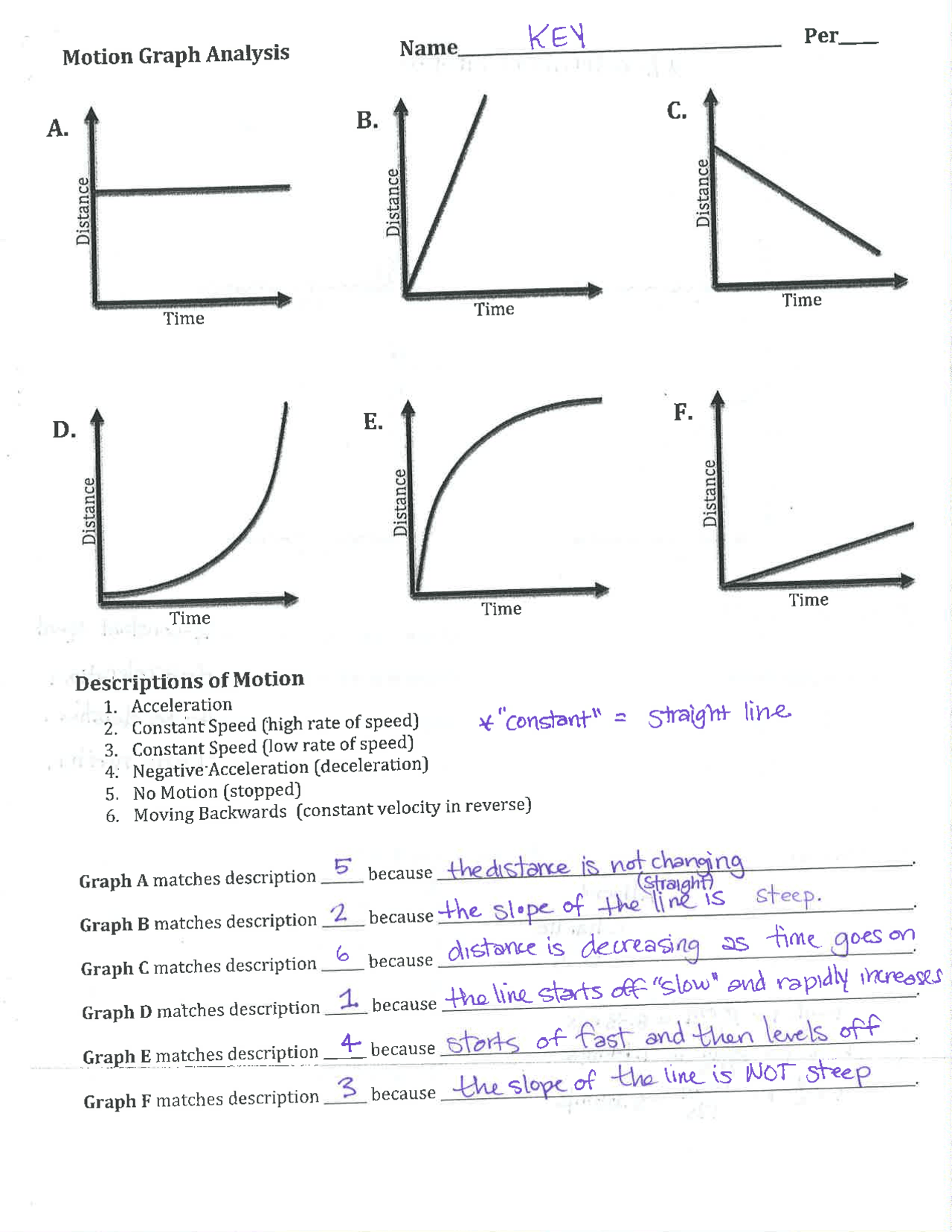
5 Tips to Master Motion Graphs and Kinematics
In the fascinating world of physics, understanding motion graphs and kinematics lays the foundation for deeper explorations into mechanics and dynamics. Whether you're a high school student grappling with your physics homework or an enthusiast trying to understand the mechanics of motion, mastering motion graphs is essential. Here, we're going to walk through 5 tips to master motion graphs and kinematics, equipping you with the tools needed to analyze and interpret these graphs with confidence.
