Master Motion Graphs: Worksheet Answers Explained
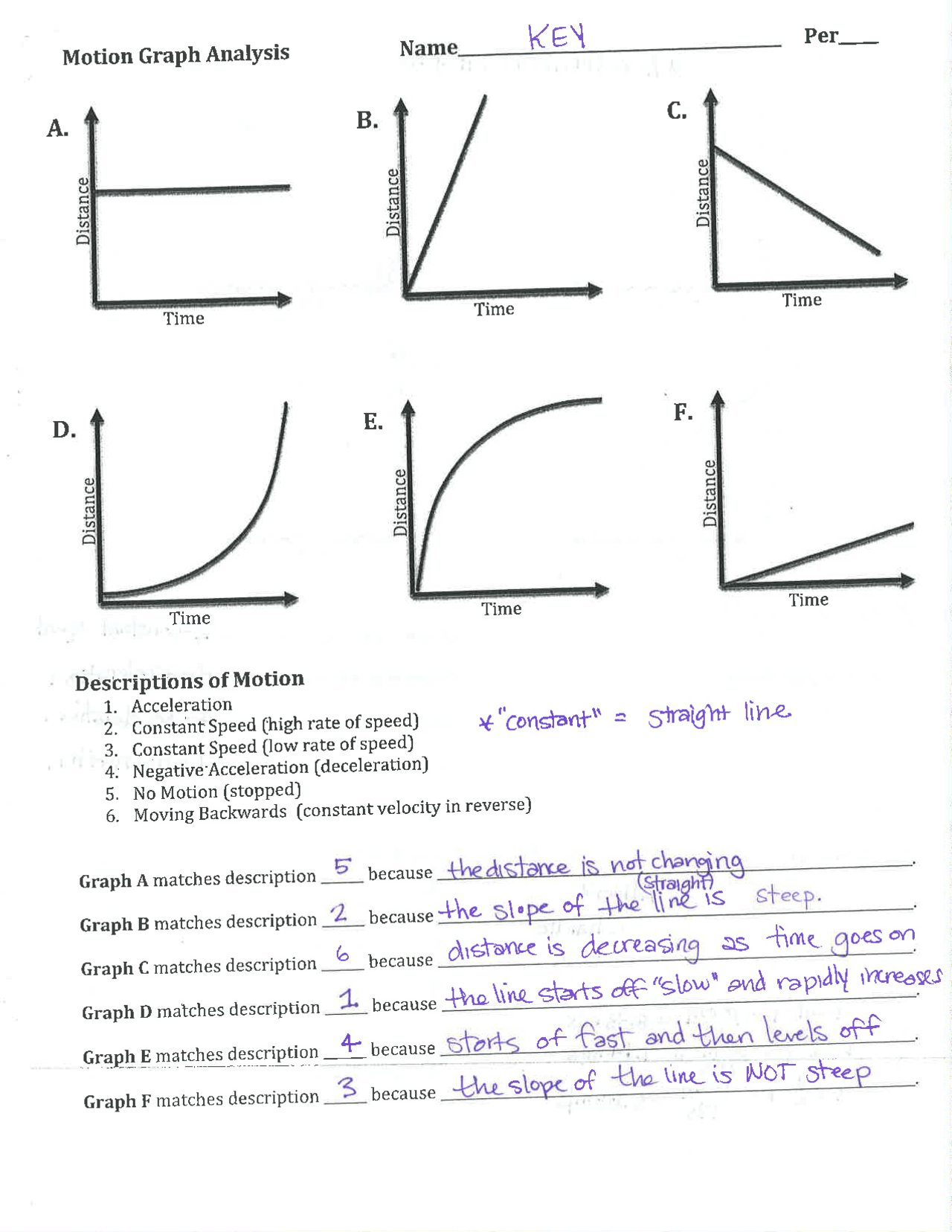
Mastering motion graphs can be a challenging yet incredibly rewarding part of physics education. These tools provide invaluable insights into an object's movement over time, making them a staple in both academic learning and real-world applications. In this extensive guide, we will delve deep into understanding and interpreting motion graphs, providing detailed answers and explanations to common worksheet questions. This will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to excel in this area of physics.
What are Motion Graphs?

