5 Ways to Master Atomic Electron Configurations Easily

Understanding atomic electron configurations might seem like a daunting task, but with the right approach, it can become second nature. In this blog post, we'll delve into five effective strategies to master atomic electron configurations effortlessly.
The Aufbau Principle and Hund’s Rule

Atomic electron configurations are dictated by two fundamental principles:
- Aufbau Principle: Electrons fill orbitals starting with the lowest energy levels.
- Hund’s Rule: Electrons spread out over degenerate orbitals before pairing up, maximizing their spin multiplicity.
To make these principles less abstract, let’s visualize them:

Here’s how you can use these rules to build electron configurations:
- Start filling from 1s orbital and proceed upwards in energy.
- When you encounter degenerate orbitals (like the p orbitals), place one electron in each before pairing.
🔬 Note: These rules ensure electrons are arranged to minimize overall energy of the atom.
The Periodic Table as a Map

The periodic table isn’t just a chart; it’s a roadmap to electron configurations:
- The s-block elements fill their s-orbitals, with hydrogen and helium being exceptions due to their electron configurations.
- The p-block elements fill their p-orbitals, with the atomic number increasing from left to right.
- d-block elements correspond to d-orbital fillings, with exceptions for irregularities like chromium and copper.
- Finally, f-block elements fill f-orbitals.
Here’s a simplified table for the periodic trend:
| Block | Orbital Filling |
|---|---|
| s-Block | 1s, 2s, 3s, etc. |
| p-Block | 2p, 3p, 4p, etc. |
| d-Block | 3d, 4d, 5d, etc. |
| f-Block | 4f, 5f, etc. |

📘 Note: The periodic table’s design shows the order of orbital filling directly from left to right, except for the transition metals.
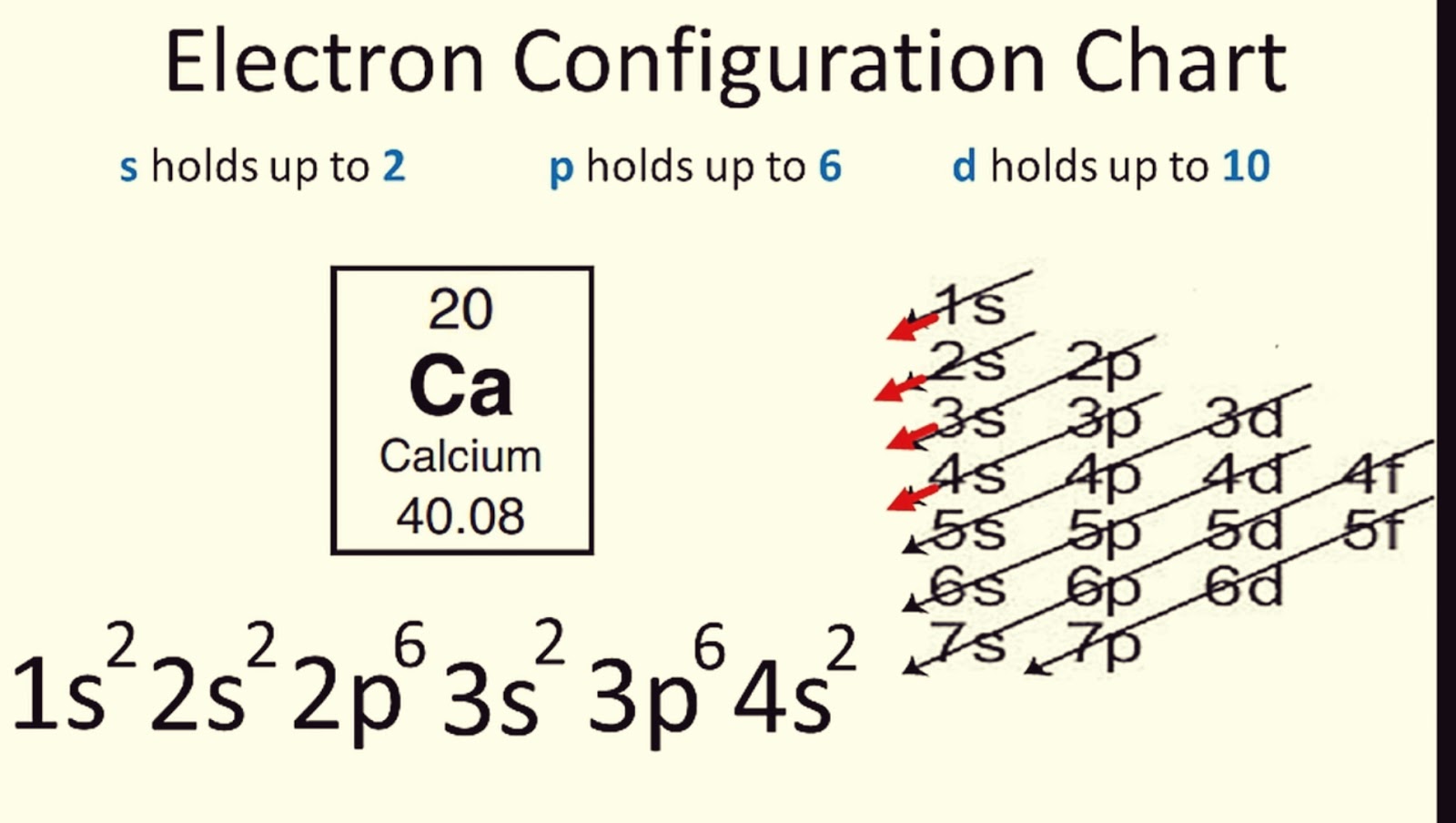
Using The Diagonal Rule (Mnemonic Device)
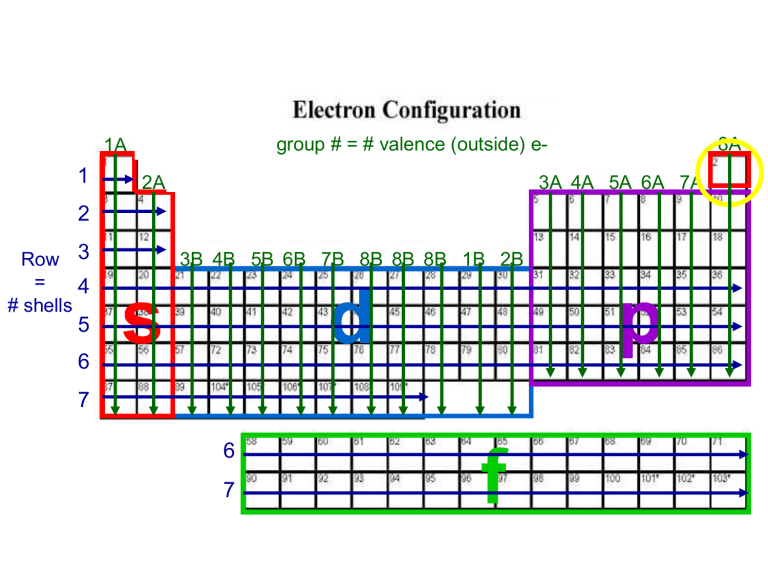
The Diagonal Rule, often depicted by arrows, is an excellent visual aid:

