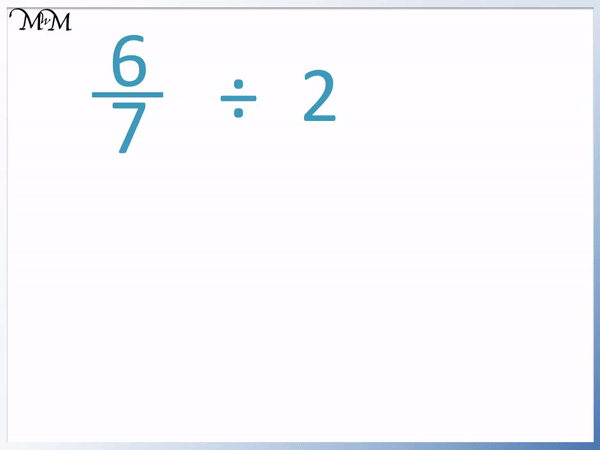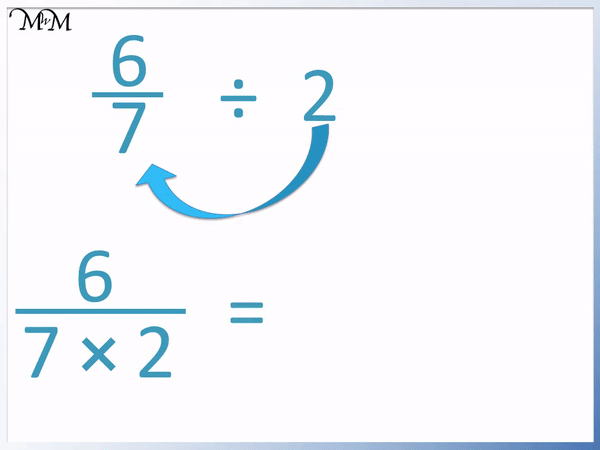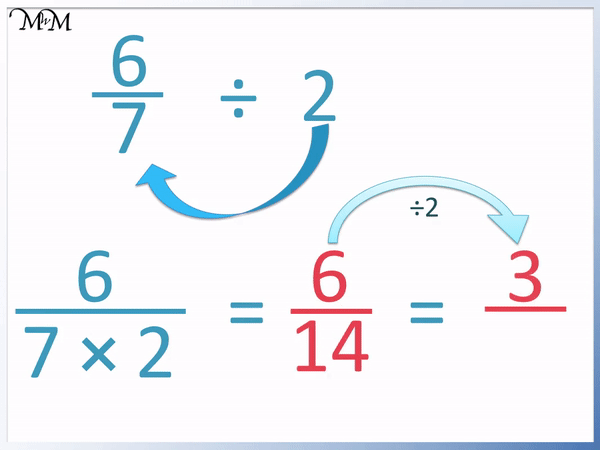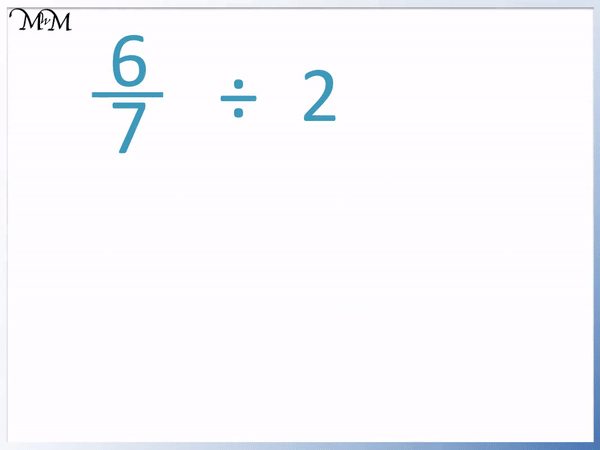5 Must-Know Tips for Mastering Velocity and Acceleration

The Fundamentals of Velocity and Acceleration

Velocity and acceleration are crucial concepts in physics, dictating the motion and behavior of objects in both everyday life and high-tech engineering applications. Understanding these principles is not only essential for scientists and engineers but also for anyone interested in the mechanics of the world around us. In this blog post, we delve into five indispensable tips to help you master the intricacies of velocity and acceleration.