Motion graphs are graphical representations of an object’s displacement, velocity, or acceleration over time. Here are the main types:
- Displacement-Time Graphs: Show how an object’s position changes with time.
- Velocity-Time Graphs: Illustrate how velocity varies over time, which can help in understanding acceleration.
- Acceleration-Time Graphs: Demonstrate how acceleration changes over time.

📌 Note: Understanding the area under a velocity-time graph gives you displacement, while the slope of this graph represents acceleration.
Key Concepts for Interpreting Motion Graphs

Understanding Slopes

The slope of a line on any motion graph has specific meanings:
- On a displacement-time graph, the slope equals velocity.
- On a velocity-time graph, the slope indicates acceleration.
- On an acceleration-time graph, the slope does not have a straightforward physical interpretation.
Recognizing Areas Under Curves

The area under a graph can also provide critical information:
- The area under a velocity-time graph gives displacement.
- Under an acceleration-time graph, the area represents the change in velocity.
Worksheet Answers and Explanations

Question 1: Identifying Velocity from Displacement-Time Graph

Consider this graph:

Worksheet Question: Determine the object’s velocity at various points.
Explanation:
- From t = 0 to t = 2 seconds, the graph has a positive slope, indicating positive velocity.
- At t = 2 seconds, the slope is zero (horizontal line), meaning the object is at rest.
- From t = 2 to t = 4 seconds, the slope is negative, showing backward movement.
Question 2: Calculating Acceleration from Velocity-Time Graph
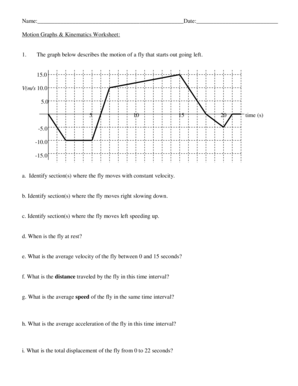
Here’s the graph:

Worksheet Question: Find the acceleration during the given time intervals.
Explanation:
- From t = 0 to t = 1 second, the slope is constant and positive, indicating constant acceleration.
- At t = 1 to t = 3 seconds, the slope is zero, so acceleration is zero.
- From t = 3 to t = 5 seconds, the graph shows negative acceleration due to the downward slope.
Question 3: Displacement Analysis from Velocity-Time Graph

Look at the following graph:

Worksheet Question: Calculate the total displacement of the object.
Explanation:
- The displacement from 0 to 2 seconds is the area under the curve: 1⁄2 * 2 * 4 = 4 m.
- From 2 to 4 seconds, the object moves backward: -1⁄2 * 2 * 2 = -2 m.
- The total displacement is 4 - 2 = 2 m.
📌 Note: Remember, positive areas contribute positively to displacement, while negative areas detract from it.
Question 4: Complex Motion Analysis

Observe this graph:

Worksheet Question: Describe the motion of the object, including its velocity, acceleration, and displacement.
Explanation:
- Velocity: Changes from positive to zero, then back to positive with increasing speed.
- Acceleration: Starts at a peak, drops to zero, then becomes positive again but less.
- Displacement: Area under the curve shows net positive displacement, with some back-and-forth motion.
Summary

Interpreting motion graphs involves understanding slopes for velocity and acceleration, areas under curves for displacement, and recognizing the types of motion depicted. Here are some key takeaways:
- Positive slopes on displacement-time graphs indicate forward motion.
- Negative slopes indicate backward or decelerating motion.
- Area calculations can be positive or negative, contributing to net displacement.
- The shape of the curve provides insights into velocity and acceleration changes.
With practice, these graphs become powerful tools to understand motion dynamics, from simple to complex scenarios, enabling you to predict and analyze an object's behavior over time.
Why are motion graphs important in physics?

+
Motion graphs help visualize and analyze an object’s movement, making complex dynamics easier to understand and solve. They are crucial for predicting how objects will move under different conditions.
How do I know if an object is at rest from a velocity-time graph?

+
An object is at rest when the velocity-time graph shows a horizontal line or the velocity is zero at any point.
What does negative acceleration on a velocity-time graph mean?
+
Negative acceleration, or deceleration, indicates that an object is slowing down or moving in the opposite direction to its velocity.