5 Essential VBA Functions for Worksheets

Mastering VBA Functions for Efficient Worksheet Management
As a spreadsheet enthusiast, you’re likely no stranger to the power of Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) in Microsoft Excel. VBA is a programming language that allows you to create and automate tasks, making your workflow more efficient and productive. In this article, we’ll explore five essential VBA functions that will take your worksheet management to the next level.
1. Workbooks.Open: Opening Workbooks with Ease
The Workbooks.Open function allows you to open workbooks programmatically, saving you time and effort. This function is particularly useful when you need to work with multiple workbooks or perform batch operations.
Example:
Sub OpenWorkbook()
Workbooks.Open "C:\Path\To\Workbook.xlsx"
End Sub
This code opens a workbook located at C:\Path\To\Workbook.xlsx.
2. Worksheets.Add: Adding New Worksheets with Precision
The Worksheets.Add function enables you to add new worksheets to a workbook with ease. You can specify the position, name, and type of worksheet to be added.
Example:
Sub AddWorksheet()
Worksheets.Add Before:=Worksheets(1)
End Sub
This code adds a new worksheet before the first worksheet in the active workbook.
3. Range.Find: Finding and Replacing Data with Ease
The Range.Find function allows you to search for specific data within a range of cells. You can also use this function to replace data, making it an essential tool for data manipulation.
Example:
Sub FindData()
Dim rng As Range
Set rng = Range("A1:A10").Find("SearchTerm")
If Not rng Is Nothing Then
rng.Value = "ReplacementText"
End If
End Sub
This code searches for the string “SearchTerm” within the range A1:A10 and replaces it with “ReplacementText” if found.
4. Looping through Worksheets: Automating Tasks with Loops
Looping through worksheets is a common task in VBA. You can use the For Each loop to iterate through all worksheets in a workbook and perform tasks on each one.
Example:
Sub LoopThroughWorksheets()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
' Perform tasks on each worksheet
ws.Cells(1, 1).Value = "Header"
Next ws
End Sub
This code loops through all worksheets in the active workbook and sets the value of cell A1 to “Header” in each worksheet.
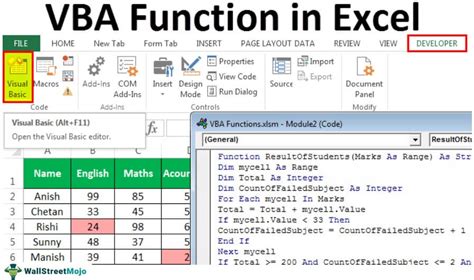
5. Error Handling: Robust Error Handling with VBA
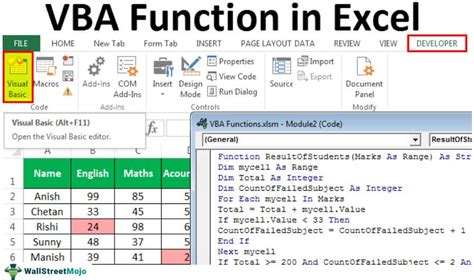
Error handling is crucial in VBA programming. You can use the On Error statement to catch and handle errors, ensuring that your code runs smoothly and efficiently.
Example:
Sub ErrorHandler()
On Error GoTo ErrorHandler
' Code that may raise an error
Range("A1").Value = "ErrorProneCode"
Exit Sub
ErrorHandler:
MsgBox "An error occurred: " & Err.Description
End Sub
This code catches any errors that may occur during the execution of the code and displays an error message with the error description.
📝 Note: Always use error handling in your VBA code to ensure robustness and prevent crashes.
Conclusion

Mastering VBA functions is essential for efficient worksheet management. By incorporating these five essential functions into your VBA arsenal, you’ll be able to automate tasks, manipulate data, and streamline your workflow. Remember to always use error handling and robust coding practices to ensure that your code runs smoothly and efficiently.
What is VBA in Excel?
+
VBA (Visual Basic for Applications) is a programming language used in Microsoft Excel to create and automate tasks, making your workflow more efficient and productive.
How do I open a workbook using VBA?
+
You can use the Workbooks.Open function to open a workbook programmatically. For example: Workbooks.Open "C:\Path\To\Workbook.xlsx"
How do I loop through worksheets in a workbook?
+
You can use the For Each loop to iterate through all worksheets in a workbook. For example: For Each ws In ThisWorkbook.Worksheets
Related Terms:
- Free worksheets vba function
- Excel VBA worksheet functions list
- Worksheets vba function formulas
- Worksheet function in Excel
- Excel worksheet functions list
- Use Excel function in VBA



