8th Grade Exponents Worksheets: Simplify Your Learning Journey
Understanding Exponents and Their Importance in Mathematics

Exponents are a fundamental concept in mathematics, often introduced to students in middle school. They provide a compact way to express repeated multiplication, making complex calculations more manageable and facilitating problem-solving in algebra, science, and beyond. For 8th graders, mastering exponents is not just about learning the rules; it's about understanding the why behind these rules, which sets the stage for advanced math topics like logarithms, polynomials, and even calculus.
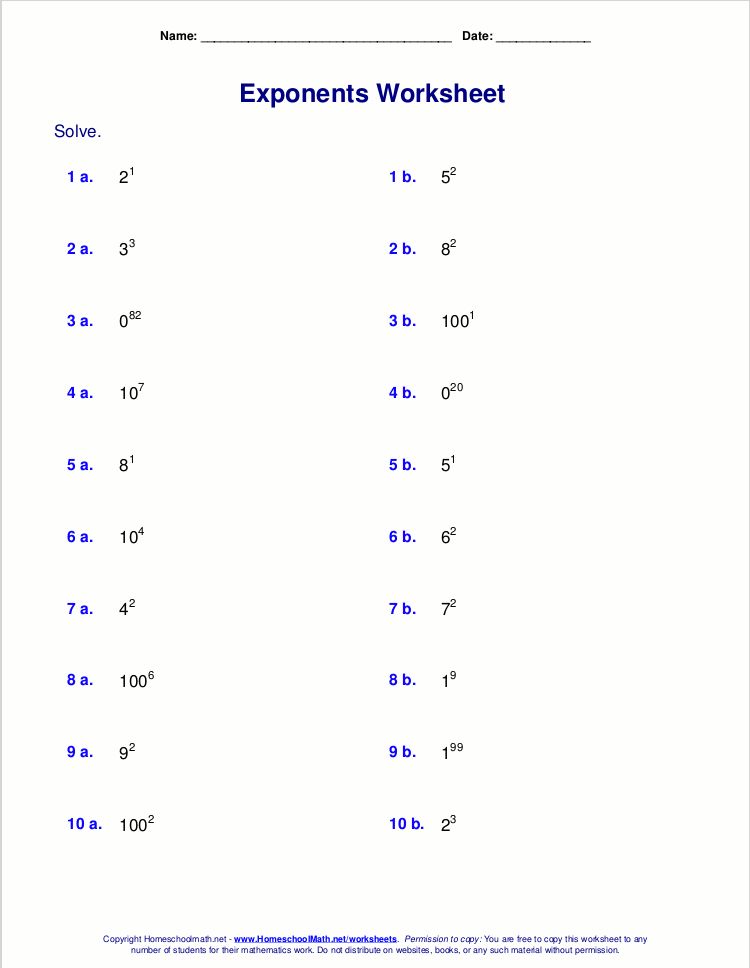
What Are Exponents?

An exponent, sometimes called a power, represents the number of times a number, called the base, is used in a multiplication. For example, in the expression 4^3, the base is 4 and the exponent is 3. This means we multiply the base by itself three times:
4^3 = 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64
Here's a quick reference for understanding exponents:
- Base: The number being raised to a power.
- Exponent (or Power): The number of times the base is multiplied by itself.
- Expression: Written as baseexponent, which means "base to the power of exponent."
Properties of Exponents

To effectively work with exponents, understanding their properties is crucial:
- Product of Powers: When multiplying two exponents with the same base, you add the exponents: a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n}
- Quotient of Powers: When dividing exponents with the same base, you subtract the exponents: a^m \div a^n = a^{m-n}
- Power of a Power: When raising an exponent to another power, you multiply the exponents: (a^m)^n = a^{m \times n}
- Power of a Product: Raising a product to an exponent means each factor gets that exponent: (ab)^m = a^m b^m
- Power of a Quotient: Raising a quotient to an exponent means both the numerator and denominator get that exponent: (a/b)^m = a^m / b^m
Example Problems

