Element Compounds and Mixtures Worksheet Answers Revealed
Understanding the fundamental differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures is crucial for anyone delving into the fascinating world of chemistry. Whether you're a student grappling with chemical concepts or an enthusiast eager to grasp these basics, this comprehensive guide will navigate you through the Element Compounds and Mixtures Worksheet Answers with clarity and depth.
What Are Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures?

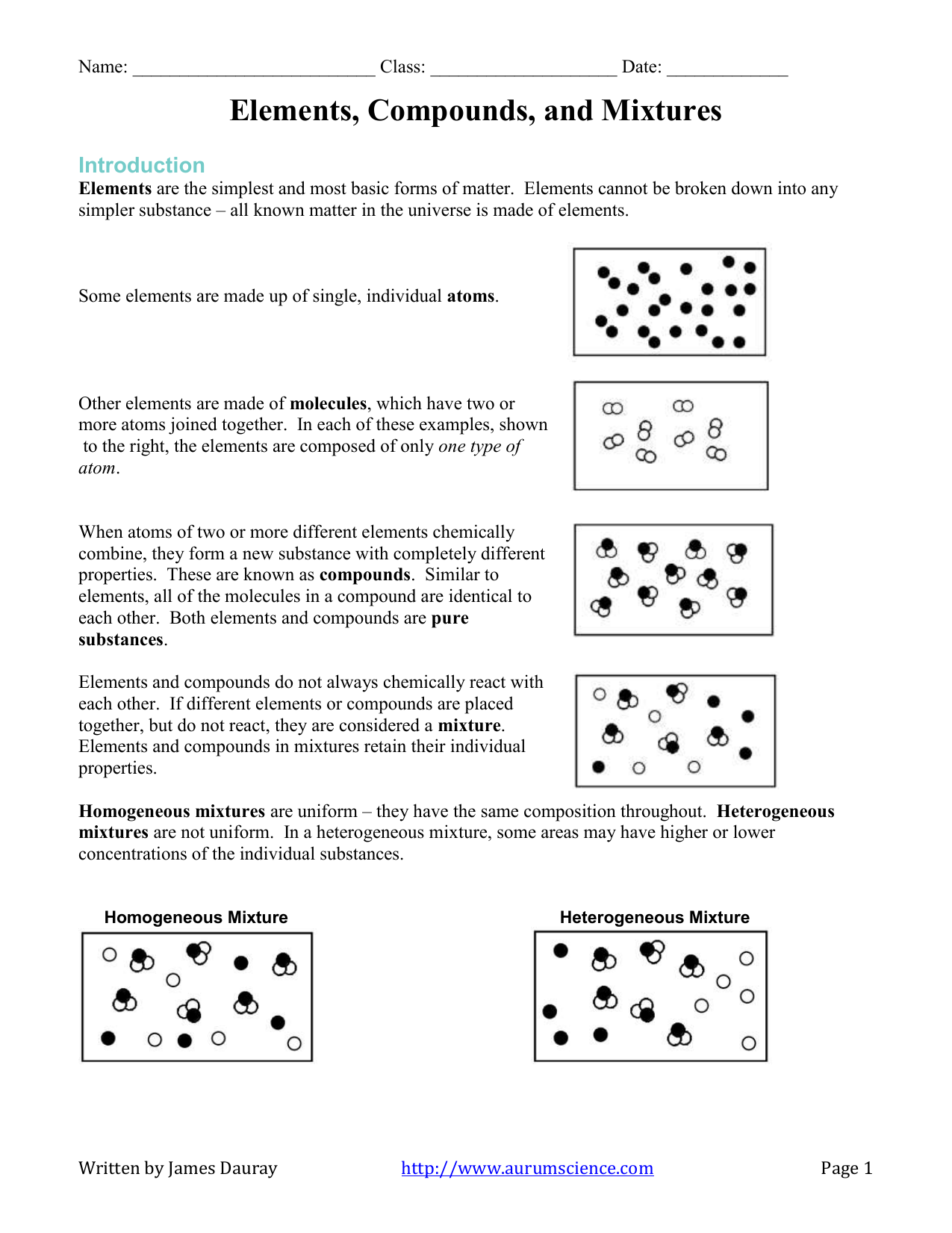
Elements are the simplest form of substances, consisting of only one type of atom. These cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples include hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), and gold (Au).
Compounds, in contrast, are composed of two or more different elements chemically bonded together in fixed ratios. For instance, water (H2O), where hydrogen and oxygen atoms bond together in a ratio of 2:1.
Mixtures occur when substances are mixed together without a chemical reaction, allowing the individual components to retain their identities. Air, with its mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases, is a common example.
Identifying Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures

Let's delve into how one can identify these different categories in a worksheet scenario:
- Element: Look for symbols or abbreviations of elements with just one capital letter (e.g., O for Oxygen, Na for Sodium) or paired letters (He for Helium, Ne for Neon). If the substance can't be decomposed into simpler substances, it's an element.
- Compound: Identify substances where two or more elements are chemically bonded in a specific proportion. Their chemical formula should reflect this, like CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) or NaOH (Sodium Hydroxide).
- Mixture: Here, look for descriptions of substances combined without chemical bonding. Mixtures might be described with terms like 'contains', 'mixed with', or visual cues in diagrams showing separate phases or components.
🔬 Note: While elements and compounds have distinct chemical properties, mixtures can be homogeneous (evenly mixed) or heterogeneous (unevenly mixed).
Worksheet Answers Breakdown

| Question Type | Element Example | Compound Example | Mixture Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| What substance? | Hydrogen (H) | Water (H2O) | Air (N2, O2, CO2) |
| Chemical Formula? | Oxygen (O) | Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Not Applicable |
| Can it be separated? | No | Yes, by electrolysis | Yes, by physical methods |
| Physical Properties? | Colorless, odorless | Colorless liquid | Variable (e.g., air varies with altitude) |

⚗️ Note: Understanding these distinctions is essential not only for academic purposes but also for real-world applications like environmental monitoring and material synthesis.
Practical Applications

Knowing the distinctions between elements, compounds, and mixtures has several practical applications:
- Material Science: Developing new materials involves understanding chemical bonding and mixture properties.
- Environmental Science: Monitoring air and water quality relies on knowing what substances are compounds or mixtures.
- Pharmacology: Drug formulation often involves creating compounds or using mixtures for specific therapeutic effects.
- Industrial Processes: From refining metals to purifying chemicals, knowing how to separate mixtures or synthesize compounds is fundamental.
To summarize, by navigating through this Element Compounds and Mixtures Worksheet Answers, you've explored the basic building blocks of matter, gaining insights into how to identify and differentiate between them. This foundational knowledge not only aids in understanding chemistry but also bridges to real-world applications, making it both academically enriching and practically applicable.
What is the difference between a compound and a mixture?

+
A compound consists of two or more elements chemically bonded in a fixed ratio. A mixture, on the other hand, involves substances mixed together without a chemical reaction, retaining their individual properties.
How can I tell if a substance is an element from a worksheet?

+
Elements will have a symbol or abbreviation with one or two capital letters that aren’t easily divisible into simpler substances by chemical means. For example, H for Hydrogen, or Fe for Iron.
Why is it important to distinguish between mixtures and compounds in environmental monitoring?

+
Mixtures in the environment, like air or water, can contain pollutants or varying concentrations of substances. Understanding the type helps in identifying and controlling sources of pollution and ensuring safe conditions.
Can a mixture ever become a compound?
+
A mixture can become a compound if a chemical reaction occurs among its components. For example, if you mix hydrogen and oxygen under certain conditions, a chemical reaction can produce water, which is a compound.
What are some techniques for separating mixtures?

+
Separation techniques include filtration, distillation, evaporation, magnetic separation, and chromatography, depending on the physical properties of the substances involved.