5 Essential Nuclear Chemistry Worksheet Tips

Nuclear chemistry, a fascinating branch of chemistry that involves the study of the atomic nucleus and its reactions, is a topic that can often seem daunting to students. Whether you're a student aiming to ace your exams or an educator looking to provide the best resources for your class, nuclear chemistry worksheets are invaluable tools. Here are five essential tips to ensure you get the most out of your nuclear chemistry worksheets:
Understand the Basics Before Diving In

Before you start working on nuclear chemistry worksheets, it’s crucial to grasp the foundational concepts:
- Nuclear Stability: Learn about what makes a nucleus stable or unstable, including the role of neutrons, protons, and the neutron-to-proton ratio.
- Radioactive Decay: Understand the different types of decay such as alpha, beta, and gamma, their characteristics, and how to balance nuclear equations.
- Decay Series: Familiarize yourself with decay chains or series, where one decay product undergoes further decay.
🔍 Note: Mastery of these basics will make solving more complex problems much easier.
Utilize Practice Problems Effectively

Practice problems are the backbone of mastering nuclear chemistry:
- Start Simple: Begin with basic equations and gradually move to more complex ones.
- Check Your Work: Always verify your solutions. Use online resources or ask your teacher for confirmation on problem-solving techniques.
- Group Study: Sometimes, discussing problems in a group can provide insights you might have missed.
Develop a Systematic Approach to Problem Solving
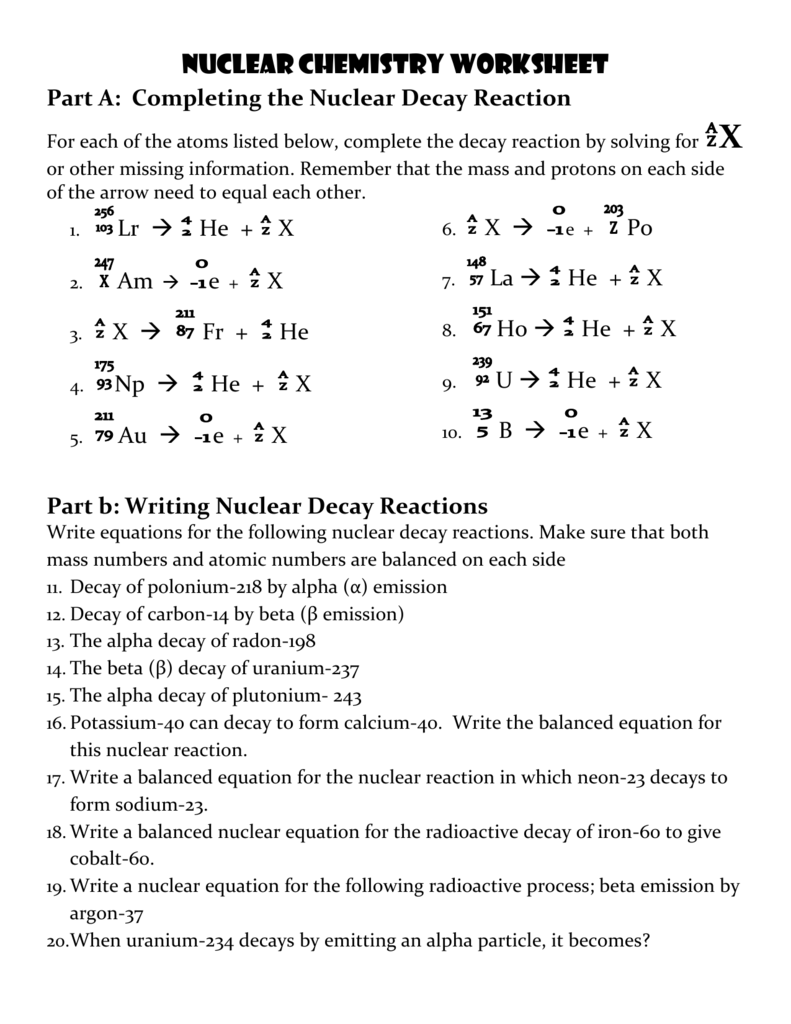
To efficiently work through nuclear chemistry problems:
- Read the Problem Carefully: Identify what information is given and what is being asked.
- Write Down Equations: Even if you’re solving mentally, writing down the nuclear equation can help keep track of changes.
- Balance the Equation: Ensure the mass and charge balance on both sides of the nuclear equation.
- Use a Step-by-Step Method: For example, in alpha decay, you subtract two protons and two neutrons, and ensure the atomic number decreases by two.
✅ Note: A systematic approach reduces errors and increases understanding of the process.
Make Use of Visual Aids

Nuclear chemistry often involves visual concepts:
- Decay Charts: Use charts that show decay chains to visualize the sequence of nuclear decays.
- Nuclear Diagrams: Sketch out the nucleus before and after a reaction to visualize changes.
- Tables: Here’s an example of how you might organize decay information:
| Radionuclide | Half-Life | Type of Decay | Daughter Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon-14 | 5,730 years | Beta-minus | Nitrogen-14 |
| Uranium-238 | 4.5 billion years | Alpha | Thorium-234 |

Connect with Real-World Applications

Linking theory to practice can greatly enhance understanding:
- Medical Applications: Explore how isotopes are used in medicine for diagnosis and treatment.
- Industrial Uses: Study how nuclear reactions are used in industries like food preservation or in smoke detectors.
- Environmental Impact: Understand how nuclear reactions affect our environment, including radioactive dating and waste disposal concerns.
These tips are designed to help students and educators navigate the complex world of nuclear chemistry worksheets more effectively. By understanding the basics, practicing systematically, using visual aids, and connecting theory with real-world applications, nuclear chemistry becomes not just an academic subject, but a tool to understand our world better.
Why is it important to balance nuclear equations?

+
Balancing nuclear equations ensures that the law of conservation of mass and charge is maintained. This means that the sum of the mass numbers and atomic numbers on both sides of the equation must be equal, which helps in understanding the nature and path of nuclear reactions.
How can I remember the different types of radioactive decay?

+
Each type of radioactive decay has unique characteristics: - Alpha Decay: Loss of an alpha particle, decreases atomic number by 2 and mass number by 4. - Beta Decay: An electron or positron is emitted, changing the atomic number by ±1. - Gamma Decay: Emission of high-energy photons, which does not change the atomic number or mass number. You can use mnemonics or visual aids to remember these changes.
What are some real-life applications of nuclear chemistry?

+
Nuclear chemistry finds numerous applications: - Medical Field: Treatments like radiotherapy for cancer or imaging techniques like PET scans. - Dating and Archaeology: Carbon-14 dating to estimate the age of ancient objects. - Energy Production: Nuclear reactors generate electricity through controlled nuclear reactions. - Agriculture: Radiation is used to sterilize pests or increase shelf life of food.
Is nuclear chemistry dangerous?

+
Nuclear chemistry deals with radioactivity, which can be hazardous if not handled properly. However, with strict safety protocols, shielding, and containment methods, many of the risks associated with nuclear reactions are mitigated. Education and proper application are key to safe use.
What is the difference between nuclear chemistry and radiochemistry?

+
Nuclear chemistry focuses on the reactions in the nucleus, like radioactive decay and nuclear reactions. Radiochemistry, on the other hand, involves the study of the chemical behavior of radioactive substances, often in the context of their use or effects in various environments.