5 Steps to Ace Chemical Equation Balancing Easily

Balancing chemical equations might seem like a daunting task, especially if you're new to the world of chemistry. However, with the right strategies and a bit of practice, it can become one of the most rewarding aspects of learning chemistry. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore five crucial steps that will help you master the art of balancing chemical equations easily.
Understanding the Basics of Chemical Equations


Before you delve into balancing equations, it's essential to understand what they represent:
- Chemical equations express the chemical reactions that occur when reactants turn into products.
- They must be balanced to satisfy the law of conservation of mass, which states that mass cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
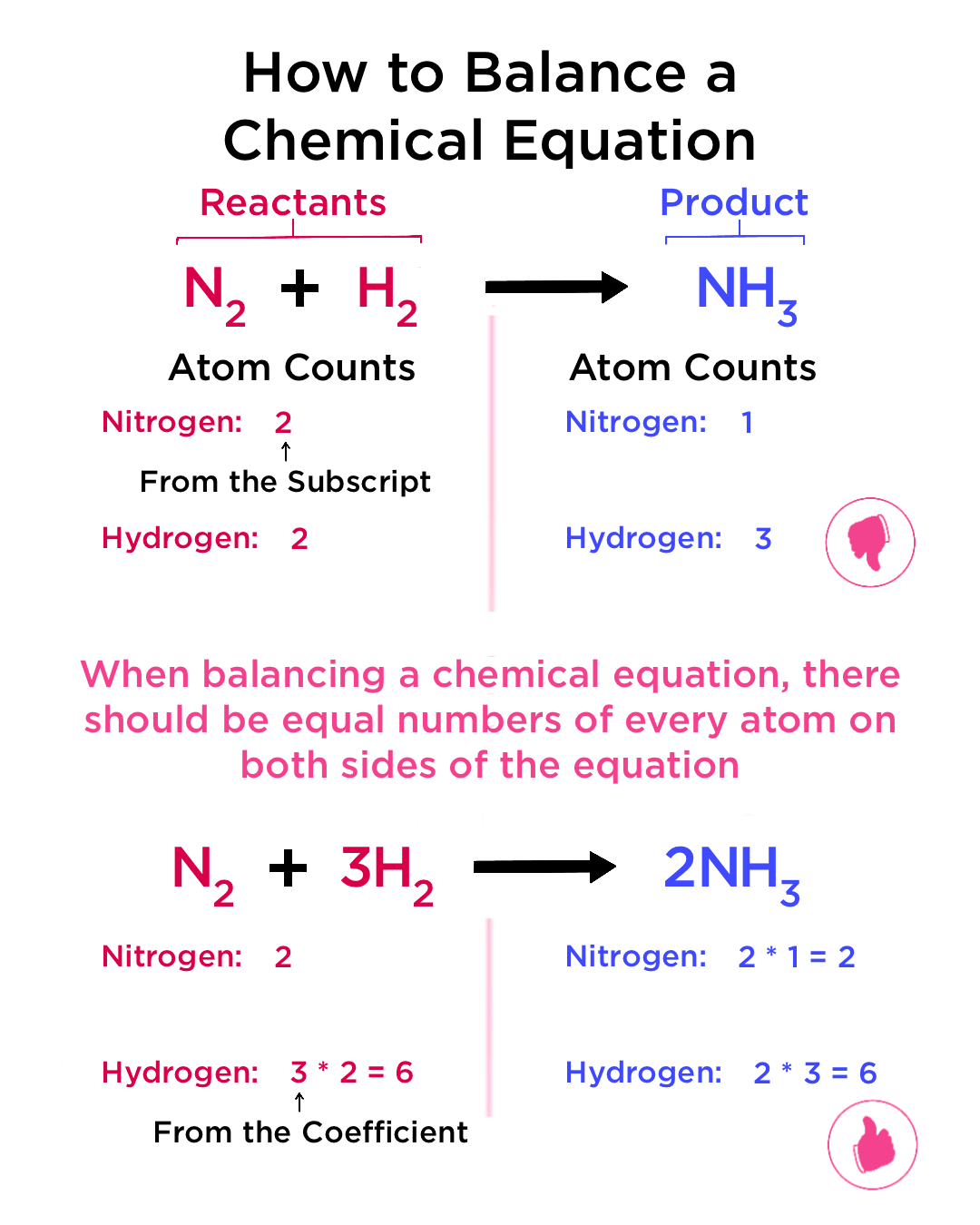
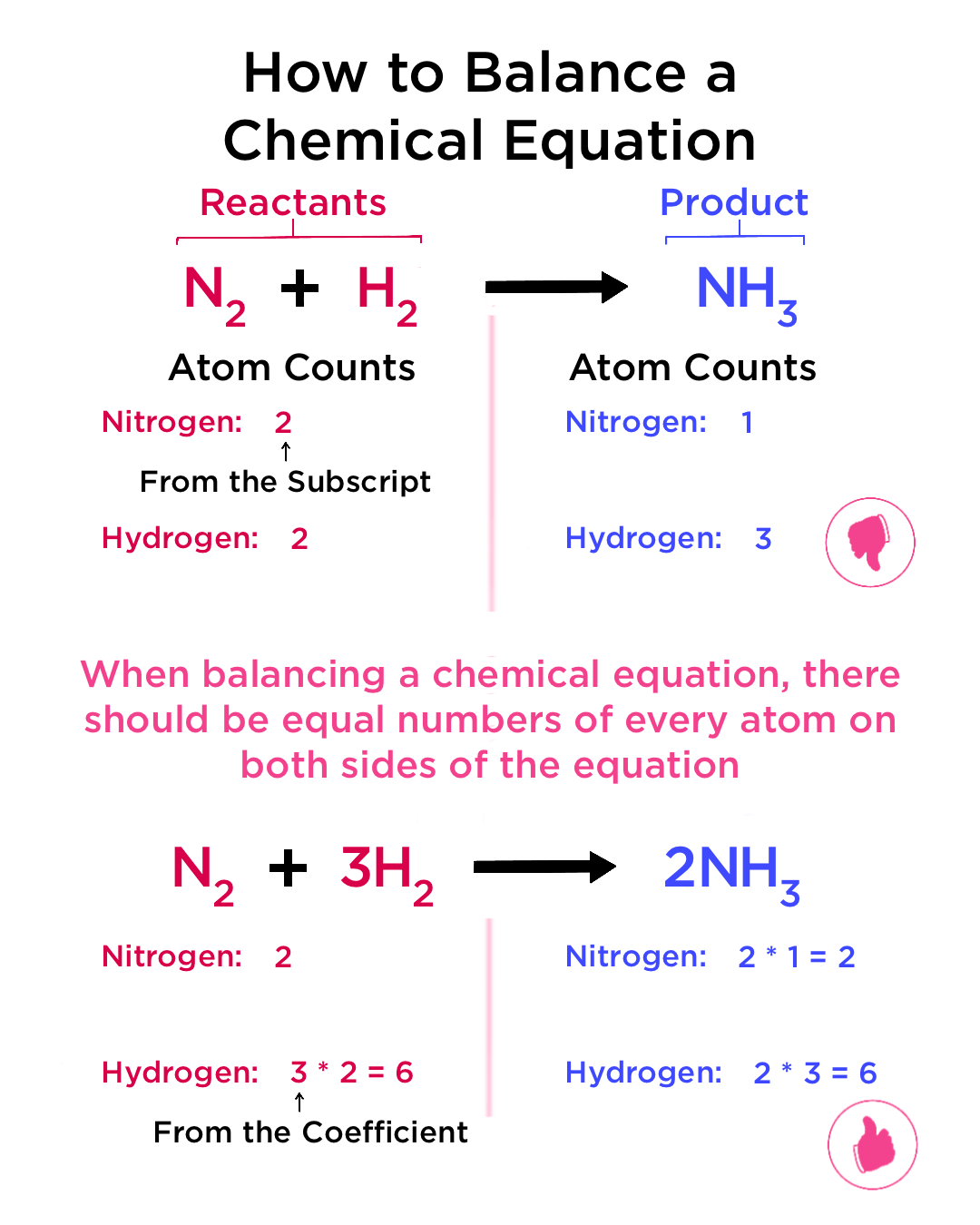
- Each atom in the reactants must appear on the product side in the same number and type.
Step 1: Write Out the Unbalanced Equation
Begin by writing the reactants on the left side of an arrow (→) and the products on the right. This should be done without any coefficients:
- For example, for the reaction of hydrogen gas with oxygen to form water, you might write:
H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
🧐 Note: Remember, at this stage, we do not balance the equation; we simply lay out the components of the reaction.
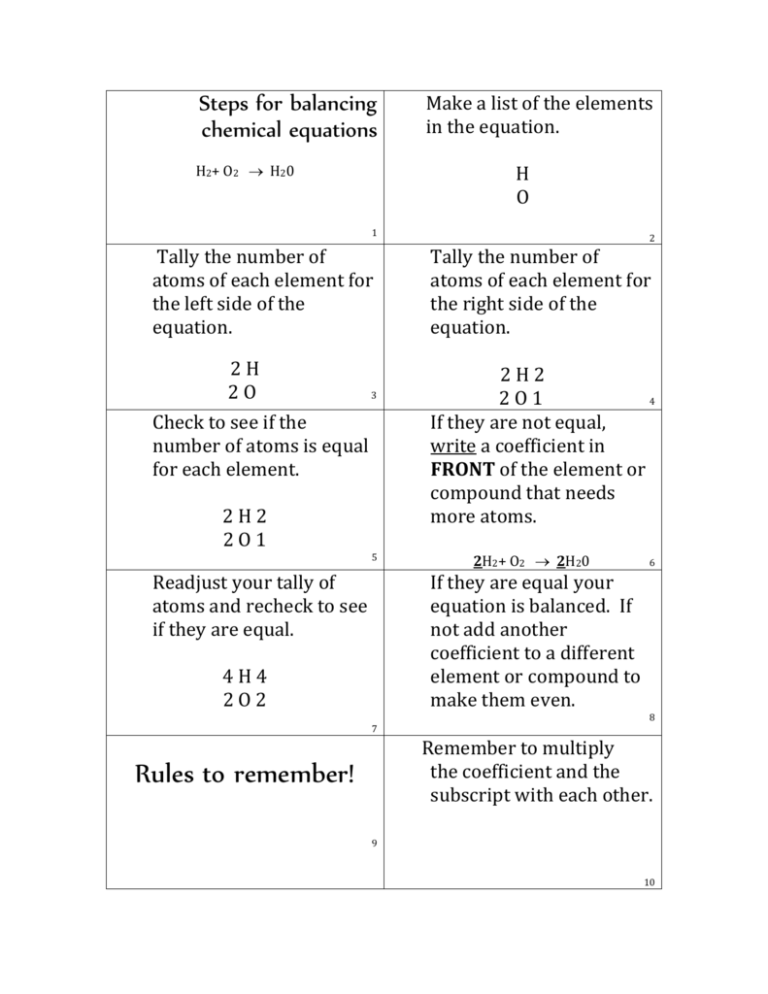
Step 2: Identify Elements and Count Atoms

