Mastering pH Calculations: Your Ultimate Worksheet Guide

Understanding pH and performing pH calculations is essential in various fields like chemistry, environmental science, and health care. Whether you're a student, a professional, or simply a curious mind, mastering how to calculate pH can offer invaluable insight into chemical reactions and solutions. Here's your ultimate guide, complete with practical examples, to help you navigate through pH calculations with ease.
Understanding pH

pH is a measure of acidity or alkalinity of a solution, defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration:
pH = -log[H+]
This simple equation is the cornerstone for all pH calculations. Here’s how to approach different scenarios:
Calculating pH from Hydrogen Ion Concentration

- If you're given the hydrogen ion concentration (H+) in moles per liter (molarity), calculating pH is straightforward.
- Example: Given [H+] = 0.001 M, the pH would be:
pH = -log(0.001) = 3So, this solution has a pH of 3, indicating it's acidic.
Calculating pH from pOH
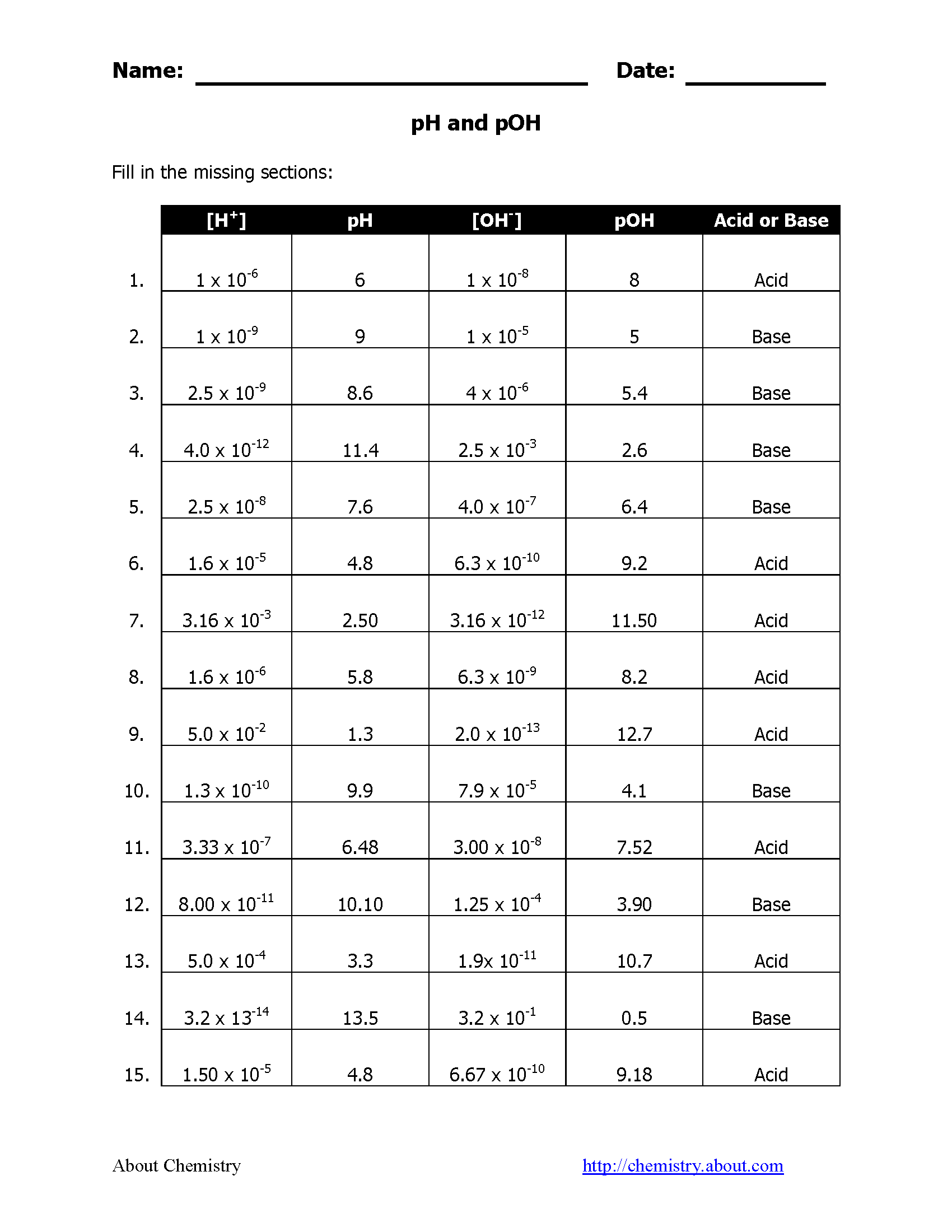
- pOH is similar to pH but measures the concentration of hydroxide ions ([OH-]). The relationship between pH and pOH is:
pH + pOH = 14
- Example: If pOH is 5, then:
pH = 14 - 5 = 9This solution is basic with a pH of 9.
Calculating pH for Strong Acids and Bases