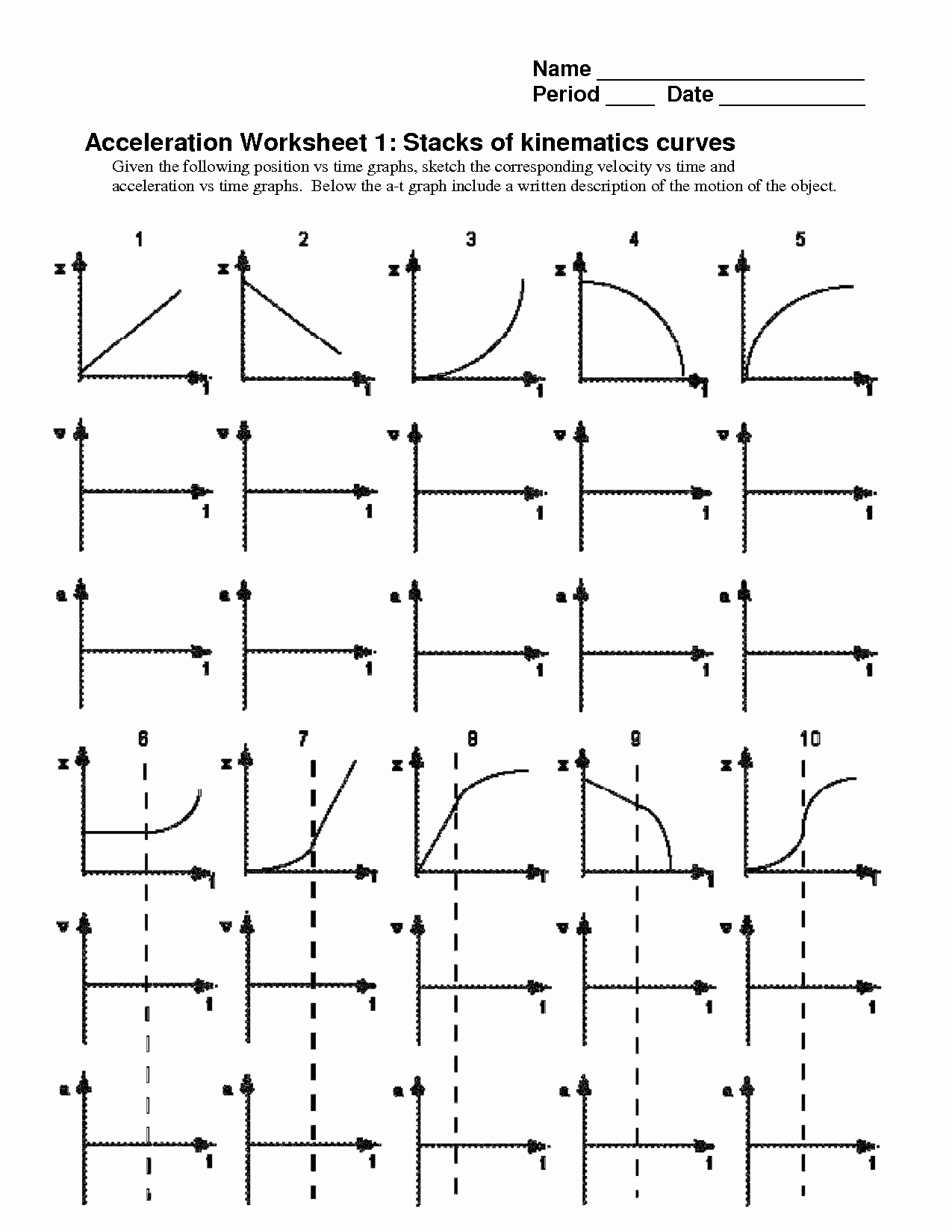
1. Understand the Basic Components of Motion Graphs

Before diving into the interpretation, one must understand what each axis represents on a motion graph:
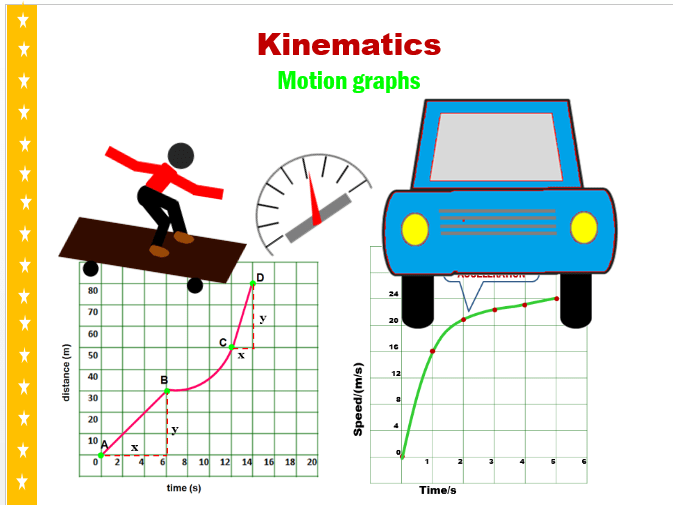
- Displacement-time graphs show how an object’s displacement changes over time. Here, time is on the horizontal axis, and displacement is on the vertical axis.
