5 Easy Steps to Label Waves on Worksheets

The process of labeling waves on worksheets can be a fundamental part of science education, especially in physics and related fields. Whether you're teaching wave mechanics in high school or preparing students for more advanced studies, mastering the art of labeling waves accurately enhances understanding. Here are five steps to help you and your students label waves correctly and efficiently.
Step 1: Understand Wave Terminology
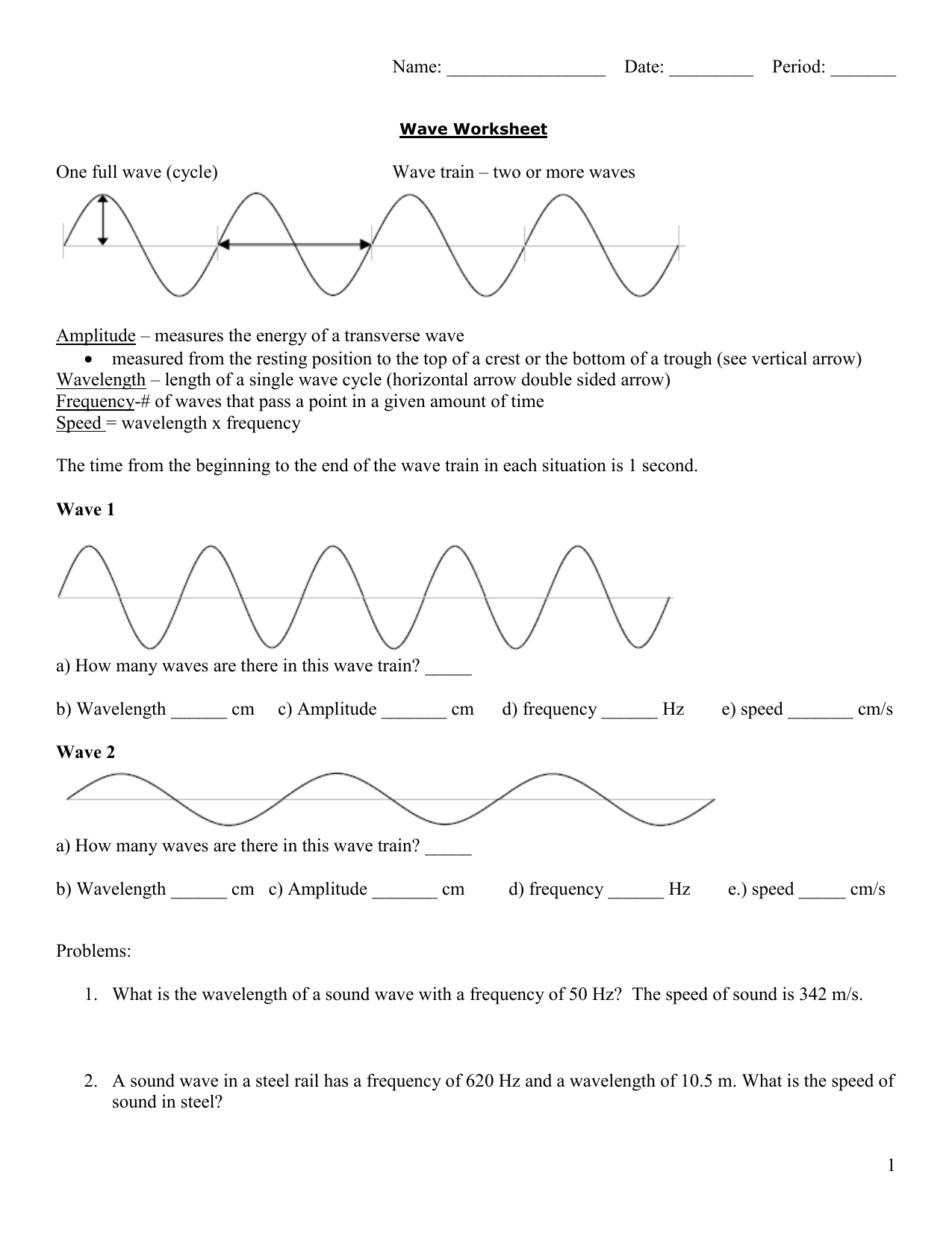
Before you can start labeling, it’s crucial to familiarize yourself with the key terms associated with waves:
- Amplitude: The maximum displacement from the equilibrium position.
- Wavelength (λ): The distance between two consecutive corresponding points of the same phase (e.g., from crest to crest).
- Crest: The highest point on a wave.
- Trough: The lowest point on a wave.
- Frequency: The number of cycles passing through a point per second, measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Period: The time it takes for one cycle of the wave to occur, the inverse of frequency.

✅ Note: Familiarizing with these terms is not only for labeling waves but also for understanding wave behavior and its applications.
Step 2: Draw the Wave

The next step is to create a visual representation of the wave. This can be done:
- By hand, if you’re using physical worksheets.
- Using software like Microsoft Excel or drawing tools in digital applications.
Ensure that your wave has clearly defined crests and troughs, making it easy to label.
Step 3: Identify Key Points

Once the wave is drawn, identify the following key points:
- The highest crest and lowest trough for amplitude measurements.
- Two successive crests or troughs to measure the wavelength.
- Points where the wave crosses the equilibrium line for phase.
Step 4: Label the Wave

Now, with your key points identified, proceed with labeling:
- Mark the amplitude by measuring from the equilibrium line to the crest or trough.
- Use a ruler or digital ruler to measure and label the wavelength.
- Indicate the crests and troughs with symbols or labels like “C” for crest and “T” for trough.
- Label the frequency and period at the edges of the wave or on an accompanying graph.
| Wave Parameter | Label |
|---|---|
| Amplitude | A |
| Wavelength | λ |
| Crest | C |
| Trough | T |
| Frequency | f |
| Period | T |

🚨 Note: Use consistent labeling across all worksheets to avoid confusion in learning.
Step 5: Review and Apply

Finally, review your work for accuracy:
- Ensure all labels are correct and positioned appropriately.
- Double-check measurements to make sure they correspond to the actual wave.
- Use this labeled wave for further analysis or discussion, such as calculating wave speed or exploring wave interference.
In summary, understanding and labeling waves correctly is a crucial skill for students and educators alike. By following these steps, one can not only accurately represent waves but also enhance the learning process, making wave mechanics more approachable and intriguing. Whether in a classroom setting or while self-studying, these practices pave the way for a deeper understanding of how waves function and interact with our environment.
Why is it important to label waves accurately?

+
Accurate labeling helps in understanding wave properties and behaviors, which is essential for further learning in physics, acoustics, optics, and other fields where waves play a significant role.
What can I do if the wave’s amplitude varies?

+
Label the maximum amplitude observed and note that it’s a variable amplitude wave. You might also want to show different amplitudes to illustrate concepts like modulation or damping.
How do I measure wave speed using labeled waves?

+
Wave speed can be calculated by multiplying the wavelength by the frequency, i.e., v = λ × f. This relationship can be derived from the labeled wave.



