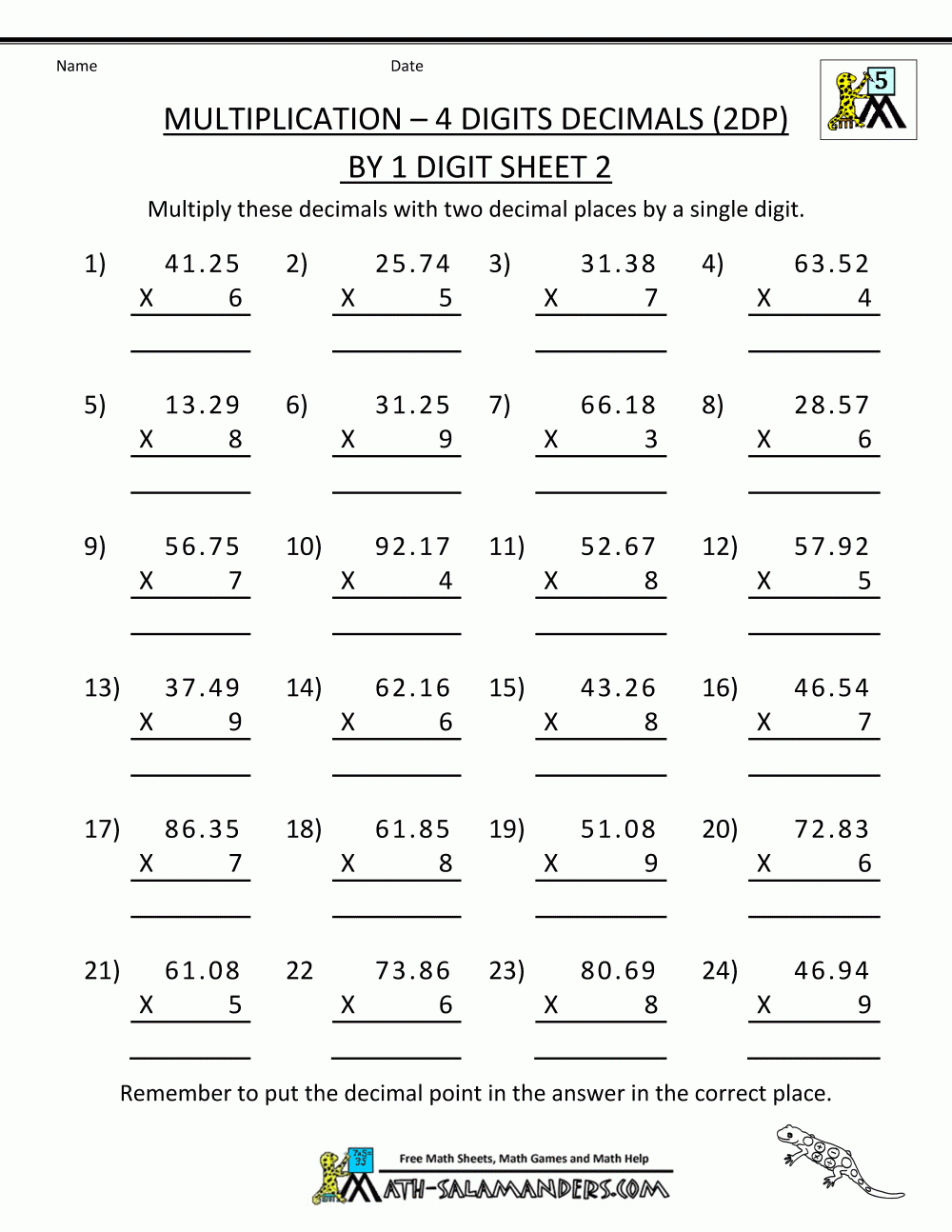
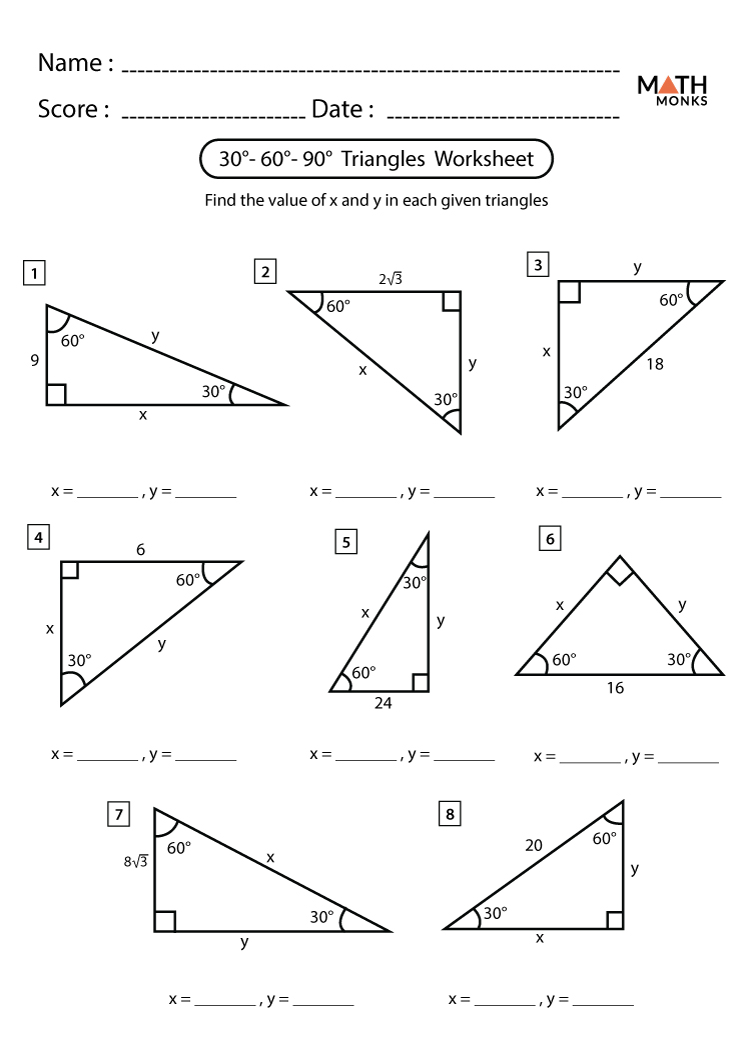
5 Essential Tips for Waves Refraction Worksheet Answers

