5 Key Features of Absolute Value Graphs Explained

In the vast landscape of mathematics, understanding the graph of absolute value functions is vital for both students and professionals alike. Whether you're working on basic algebra or tackling more complex problems in calculus, the absolute value graph serves as a cornerstone for various mathematical explorations. This article delves into five key features of absolute value graphs that help demystify their behaviors and applications.
The V-Shape
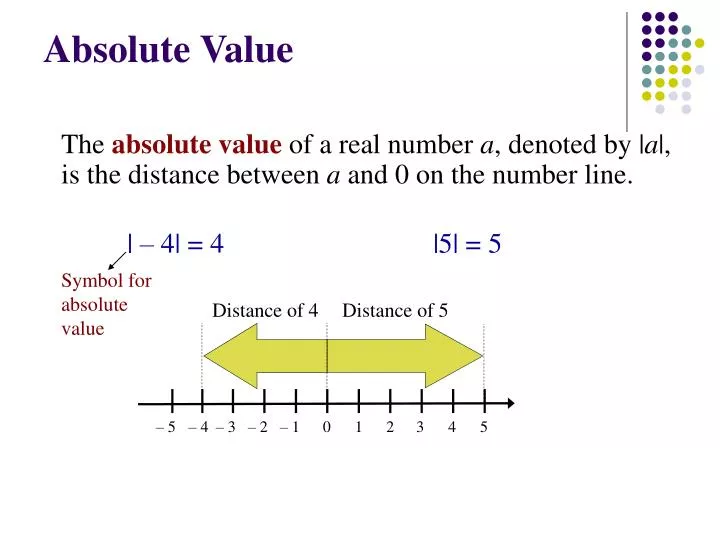

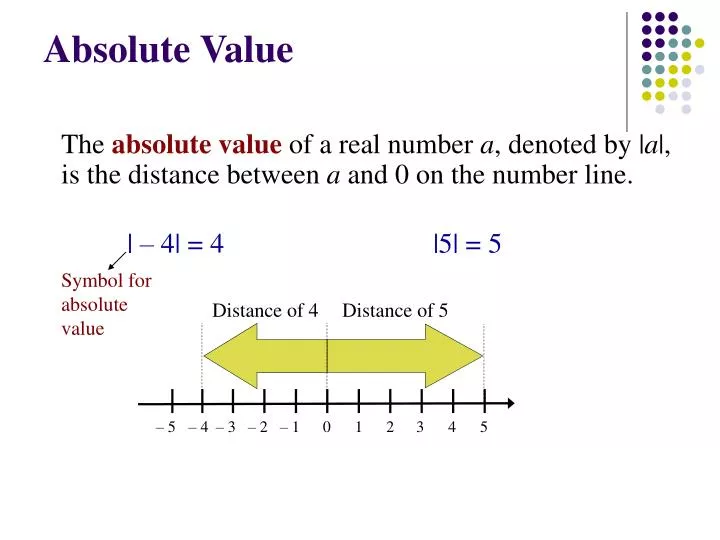
The most distinctive feature of an absolute value graph is its V-shape. When we plot an absolute value function like |x|, the graph looks like the letter V:
- It opens upward or downward, depending on the sign inside the absolute value bars.
- The V-shape is formed due to the function always returning non-negative values, which makes the graph symmetrical about the vertical axis.
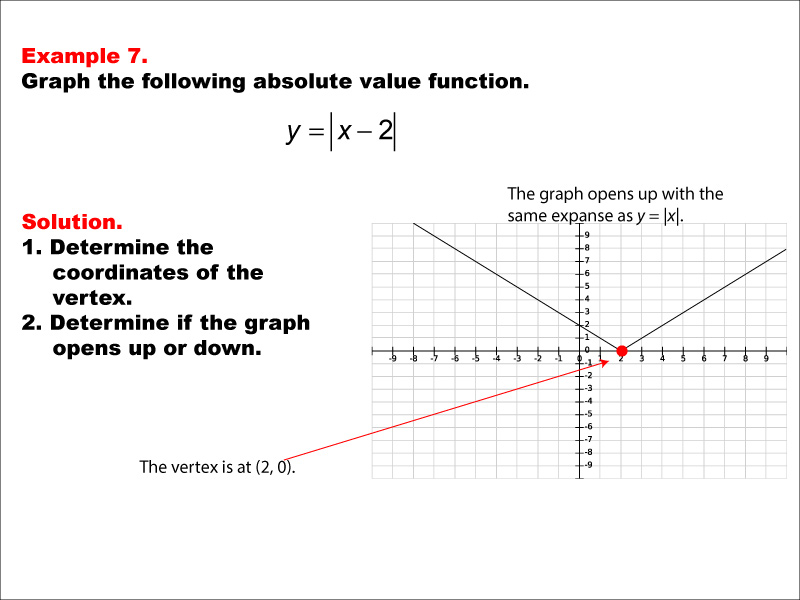
The exact point of this V-shape, or the vertex, is where the function changes direction. For |x|, this vertex is at (0,0).
Vertex and Axis of Symmetry