- Velocity-time graphs depict how velocity changes with respect to time. Time is on the x-axis, and velocity on the y-axis.
- Acceleration-time graphs illustrate acceleration versus time, with time on the x-axis and acceleration on the y-axis.
Remember, the slope of each line in these graphs has significant meaning:
- The slope in a displacement-time graph represents velocity.
- In a velocity-time graph, the slope signifies acceleration.
- For acceleration-time graphs, the area under the curve represents the change in velocity.
2. Practice Sketching Graphs
Sketching motion graphs manually can help solidify your understanding. Here’s a simple exercise:
- Sketch a graph for an object moving at constant velocity.
- Sketch another for an object with varying velocity or acceleration.
- Compare your sketches with examples online or in textbooks to see how well you’ve captured the motion.
📝 Note: Ensure your graphs are properly labeled, with clear axes scales, and a legend if necessary to illustrate different segments of motion.
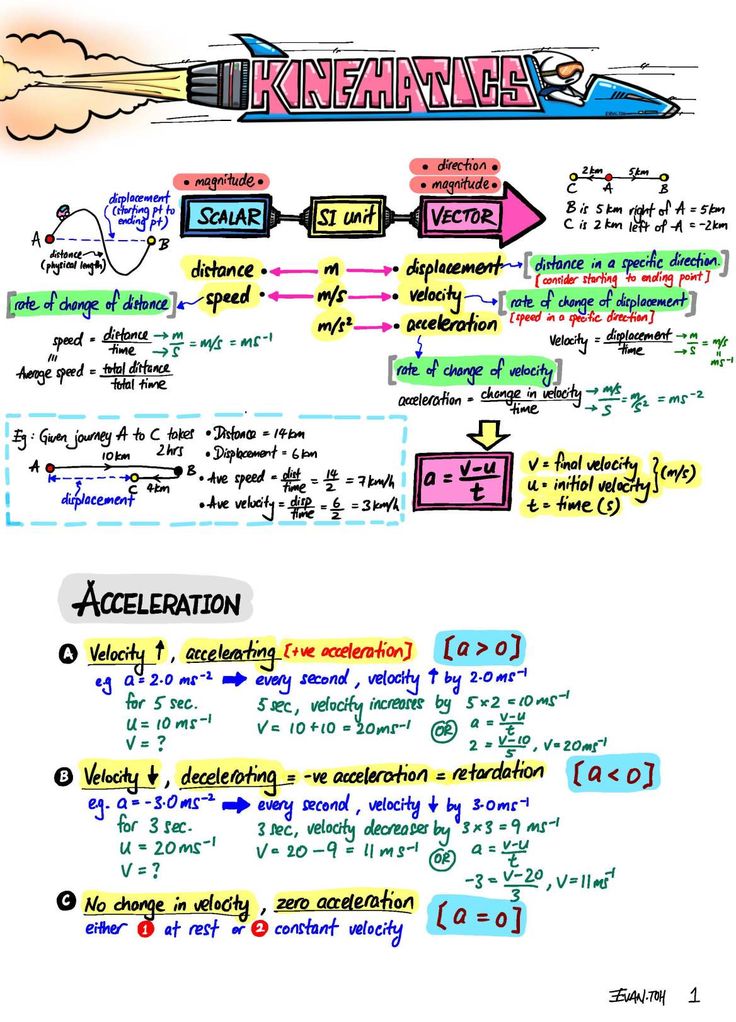
3. Develop Interpretation Skills
Reading a motion graph involves:
- Analyzing slope: Positive slope indicates motion in the positive direction, negative slope in the opposite. A horizontal line means the object is at rest or moving at constant speed in a velocity-time graph.
- Area under the curve: On a velocity-time graph, this gives displacement; on an acceleration-time graph, it’s the change in velocity.
- Curvature and trends: Understanding these can tell you about changes in velocity or acceleration. A convex curve upwards indicates increasing velocity or acceleration, and downwards for decreasing.
4. Use Technology to Your Advantage

Many educational apps and simulations can visualize motion graphs in real-time:
- Applications like Desmos, GeoGebra, or PhET Interactive Simulations allow for interactive graph creation and exploration.
