Units of Force Explained
Introduction to Units of Force

The concept of force is fundamental in physics and engineering, and understanding its units is crucial for accurate calculations and measurements. Force is a push or pull that causes an object to change its state of motion, and it is measured in various units depending on the system of measurement being used. In this article, we will delve into the different units of force, their definitions, and how they are used in various contexts.
SI Unit of Force: Newton

The International System of Units (SI) defines the unit of force as the Newton (N). One Newton is the force required to accelerate a 1-kilogram object by 1 meter per second squared. The Newton is a derived unit, which means it is defined in terms of other base units. In this case, it is defined as the product of mass (kilogram) and acceleration (meter per second squared). The Newton is widely used in scientific and engineering applications, and it is the standard unit of force in the SI system.
Other Units of Force
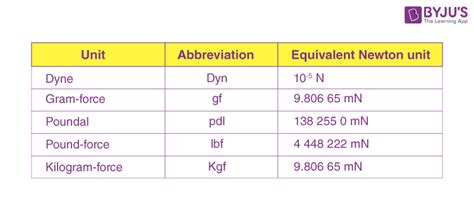
While the Newton is the standard unit of force, there are other units that are used in specific contexts or in different systems of measurement. Some of these units include: * Pound-force (lbf): This unit is commonly used in the United States and is defined as the force required to accelerate a 1-pound object by 32.174 feet per second squared. * Kilopond (kp): This unit is used in some European countries and is defined as the force required to accelerate a 1-kilogram object by 9.80665 meters per second squared. * Dyne: This unit is part of the CGS (Centimeter-Gram-Second) system and is defined as the force required to accelerate a 1-gram object by 1 centimeter per second squared.
Conversion Between Units of Force

Converting between different units of force is essential in many applications, especially when working with different systems of measurement. The following table shows the conversion factors between some common units of force:
| Unit | Conversion Factor |
|---|---|
| Newton (N) | 1 N = 0.2248 lbf |
| Pound-force (lbf) | 1 lbf = 4.448 N |
| Kilopond (kp) | 1 kp = 9.80665 N |
| Dyne | 1 dyne = 0.00001 N |

📝 Note: When converting between units of force, it is essential to ensure that the conversion factors are accurate and up-to-date to avoid errors in calculations.
Applications of Units of Force

Understanding the different units of force and how to convert between them is crucial in various applications, including: * Engineering: Forces are used to design and analyze structures, mechanisms, and systems. * Physics: Forces are used to describe the motion of objects and the interactions between them. * Materials science: Forces are used to test the strength and properties of materials. * Biomechanics: Forces are used to study the movement and function of living organisms.
Best Practices for Working with Units of Force

When working with units of force, it is essential to follow best practices to ensure accuracy and consistency. Some of these best practices include: * Always specify the unit of force when reporting measurements or calculations. * Use the correct conversion factors when converting between units of force. * Ensure that the units of force are consistent throughout calculations and analyses. * Use dimensional analysis to check the consistency of units in equations and calculations.
In summary, understanding the different units of force and how to convert between them is essential in various applications, including engineering, physics, materials science, and biomechanics. By following best practices and using the correct conversion factors, we can ensure accuracy and consistency in our calculations and measurements.
What is the SI unit of force?

+
The SI unit of force is the Newton (N), which is defined as the force required to accelerate a 1-kilogram object by 1 meter per second squared.
How do I convert between different units of force?

+
To convert between different units of force, use the conversion factors provided in the table above. For example, to convert from Newtons to pound-force, multiply the value in Newtons by 0.2248.
What are some common applications of units of force?

+
Units of force are used in various applications, including engineering, physics, materials science, and biomechanics. They are used to design and analyze structures, mechanisms, and systems, as well as to test the strength and properties of materials.