5 Essential Answers for Atomic Structure Worksheet

Atomic structure forms the backbone of modern chemistry, providing the foundation upon which our understanding of matter and its interactions is built. This blog post aims to delve into the complexities and intricacies of atomic structure, offering clear, insightful answers to common questions encountered in atomic structure worksheets. Whether you're a student preparing for a chemistry test or an educator looking for explanations to teach, these essential answers will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the atomic world.
What is an Atom and Its Basic Components?
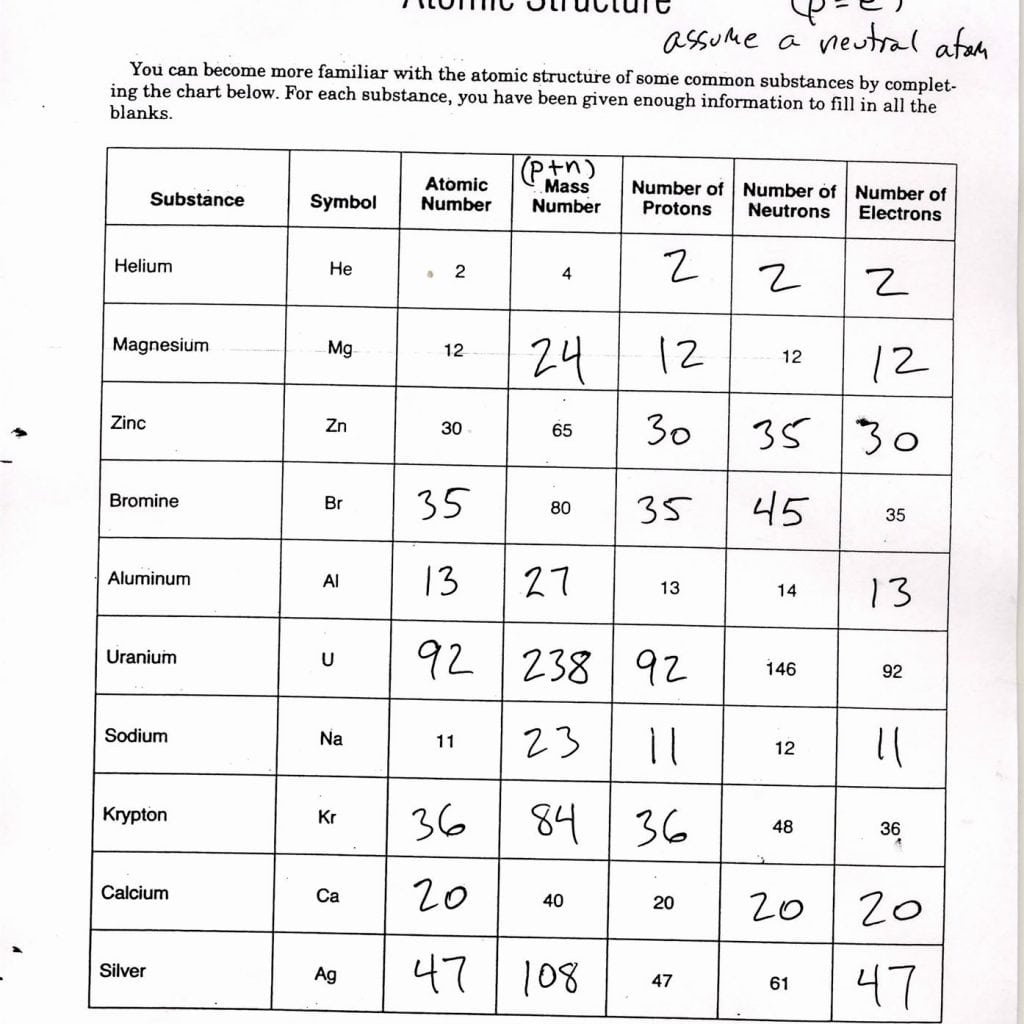
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the chemical identity of an element. At its core, an atom consists of three fundamental particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom. Their number determines the element's atomic number.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus, influencing an atom's chemical behavior.
- Neutrons: Neutral particles within the nucleus, which contribute to the atom's mass without affecting its chemical properties.
🔎 Note: While all atoms of an element have the same number of protons, they can differ in the number of neutrons, creating isotopes.
How Does the Bohr Model Represent Atomic Structure?