1. Comprehend the Difference

Before diving into the specifics, it's vital to distinguish between velocity and acceleration:
- Velocity: This is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude (speed) and direction. It describes the rate at which an object changes its position. Here are some points to remember:
- Velocity can be negative, indicating the direction opposite to the positive reference frame.
- Average velocity is calculated over a period, whereas instantaneous velocity is measured at a specific point in time.
- Acceleration: Also a vector quantity, acceleration describes how velocity changes over time:
- Acceleration can change the speed, direction, or both of velocity.
- Positive acceleration means speeding up, and negative acceleration (deceleration) means slowing down.
2. Apply the Equations Correctly

To grasp velocity and acceleration, knowing the key equations is fundamental:
| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| \[v = \frac{\Delta x}{\Delta t}\] | Velocity is distance over time. |
| \[a = \frac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}\] | Acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the change in time. |
| \[v = u + at\] | Final velocity with constant acceleration, where u is the initial velocity. |
| \[v^2 = u^2 + 2as\] | Velocity squared considering acceleration and distance traveled. |

These equations provide a direct pathway to calculate unknown variables in problems involving motion.
3. Understand the Concept of Instantaneous Values

When analyzing motion, especially for objects with changing velocity, consider:
- Instantaneous velocity: The velocity at a single point in time, which can be derived from the slope of a position-time graph.
- Instantaneous acceleration: Similarly, this is the acceleration at a specific instant, found as the slope of the velocity-time graph.
💡 Note: Instantaneous values often provide more precise information about an object’s motion.
4. Relate Forces to Acceleration

In accordance with Newton's Second Law (F = ma), force is directly proportional to acceleration:
- The greater the force applied to an object, the greater its acceleration, assuming mass remains constant.
- Force, mass, and acceleration have an intimate relationship:
- If force is doubled, acceleration will also double, keeping mass constant.
- This can be visually represented in force diagrams or free body diagrams.

5. Use the Right Tools for Analysis

Here are some modern and classic tools used to analyze velocity and acceleration:
- Physics Simulation Software: Software like PhET or Algodoo can simulate physical scenarios, allowing you to observe velocity and acceleration in virtual environments.
- Data Loggers and Motion Sensors: These devices measure real-time data, providing accurate velocity and acceleration values.
- Graphing Calculators: These tools are great for plotting position, velocity, and acceleration graphs.
- Smartphones with Physics Apps: Many modern smartphones come equipped with apps that can use their sensors to measure motion.
🔍 Note: The use of technology can enhance understanding by providing real-world data and interactive learning.
Throughout this journey, mastering velocity and acceleration hinges on understanding their definitions, correctly applying relevant equations, recognizing instantaneous values, correlating with forces, and utilizing tools effectively. As we conclude our exploration, these principles not only elucidate the motion of objects but also empower us to manipulate and predict the behavior of systems in physics.
In wrapping up this post, keep in mind the dynamic interplay between force, mass, and acceleration. The mastery of these concepts will serve you well in understanding complex scenarios in motion, whether in school, industry, or casual curiosity.
What is the difference between speed and velocity?

+
Speed is a scalar quantity measuring only the magnitude (rate of movement). Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that includes both magnitude and direction, providing a more complete description of motion.
How does negative acceleration work?

+
Negative acceleration, often called deceleration, means the object is slowing down. However, if the velocity is increasing in the opposite direction to the positive reference frame, acceleration can still be positive while the speed decreases.
Why is understanding instantaneous velocity important?

+
Instantaneous velocity provides precise information about an object’s motion at a particular moment. It’s crucial for understanding how velocity changes over time, which is essential in scenarios with varying forces or acceleration.