- Try altering initial conditions to see how graphs change, providing a dynamic learning experience.
| App | Features |
|---|---|
| Desmos | Graphing calculator, can simulate motion graphs |
| GeoGebra | Interactive geometry and algebra software |
| PhET | Simulations that show real-time effects of motion |
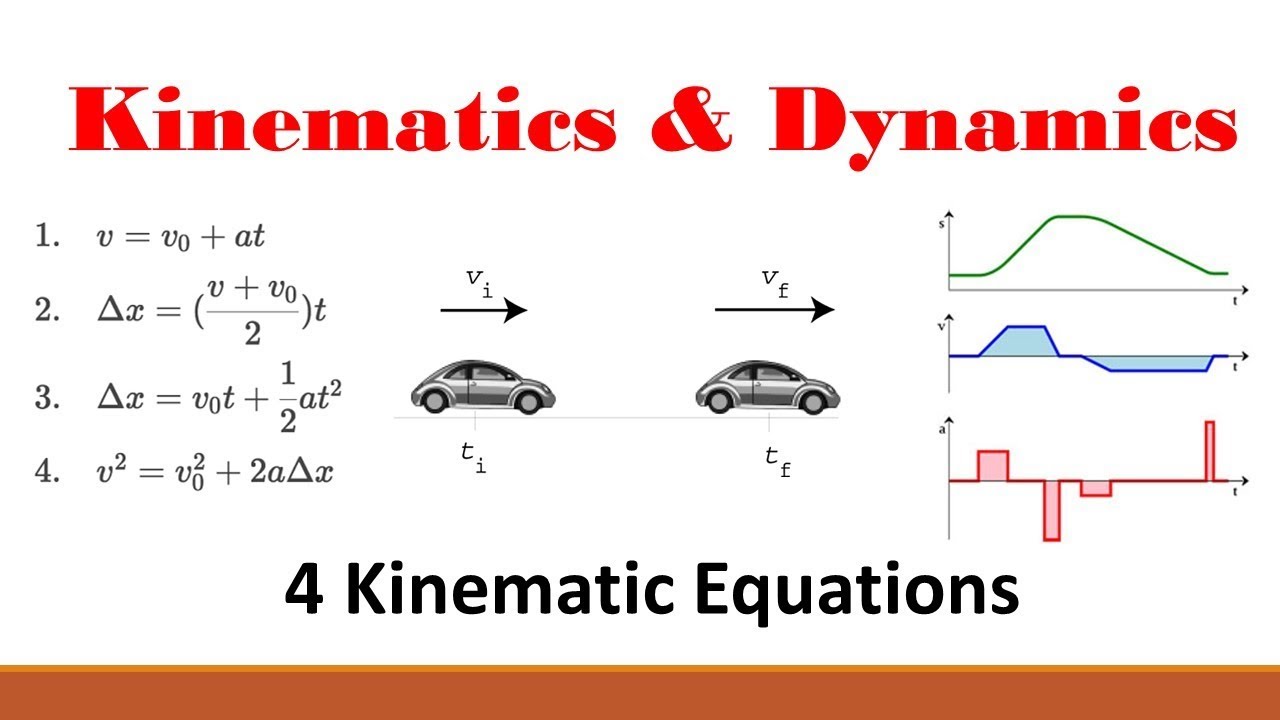
5. Integrate Kinematic Equations
Relating graphs to the kinematic equations can enhance your understanding:
- The basic kinematic equations (like v = u + at, or s = ut + 0.5at²) should be part of your graph interpretation toolkit.
- Use these equations to solve for variables not directly shown on the graph. For instance, given the slope (velocity) in a displacement-time graph, use it to find acceleration.
- Understand how different parts of these equations relate to the graphical representation of motion.
Graphical understanding and kinematic analysis are intertwined. By mastering motion graphs, you not only grasp fundamental physics concepts but also gain the ability to visualize and predict the motion of objects in complex scenarios. This knowledge is essential for students in physical sciences, engineering, and anyone with an interest in how the world moves. Keep practicing, exploring, and connecting the dots between graphs and physical motion, and soon you'll be navigating the principles of kinematics with confidence and skill.
What do you mean by the slope of a graph?
+
The slope of a graph refers to the rate at which one variable changes with respect to another. In motion graphs, the slope represents:
- The velocity on a displacement-time graph.
- The acceleration on a velocity-time graph.
How can technology help in understanding motion graphs?
