5 Key Answers to Functions Worksheet Explained

In the fascinating world of mathematics, functions worksheets are invaluable tools for students to practice and master various concepts. Here, we delve into the essence of functions by examining five key problems often found in educational worksheets, explaining each step-by-step to enhance understanding and proficiency in this mathematical field.
Function Definitions and Notation

A function, at its core, is a relationship between a set of inputs (called the domain) and a set of possible outputs (called the codomain), where each input is related to exactly one output. Here’s how we typically represent a function:
- f(x) = y: Where ‘f’ denotes the function, ‘x’ is the input, and ‘y’ is the output.
The understanding of function notation is crucial as it forms the basis of all function-related calculations and conceptual applications.
Evaluating Functions

Let’s tackle an example:
Evaluate f(x) = x^2 - 3x + 2 when x = 4.
The process involves:
- Substituting x with 4 in the function:
f(4) = 4^2 - 3*4 + 2f(4) = 16 - 12 + 2f(4) = 6- Thus, when x is 4, the value of the function f is 6.
⚠️ Note: Ensure to perform operations in the correct order (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division from left to right, Addition and Subtraction from left to right - PEMDAS).
Finding Inverse Functions
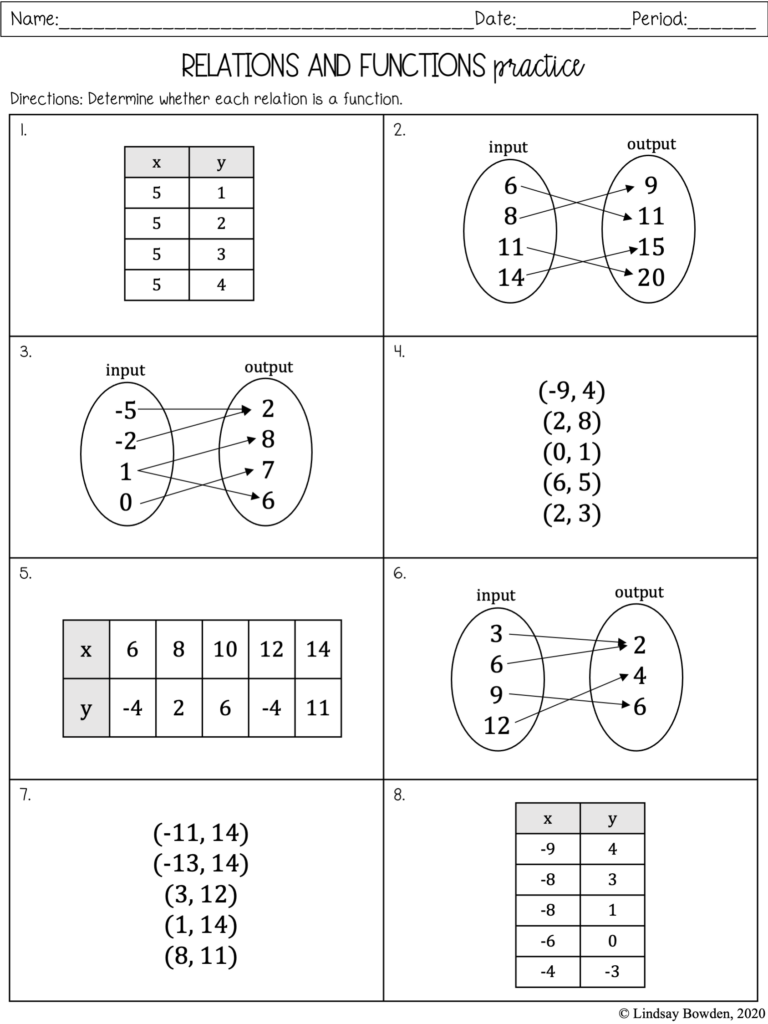
Consider a function f(x) = 2x + 3. Here’s how to find its inverse:
- Replace
f(x)withyfor simplicity: - Swap
xandyto reflect the inversion: - Solve for
y: - The inverse function is:
y = 2x + 3x = 2y + 3x = 2y + 3
x - 3 = 2y
y = (x - 3) / 2f^-1(x) = (x - 3) / 2Remember, the inverse function reverses the operations of the original function, taking the output as the input.
Domain and Range

Understanding the domain (all possible inputs) and range (all possible outputs) of a function can often be a key part of worksheet exercises. Let’s look at an example:
| Function | Domain | Range |
|---|---|---|
| f(x) = √(x - 1) | x ≥ 1 | y ≥ 0 |

Here, the square root function demands that x - 1 must be greater than or equal to 0, and thus, only non-negative results can exist for the range.
Graphing Functions

Understanding how to graph functions is often included in exercises. Here’s how we approach graphing f(x) = 2x:
- Identify key points like intercepts and slope.
- The function passes through (0, 0) - the origin, as 2 times 0 is 0.
- The slope is 2, meaning for every increase of 1 in x, y increases by 2.
By plotting these points and drawing a line, the graph of f(x) = 2x becomes clear.
🔍 Note: Use graph paper or graphing software for accuracy when plotting functions.
In summary, functions are a fundamental concept in mathematics, connecting inputs to outputs in a well-defined manner. Through examining function notation, evaluating functions, understanding inverses, determining domain and range, and graphing, we unlock deeper insights into mathematical patterns and relationships. By mastering these skills, students can approach more complex problems with confidence.
Why is function notation important?

+
Function notation is crucial because it provides a systematic way to express relationships between sets of numbers or variables, facilitating communication, simplification, and manipulation in mathematical contexts.
What is an inverse function?

+
An inverse function undoes the action of another function. If f maps x to y, then the inverse f^-1 maps y back to x, essentially reversing the process.
How do I determine the domain of a function?

+
Identify all real numbers for which the function is defined. Exclude values that would cause undefined operations like division by zero or negative square roots.