- Nutrient-Dense Carbs: Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes provide vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants.
- Refined Carbs: These are stripped of nutrients and fiber, like white bread or sugary snacks. They offer quick energy but lack nutritional value.
- Processed Foods: These can contain high levels of sugars and additives, potentially causing energy spikes and crashes.
📊 Note: A balanced approach to carbohydrates usually involves a combination of simple and complex carbs tailored to your activity level and fitness goals.
Carbohydrate Needs Based on Fitness Goals

Different fitness goals influence carbohydrate needs:
| Goal | Carbohydrate Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Weight Loss | Low to moderate carb intake to maintain energy levels while creating a caloric deficit. |
| Muscle Gain | Higher carb intake to fuel workouts and support protein synthesis during recovery. |
| Performance | High carb intake, especially for endurance athletes, to maximize glycogen stores and performance. |

Carbohydrates for Fitness: Practical Tips

- Experiment with carb loading strategies before long events to find what works best for you.
- Ensure a mix of carbs, fats, and proteins in every meal for balanced nutrition.
- Use simple carbs during workouts for immediate energy and complex carbs outside of workouts for sustained energy and recovery.
- Monitor how different carbs affect your energy, digestion, and workout performance.
To wrap up, understanding carbohydrates is pivotal for fitness enthusiasts aiming to optimize performance, recovery, and overall health. Your carb intake should be tailored to your fitness goals, the type of exercise you’re engaging in, and the timing of your meals. By choosing high-quality carbs and eating them at the right time, you can fuel your workouts effectively and support your body’s recovery process. Remember, individual needs can differ, and what works for one person might not work for another, so listening to your body and perhaps consulting a nutritionist can help you find your personal carb sweet spot.
Can I lose weight on a high-carb diet?

+
Yes, you can lose weight on a high-carb diet if your total calorie intake is less than what you burn. The key is not to demonize carbs but to balance them with a caloric deficit.
What are the best carbs to eat before a workout?

+
Best pre-workout carbs include whole grains, fruits like bananas for quick digestion, and oatmeal for sustained energy. Timing is key - eat them 1-4 hours before exercising.
How do I know if I’m consuming the right amount of carbs for my workouts?

+
Track your performance, energy levels, and how you feel during and after workouts. If you experience energy dips or poor recovery, adjusting your carb intake might be necessary.