5 Easy Steps to Master Addition on a Number Line

In the world of mathematics, understanding basic operations like addition through visual methods can significantly improve learning and retention, especially for young minds. One such visual tool is the number line, a simple yet powerful aid in teaching children how to add numbers. Whether you're a teacher, a parent, or a student looking to better your arithmetic skills, mastering addition on a number line is not just educational but can be incredibly fun as well. Here are five easy steps to get you started:
Step 1: Understand the Number Line

The number line is a straight line that represents numbers from negative to positive infinity, with zero usually placed at the center. Here are some key points:
- Each number is placed at an equal distance from its neighbors.
- Movement to the right increases the value, and to the left, decreases it.
- Zero is the baseline or the midpoint in many scenarios.

Step 2: Identify the First Number
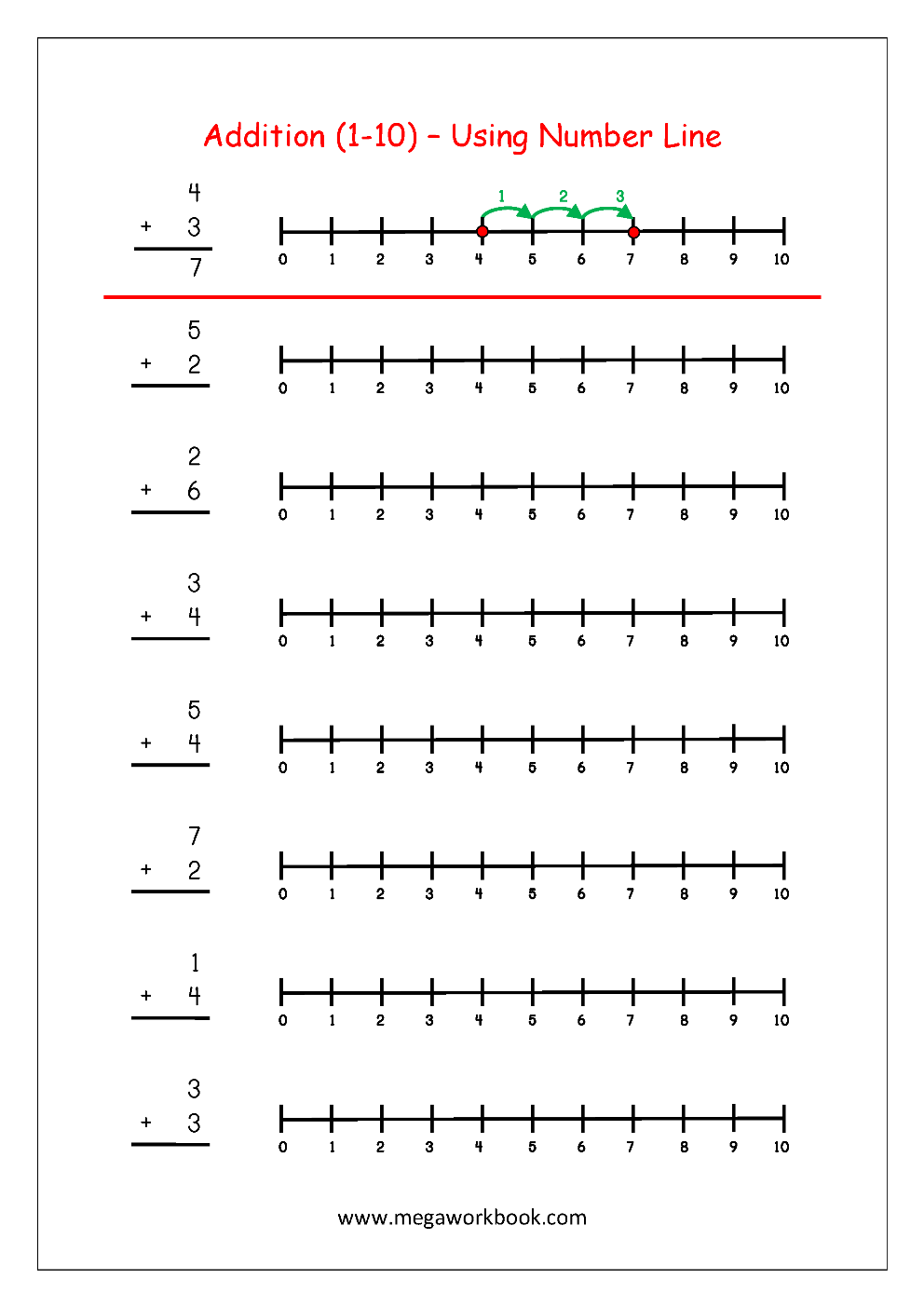
To perform addition on a number line, start with the first number in the equation:
- Locate the number on the line.
- This number will be your starting point.
Example: If you’re adding 5 + 3, locate 5 on the number line.
Step 3: Add the Second Number

Once you have your starting point:
- Move to the right on the number line by the number of steps equal to the second number you want to add.
- If you are adding a negative number, you would move to the left instead.
Example: For the previous example, move 3 steps to the right from 5.
| Steps Moved | Landing on |
|---|---|
| 1 | 6 |
| 2 | 7 |
| 3 | 8 |

Step 4: Check Your Answer

After completing the addition, confirm your result:
- The number you’ve landed on is the sum of your equation.
- Double-check the movement to ensure accuracy.
🚀 Note: It’s always a good idea to check your answer by counting from the starting number to the number you landed on, or by using another method like number bonds or a calculator.
Step 5: Practice and Master

Like any skill, practice is key:
- Use different pairs of numbers for practice.
- Incorporate negative numbers for added challenge.
- Create number line games or activities to keep the learning process engaging.
Understanding and using addition on a number line not only helps with basic arithmetic but also serves as a foundation for understanding more complex mathematical concepts such as algebra and calculus. The visual nature of the number line makes abstract numerical concepts more concrete and accessible to learners of all ages.
The simplicity of moving along the line to perform addition can make math less intimidating and more fun, which can encourage continued learning and exploration in mathematics. This tool also helps with spatial awareness and mental math abilities, which are crucial in everyday life.
Summing up, mastering addition on a number line requires understanding its structure, starting with the first number, moving along the line as instructed by the second number, checking your answer, and practicing regularly. Through these steps, one can enhance their numerical fluency, making complex problems more manageable and enjoyable. The journey of learning doesn't stop here; as you progress in math, you'll find the number line indispensable in various other mathematical operations.
Why is using a number line helpful for teaching addition?
+
Number lines provide a visual representation of numbers, which aids in understanding the concept of addition as moving along a line. This visual cue can help children grasp the idea that adding increases the value of the number by visualizing the movement.
Can I use a number line to subtract as well?

+
Yes, subtraction on a number line involves moving to the left instead of right, which represents decreasing the value.
What should I do if I encounter negative numbers on a number line?
+
When dealing with negative numbers, continue the number line to the left past zero. Moving leftward represents subtraction or adding negative numbers.
How can I make learning on a number line more interactive?

+
Use games, apps, or physical activities where children physically move along a number line drawn on the ground or a wall. Interactive whiteboards or digital tools can also make learning dynamic and engaging.