5 Ways About ATC
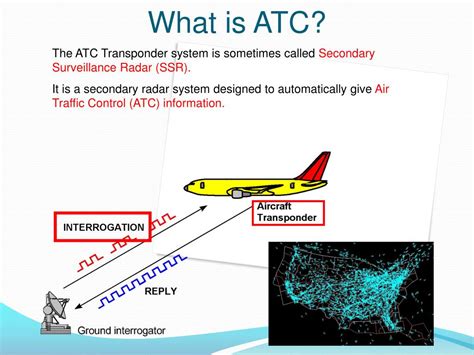
Introduction to Air Traffic Control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a critical component of the aviation system, responsible for ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft through the national airspace system. The primary goal of ATC is to prevent collisions between aircraft, provide efficient routing and separation of aircraft, and ensure the safe and expeditious flow of air traffic. In this blog post, we will explore five key aspects of air traffic control and their importance in the aviation industry.
1. Roles and Responsibilities of Air Traffic Controllers

Air traffic controllers play a vital role in the aviation system, and their responsibilities can be broadly categorized into several areas. These include: * Ground Control: responsible for guiding aircraft on the ground, including taxiing and takeoff. * Tower Control: responsible for controlling aircraft in the vicinity of the airport, including takeoff, landing, and ground operations. * Approach Control: responsible for guiding aircraft as they approach the airport, including providing instructions for descent and landing. * Center Control: responsible for controlling aircraft in the en route phase of flight, including providing instructions for routing and altitude changes. These roles require a high level of skill, attention to detail, and communication skills to ensure the safe and efficient movement of aircraft.
2. Air Traffic Control Systems and Technologies

The air traffic control system relies on a range of technologies and systems to manage air traffic. These include: * Radar systems: used to track the location and altitude of aircraft. * Communication systems: used to communicate with aircraft, including radio and data link communications. * Automation systems: used to automate routine tasks and provide decision-support tools for air traffic controllers. * Surveillance systems: used to track the location and movement of aircraft, including ADS-B (Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast) and multilateration systems. These systems and technologies are critical to the safe and efficient operation of the air traffic control system.
3. Challenges Facing Air Traffic Control

The air traffic control system faces a range of challenges, including: * Increasing air traffic demand: as the number of aircraft in the skies continues to grow, air traffic control must adapt to manage the increased demand. * Weather and environmental factors: weather and environmental factors, such as thunderstorms and volcanic ash, can impact air traffic control operations. * Cybersecurity threats: the air traffic control system is vulnerable to cybersecurity threats, which can impact the safety and efficiency of air traffic control operations. * Controller workload and fatigue: air traffic controllers must manage a high workload and work long hours, which can lead to fatigue and decreased performance.
4. Future Developments in Air Traffic Control

The air traffic control system is undergoing significant changes, driven by advances in technology and changes in air traffic demand. Some of the key future developments include: * NextGen: a US-based initiative to modernize the air traffic control system, including the use of ADS-B and other advanced technologies. * Single European Sky: a European initiative to create a single, unified air traffic control system across the European Union. * Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs): the increasing use of UAVs is driving the need for new air traffic control systems and procedures. * Artificial intelligence and machine learning: the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning is being explored to improve air traffic control operations and decision-making.
5. Training and Certification for Air Traffic Controllers

Air traffic controllers must undergo rigorous training and certification to perform their duties. This includes: * Initial training: new air traffic controllers must undergo initial training, which includes classroom instruction and simulation training. * On-the-job training: air traffic controllers must also undergo on-the-job training, where they work alongside experienced controllers to gain practical experience. * Certification: air traffic controllers must be certified by the relevant aviation authority, which involves passing a series of exams and assessments. * Recurrent training: air traffic controllers must also undergo recurrent training, which includes regular assessments and training to ensure they remain competent and up-to-date with the latest procedures and technologies.
📝 Note: The training and certification requirements for air traffic controllers vary by country and aviation authority, but the principles remain the same.
To summarize, air traffic control is a critical component of the aviation system, responsible for ensuring the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. The roles and responsibilities of air traffic controllers are varied and complex, and the system relies on a range of technologies and systems to manage air traffic. Despite the challenges facing air traffic control, the system is undergoing significant changes, driven by advances in technology and changes in air traffic demand. The training and certification of air traffic controllers are critical to ensuring the safe and efficient operation of the air traffic control system.
What is the primary goal of air traffic control?

+
The primary goal of air traffic control is to prevent collisions between aircraft, provide efficient routing and separation of aircraft, and ensure the safe and expeditious flow of air traffic.
What are the different types of air traffic control?
+
There are several types of air traffic control, including ground control, tower control, approach control, and center control.
What is the role of technology in air traffic control?

+
Technology plays a critical role in air traffic control, including radar systems, communication systems, automation systems, and surveillance systems.