The Bohr model, proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, visualizes the atom with:
- A central nucleus containing protons and neutrons.
- Electrons moving in fixed orbits or energy levels around the nucleus, similar to planets orbiting the sun.
| Energy Level (n) | Maximum Number of Electrons |
|---|---|
| 1 | 2 |
| 2 | 8 |
| 3 | 18 |
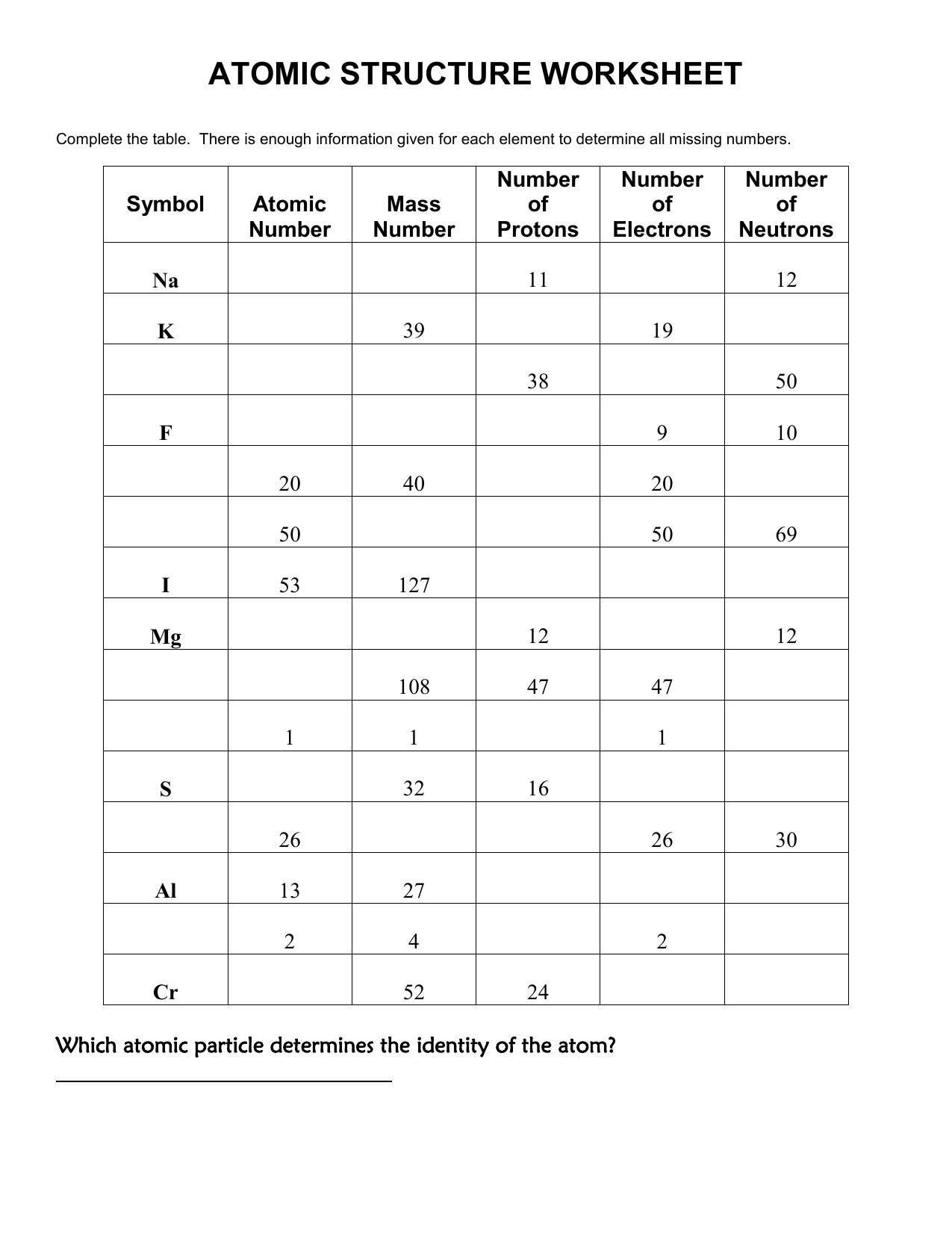
The Bohr model also introduced the concept of quantum levels, where electrons can only occupy certain orbits, explaining why atoms emit or absorb energy in discrete amounts.
What are Isotopes, and How Do They Affect Atomic Mass?

Isotopes are atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons. Here's how they impact the atomic mass:
- Each isotope of an element has a unique mass number (sum of protons and neutrons).
- The average atomic mass listed on the periodic table is a weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes, accounting for their relative abundance.
💡 Note: The existence of isotopes means that the atomic mass of an element can be a non-integer value, reflecting the average of these isotopic masses.
Why Does Atomic Size Decrease Across a Period?

As you move from left to right across a period in the periodic table, the atomic size tends to decrease due to:
- Increased nuclear charge: Each element has one more proton than the previous one, pulling electrons closer to the nucleus.
- Effectiveness of electron shielding: While there are more electrons, they are added to the same energy level, not significantly increasing electron-electron repulsion.
This trend showcases the complex interplay between the forces within an atom that dictate its overall size.
How Does Atomic Structure Explain Chemical Bonding?

The valence electrons, the electrons in the outermost shell of an atom, determine its:
- Reactivity: Atoms strive for a full outer shell, influencing their willingness to bond.
- Bonding type: Whether an atom will form ionic or covalent bonds depends on its ability to gain, lose, or share electrons.
This understanding of atomic structure is crucial for predicting how elements will interact to form compounds, molecules, and ions.
The insights into atomic structure provided in this post illuminate the remarkable world beneath our observable universe. Understanding how atoms are constructed, their behavior, and the interactions between their constituents not only deepens our appreciation for chemistry but also underpins much of modern science and technology. By grasping these essential aspects of atomic structure, we gain a clearer view of the molecular dance that shapes our physical and chemical environment.
Why is it important to know about isotopes?

+
Understanding isotopes is vital in fields like radiocarbon dating, nuclear medicine, and geochemistry, as they can provide unique information about the age, origin, and behavior of materials.
What is the significance of electron shells?

+
Electron shells define the chemical properties of atoms. They determine how an atom interacts with others to form compounds, influencing its stability and reactivity.
How does the atomic structure influence the periodic table?

+
The periodic table is organized based on the electron configurations of atoms. It groups elements with similar properties in columns and arranges them by increasing atomic number, reflecting the underlying atomic structure.