Next, tally up the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation:
| Element | Reactants | Products |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen (O) | 2 | 1 |

In this case, we see an imbalance in the oxygen atoms.
Step 3: Use Coefficients to Balance the Equation

Here, we use the smallest whole numbers possible to balance the number of atoms on both sides. Continue:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
By adding a coefficient of 2 in front of H₂O, we ensure:
- Hydrogen atoms are now balanced (4 on both sides)
- Oxygen atoms are also balanced (2 on both sides)
⚠️ Note: Remember never to change the subscripts as that would alter the substance itself, only coefficients can be adjusted to balance the equation.
Step 4: Double-Check Your Work

After balancing, recheck the counts to confirm each element is balanced:
- Hydrogen - 4 on both sides
- Oxygen - 2 on both sides
Step 5: Practice Regularly

The key to mastering chemical equation balancing is consistent practice:
- Use online resources or textbooks for varied practice problems.
- Keep a running log of reactions you have balanced.
- Compare your balanced equations with the answers or verify them with simulation tools.
With time, balancing equations will become intuitive, and you'll be able to balance complex reactions swiftly.
In this journey towards understanding and excelling in balancing chemical equations, we've explored the essential steps to make the process seamless. From the foundation of understanding what chemical reactions represent, through to the careful adjustment of coefficients to balance atoms, each step builds upon the last to create a comprehensive skill set.
Why do chemical equations need to be balanced?
+
Chemical equations must be balanced to uphold the law of conservation of mass, ensuring that no atoms are lost or gained during a reaction.
Can I change the subscript in a chemical formula when balancing?
+
No, you should not alter the subscripts as it changes the identity of the compound. Only coefficients should be modified to balance equations.
What if there are polyatomic ions in the equation?

+
Balance polyatomic ions as a single unit when they appear unchanged on both sides of the equation. If they dissociate, balance the individual atoms.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when balancing equations?

+
Avoid changing subscripts, forgetting to multiply coefficients when counting atoms, and not verifying the equation after balancing.