The vertex of an absolute value graph is where the maximum or minimum value of the function occurs:
- For functions like |x + a| or |x| - b, the vertex shifts horizontally or vertically from the origin.
- The axis of symmetry is a vertical line passing through the vertex, ensuring that the graph looks identical on both sides.
Here’s how you can find the vertex and axis of symmetry:
- If the function is of the form |x - h| + k, then (h, k) is the vertex.
- The axis of symmetry will always be x = h.
📝 Note: Remember that shifts in absolute value functions are performed in reverse. A positive value inside the absolute value shifts left, and outside shifts up.
Changes in Slope

The graph of an absolute value function displays a notable change in slope at the vertex:
- Before the vertex, the slope is negative, meaning the graph falls from left to right.
- After the vertex, the slope becomes positive, showing the graph rising from left to right.
This is due to the definition of the absolute value, where |x| = x for x ≥ 0, and |x| = -x for x < 0, which effectively mirrors the negative part over the x-axis.
Transformation through Parameters
Absolute value graphs can be transformed in various ways by adjusting the parameters within the function:
| Parameter | Transformation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| a|x + h| + k | a: Stretch or Compression | a = 2: Vertical Stretch |
| h: Horizontal Shift | h = -3: Shift Right 3 units | |
| k: Vertical Shift | k = 4: Shift Up 4 units | |
| Combining Parameters | |2x + 6| - 2: Complex Transformation |

📝 Note: Understanding how these parameters affect the graph can greatly enhance your ability to graph and interpret absolute value functions quickly.
Intersection with Axes


Where an absolute value graph intersects the axes can reveal valuable information about the function:
- The x-intercept(s) occurs when y = 0, which means solving for x in |x + h| + k = 0.
- The y-intercept is the point where x = 0. For the function |x|, this is always at (0,0), but for shifted functions, it depends on the k value.
📝 Note: If the absolute value function includes parameters like a or h, you might need to solve an equation or a system of equations to find the intercepts.
Through this exploration of the five key features, we've seen how absolute value graphs are structured, transformed, and analyzed. These graphs offer insights into mathematical functions, enabling us to predict behaviors, solve equations, and understand the underlying principles of symmetry and transformation in algebra. As we've discovered, the symmetrical nature of absolute value functions, their unique V-shape, and the transformations they undergo provide a fundamental understanding of one of the most recognized functions in mathematics.
What is the significance of the axis of symmetry in an absolute value graph?

+
The axis of symmetry in an absolute value graph signifies the line where the graph is reflected, ensuring that the function’s behavior on one side mirrors the other. This symmetry aids in solving equations and understanding the function’s nature.
How do changes in the parameters affect the graph of an absolute value function?

+
Parameters a, h, and k in an absolute value function lead to transformations like vertical stretch or compression, horizontal and vertical shifts. Each parameter has a distinct effect on the graph’s position and shape.
Can an absolute value graph have more than one x-intercept?
+
Yes, an absolute value graph can have zero, one, or two x-intercepts. The number of intercepts depends on the position of the graph relative to the x-axis, dictated by the function’s parameters.