Understanding Waves Refraction and Its Importance in Education

When diving into the fascinating world of physics, particularly waves, you'll encounter refraction, a key phenomenon where waves change direction upon moving from one medium to another due to changes in their velocity. This principle is not just a staple in physics education but also has practical applications across various fields. Here, we'll explore five essential tips to master the waves refraction worksheet, ensuring a thorough understanding and accurate answers.
1. Grasp the Basics of Refraction

Before attempting the worksheet, it's vital to have a solid grasp on the concept of refraction:
- Definition: Refraction occurs when waves (light, sound, etc.) change direction as they pass from one medium into another.
- Snell’s Law: This law quantifies refraction through the formula \sin(\theta_1)/\sin(\theta_2) = v_1/v_2 = n_2/n_1, where \theta is the angle from the normal, v is the wave velocity, and n is the index of refraction.
📚 Note: Remember, refraction is not just limited to light but can occur with any wave, including sound waves, in different media.
2. Visualize the Path of Light

Refraction involves visualizing how light travels through different media, which can often be counterintuitive:
- Light tends to bend towards the normal line when entering a denser medium and away from it when entering a less dense one.
- Use diagrams to trace the path of light. These visual representations can clarify which way light will refract and at what angle.
An effective way to visualize this:
| Diagram | Description |
 |
Example of light bending as it passes from air into glass or water. |

3. Apply the Correct Mathematical Formulas

When solving problems:
- Always start with Snell's Law for simple refraction cases.
- For more complex situations, use the lensmaker's equation or other relevant formulas. Ensure you apply the correct formula for the given scenario.
✏️ Note: Accuracy in applying formulas is critical, especially when dealing with different wavelengths or mediums.
4. Consider the Angle of Incidence

Understanding how the angle of incidence affects refraction is crucial:
- The angle of incidence determines how much light will bend when it enters a new medium.
- Recognize the difference between the critical angle, which leads to total internal reflection, and other angles.
5. Practice Problem-Solving

Consistent practice is the key to mastering refraction:
- Start with simple refraction problems and gradually move to more complex scenarios.
- Work through example questions provided in textbooks or online resources.
- Use online simulations or physical tools like prisms to experiment with refraction principles.
🧠 Note: Solving problems not only reinforces your understanding but also builds your intuition for real-world applications.
In wrapping up our journey through waves refraction, it’s clear that understanding this concept opens doors to various scientific and technological advancements. From optical fibers in telecommunications to the design of eyeglasses, refraction plays a pivotal role. By mastering the tips provided, you’re not just solving worksheets; you’re laying the foundation for a deeper appreciation of the world around you, where light and other waves interact in fascinating ways.
Now, let’s dive into some commonly asked questions about refraction to solidify our understanding:
Why does light bend when it enters a different medium?

+
Light bends due to a change in its speed when entering a medium with a different index of refraction. The denser the medium, the slower light travels, causing it to bend towards the normal line.
Can sound waves also refract?

+
Yes, sound waves can refract when passing through different air temperatures, densities, or moving from one medium to another.
What is the difference between reflection and refraction?

+
Reflection occurs when waves bounce off a surface at the same angle they hit it, whereas refraction involves the change in direction as waves move from one medium to another due to changes in velocity.
How does refraction affect optical instruments?

+
Refraction is fundamental in optical instruments like telescopes, microscopes, and lenses, where the bending of light through lenses focuses images onto screens or our eyes.
What causes the phenomenon of the mirage?

+
Mirages are caused by the refraction of light in layers of air with different temperatures near the ground, creating the illusion of water or a distorted image.