Explore Bill Nye's Buoyancy Worksheet - Fun Science!

Bill Nye, the Science Guy, has long been a beloved figure in educational science television, making complex scientific concepts accessible and entertaining for viewers of all ages. One of the myriad topics Bill Nye has tackled in his extensive catalog is buoyancy, a principle of fluid mechanics that explains why certain objects float or sink in liquids. Today, we delve into Bill Nye's Buoyancy Worksheet, exploring how this educational resource can turn learning about buoyancy into an engaging adventure for students.
What is Buoyancy?
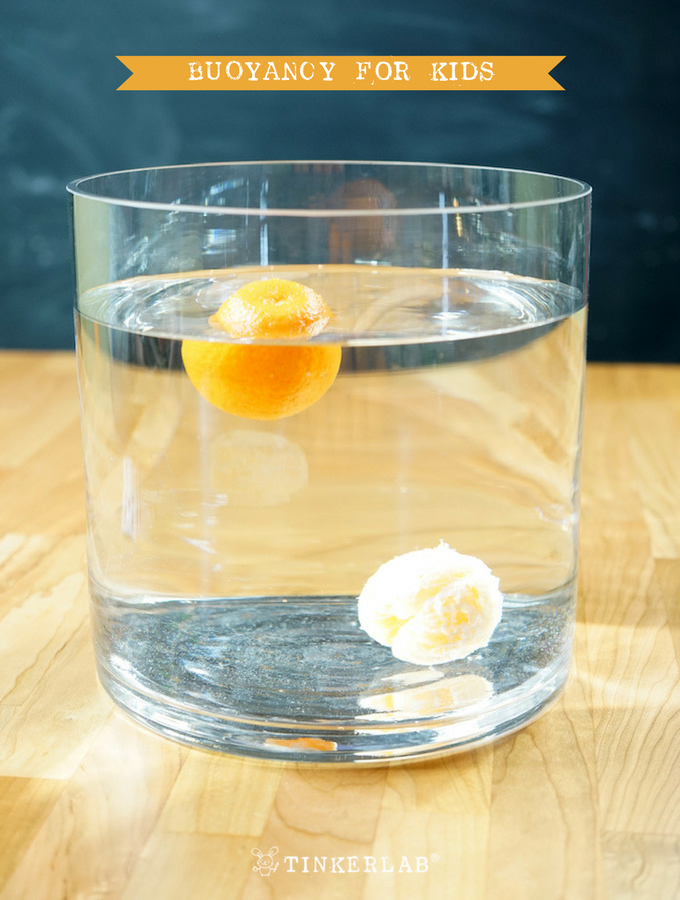

Before diving into the worksheet, let’s understand buoyancy. At its core, buoyancy is the force exerted on an object immersed in a fluid, which opposes the weight of the immersed object. If the buoyant force is greater than the object’s weight, the object floats. If it’s less, the object sinks.
Bill Nye’s Approach to Buoyancy Education

Bill Nye’s approach to teaching buoyancy is both educational and entertaining:
- Humor and Engagement: Nye uses humor to keep viewers engaged. His catchphrases like “Science rules!” or “Do not try this at home!” are memorable and help in making the learning experience fun.
- Visual Experiments: Experiments are a staple in Nye’s shows, making abstract concepts tangible. His buoyancy experiments often involve everyday objects or liquids like water, oils, and even soda cans to illustrate buoyancy.
- Simple, Clear Explanations: Nye breaks down complex ideas into simple language, ensuring students of various age groups can understand the science behind buoyancy.
- Interactive Learning: Worksheets like the one on buoyancy encourage students to think critically and apply their knowledge through practical exercises.
The Buoyancy Worksheet Breakdown

Here’s what you can expect from Bill Nye’s Buoyancy Worksheet:
- Introduction to Archimedes’ Principle: The worksheet might start with a brief overview of Archimedes’ principle, which states that an object immersed in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
- Questions on Density: Since density plays a crucial role in buoyancy, there would be questions like:
- Why does ice float on water?
- Calculate the density of an object that floats in water.
- Real-World Applications: Examples could include:
- The buoyancy of ships
- Why submarines can change their buoyancy
- Experiments and Observations: Students might be asked to perform simple experiments:
- Floating an egg in saltwater vs. freshwater
- Using a hydrometer to measure liquid density
- Critical Thinking Exercises: Questions designed to encourage critical thinking:
- Explain why helium balloons rise while hot air balloons need to heat the air to do the same.
- Why does a tennis ball float, but a golf ball does not?
🌍 Note: The buoyant force is always directed upward, opposing the gravity that pulls the object down.
Making Learning Fun with Bill Nye’s Worksheets

Bill Nye’s worksheets aren’t just about passive learning. They incorporate:
- Interactive Activities: Experiments or small projects that students can do at home or in the classroom.
- Application of Concepts: Real-world scenarios where buoyancy plays a role, from understanding why certain objects are designed the way they are, to how buoyancy affects our daily lives.
- Critical Thinking: Encouraging students to think beyond the obvious, asking why things float or sink and how this knowledge can be applied in innovative ways.
The Educational Impact

Here’s how engaging with Bill Nye’s buoyancy worksheet can benefit students:
- Enhanced Understanding: Students develop a better grasp of buoyancy, density, and fluid mechanics, crucial concepts in science education.
- Hands-On Experience: The activities foster a kinesthetic learning environment, promoting hands-on exploration of scientific principles.
- Critical Thinking: Encourages analytical thinking as students are prompted to solve buoyancy-related problems or design their own experiments.
- Interest in Science: By making science fun and engaging, Bill Nye ignites curiosity and can lead to a lifelong passion for scientific inquiry.
What is the difference between buoyancy and density?

+
Buoyancy refers to the upward force exerted on an object in a fluid, while density is a measure of mass per unit volume. Density affects buoyancy; if an object has a density less than the fluid it’s in, it will float due to the greater buoyant force.
Can you change an object’s buoyancy?

+
Yes, you can change an object’s buoyancy by altering its volume or density, or by changing the density of the fluid it is in. For example, adding air to a balloon makes it float in air, while increasing the salinity of water can make objects float that would otherwise sink in freshwater.
Why do ships float?
+
Ships float because they displace a weight of water equal to their own total weight. Despite being made of steel, which is denser than water, their overall density, including all the empty spaces, is less than that of water, allowing them to float.