Strong acids and bases dissociate completely in water, making pH calculations simpler:
- For a strong acid like hydrochloric acid (HCl), the concentration of H+ is the same as the initial acid concentration.
- For a strong base like sodium hydroxide (NaOH), you'll find the OH- concentration, then use the relationship between pH and pOH.
Example: For 0.1 M HCl, the pH is:
pH = -log(0.1) = 1Calculating pH for Weak Acids and Bases

- Weak acids and bases partially dissociate, requiring the use of equilibrium constants (Ka for acids and Kb for bases) or the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for buffer solutions:
pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA])
- Example: For a 0.1 M solution of acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 x 10-5):
pH = -log(1.8 x 10^-5) + log( [acetate]/ [acetic acid] )This calculation gets more complex, but here, assuming you have equal amounts of acetic acid and acetate, the pH would be close to the pKa of acetic acid (around 4.74).
| Acid/Base Type | Calculation Method |
|---|---|
| Strong Acids | pH = -log[H+] |
| Strong Bases | pOH = -log[OH-], pH = 14 - pOH |
| Weak Acids | Use Ka or Henderson-Hasselbalch |
| Weak Bases | Use Kb or Henderson-Hasselbalch |

⚠️ Note: Remember, pH values range from 0 to 14. Values below 7 are acidic, 7 is neutral, and above 7 are alkaline. This is a simple rule to keep in mind when calculating pH.
FAQ Section

What if my solution is neither strong nor weak?

+
If your solution doesn't fall neatly into strong or weak categories, you might be dealing with a salt or mixture. The pH could be influenced by several factors like hydrolysis, solubility product, and common ion effect. More complex equilibrium calculations might be needed, considering the different species in the solution.
Can I use a calculator for pH calculations?
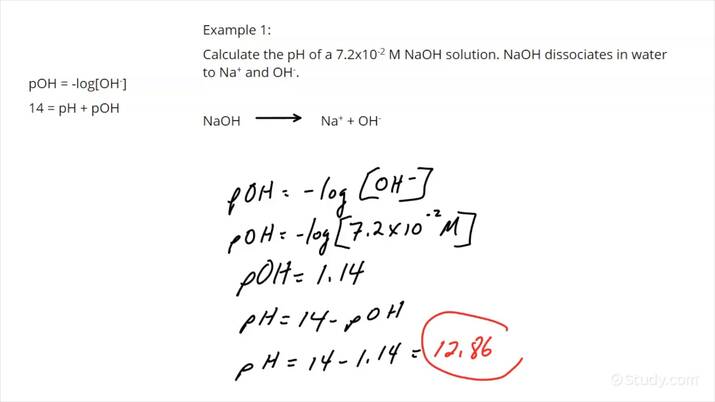
+
Yes, calculators with logarithm functions are commonly used for pH calculations. However, understanding the principles and how to solve these problems manually is beneficial for learning and problem-solving in different contexts.
How accurate do I need to be with pH calculations?

+
The required accuracy depends on your application. In laboratory settings, you might need precision to several decimal places. For general chemistry or educational purposes, rounding to the nearest whole number or one decimal place is often sufficient.
To conclude, mastering pH calculations involves understanding fundamental concepts like hydrogen ion concentration, logarithms, equilibrium constants, and the relationship between pH and pOH. With practice, you’ll become adept at determining pH for a wide range of solutions, from simple strong acids and bases to more complex mixtures and buffers. This knowledge not only aids in academic and professional settings but also enriches your understanding of the chemical world around us.