To apply this rule:
- Start at the top-left of the table and move right until you hit the element’s period, then move diagonally down-left.
- Follow the arrows until you’ve accounted for all the electrons.
This visual method helps in remembering the order of orbital filling without memorizing complex rules.
Practice and Problem Solving

The key to mastering electron configurations is practice. Here are some tips:
- Repetition: Write configurations for multiple elements until it’s almost second nature.
- Understand Exceptions: Learn elements that don’t follow the usual pattern, like chromium (which has a half-filled d-subshell).
- Work Backwards: Given an electron configuration, determine the element by tracing back through the periodic table.
✏️ Note: Practice doesn’t just improve speed but also helps in recognizing patterns and anomalies in electron configurations.
Interactive Tools and Apps

Today’s technology offers interactive tools to help with electron configurations:
- Online Orbital Fillers: Web apps that let you fill orbitals interactively to see the configurations.
- Educational Apps: Download educational chemistry apps with features like electron configuration games or simulations.
- Interactive Periodic Tables: Websites or software with interactive features where you can click on an element to see its electron configuration.
📱 Note: Using interactive tools can make learning electron configurations engaging and even fun.
By following these strategies, you'll find mastering electron configurations not just achievable but also enjoyable. The interplay of understanding fundamental principles, using visual aids like the periodic table and the Diagonal Rule, practicing actively, and leveraging modern tools will guide you towards a deep comprehension of atomic electron configurations. In your journey, don't shy away from the anomalies or irregularities; instead, embrace them as opportunities to refine your understanding. Remember, every electron has its place, and with these techniques, you'll confidently place each one.
Why is it important to understand electron configurations?
+
Understanding electron configurations is fundamental for comprehending chemical reactions, predicting atomic properties like magnetism, and interpreting the periodic trends in chemistry.
What is the Aufbau Principle?

+
The Aufbau Principle states that electrons occupy orbitals starting from the lowest available energy level.
How does Hund’s Rule work?

+
Hund’s Rule dictates that within a given subshell, electrons occupy all available degenerate orbitals singly before pairing up, and all unpaired electrons have the same spin.