+
Technology, through simulations and graphing apps, allows for:
- Dynamic visualization of motion in real-time, aiding in understanding complex concepts.
- Interactive experimentation, letting you alter variables to see their effects on motion.
What is the significance of the area under the velocity-time graph?
+
The area under the velocity-time graph represents the displacement of an object. This is because displacement is the integral of velocity with respect to time.
Can motion graphs help in predicting future positions?
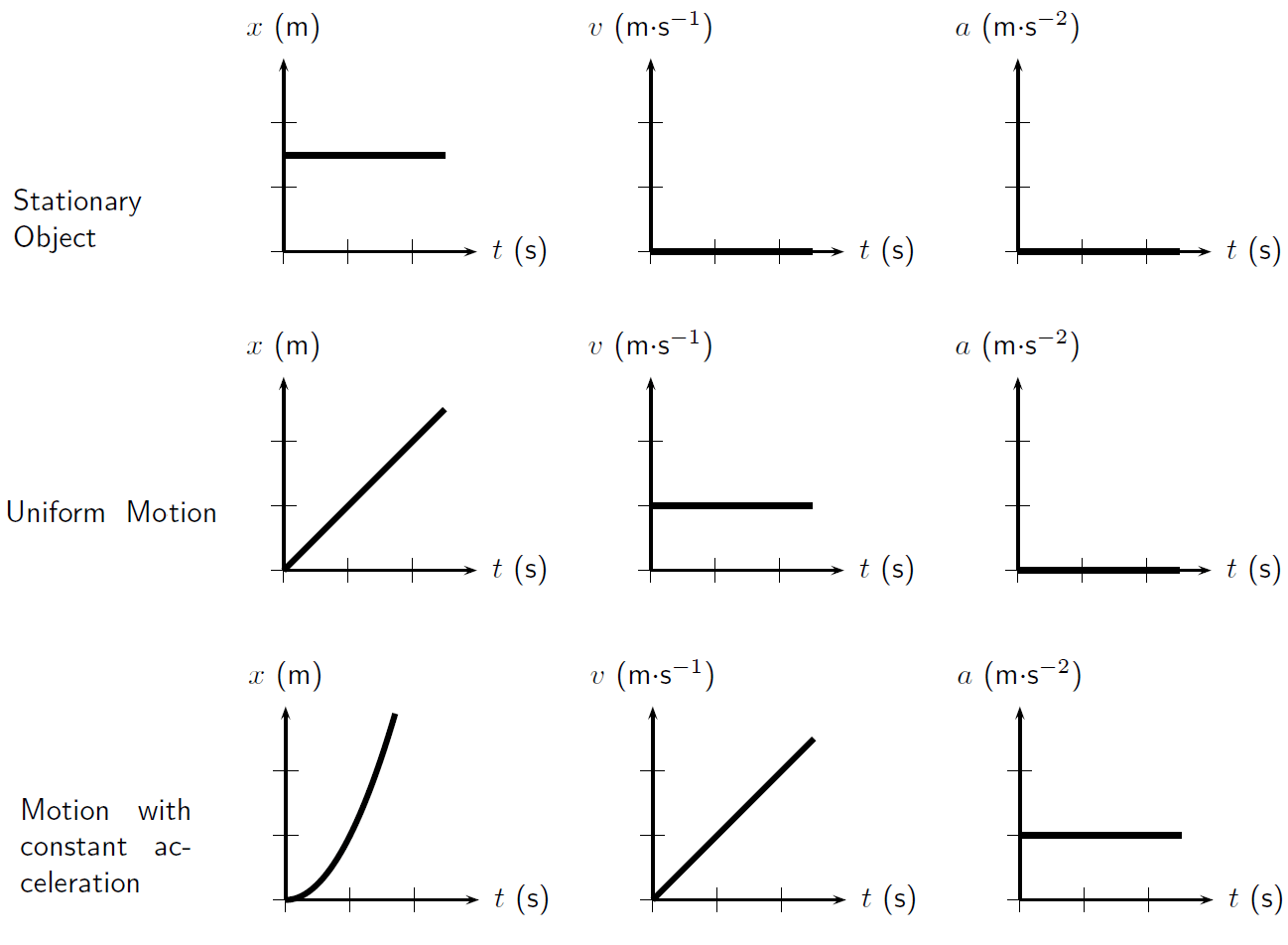
+
Yes, by analyzing the slope and shape of motion graphs, you can predict an object’s future position. For instance, if an object has a constant velocity, its future displacement can be calculated from the slope of the line on the graph.