Let's delve into some examples to illustrate how these properties are applied:
- Product of Powers: 5^2 \times 5^3 = 5^{2+3} = 5^5 = 3125
- Quotient of Powers: 9^5 \div 9^3 = 9^{5-3} = 9^2 = 81
- Power of a Power: (2^2)^3 = 2^{2 \times 3} = 2^6 = 64
- Power of a Product: (3x)^2 = 3^2 \times x^2 = 9x^2
- Power of a Quotient: (4/5)^2 = 4^2 / 5^2 = 16 / 25
🔍 Note: Practice helps solidify your understanding. Engage in worksheet exercises regularly to become comfortable with these rules.
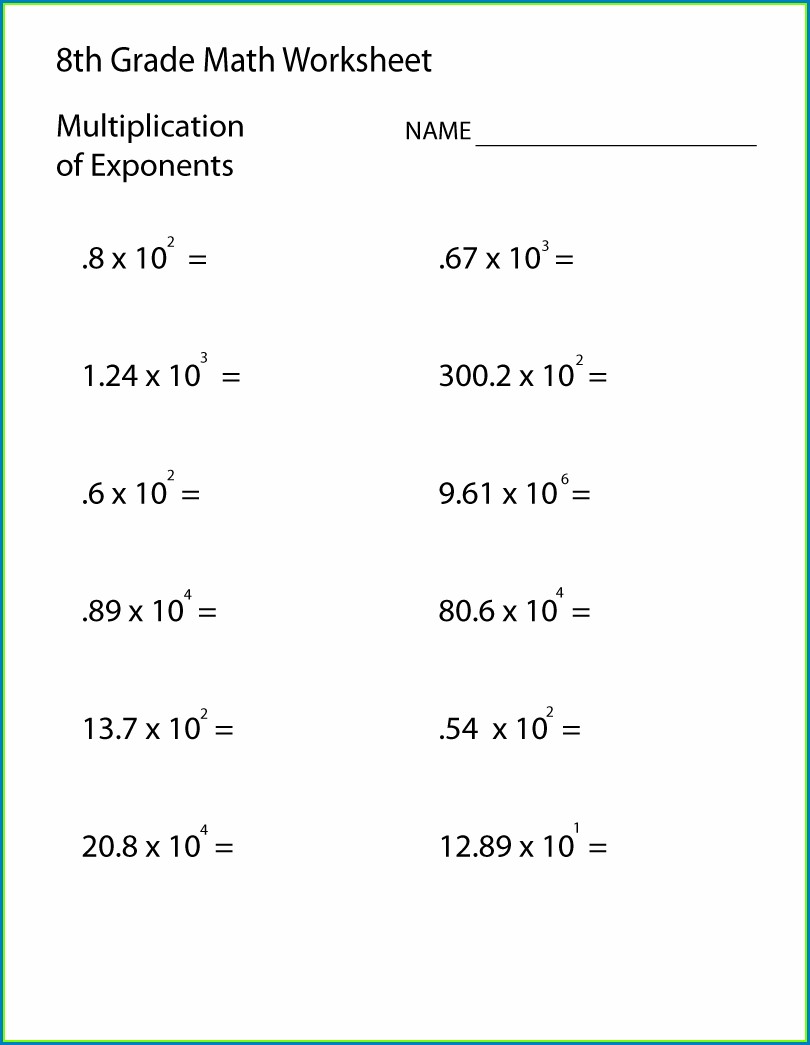
Simplifying Exponents Using Worksheets

Worksheets are an invaluable tool for students learning exponents. They provide:
- Structured practice to apply exponent rules.
- Immediate feedback for learning from mistakes.
- A progressive approach to tackling complex problems.
Here's a simple table to organize different types of exponents exercises:
| Type of Exercise | Goal | Example Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Operations | Understand and apply basic properties. | 6^4 \div 6^2 |
| Negative Exponents | Master the concept of negative exponents. | 2^{-3} |
| Fractional Exponents | Learn about roots and rational exponents. | 16^{1/2} |
| Scientific Notation | Practice converting between standard and scientific notation. | Convert 45,000,000 to scientific notation |
| Multi-Step Problems | Combine all exponent properties for complex problems. | ((3^2)^2) \div (3 \times 3^{-3}) |

🔍 Note: Worksheets should start from basic to more advanced exercises, allowing students to build confidence as they progress.
Strategies for Learning Exponents

To truly excel at exponents, consider these strategies:
- Practice: Regularly work through exponent problems to internalize the rules.
- Understand the Concept: Beyond memorizing rules, know why they work to enhance your mathematical intuition.
- Visual Aids: Use diagrams or mind maps to visualize how exponents work and how they relate to each other.
- Real-Life Applications: Relate exponents to real-world scenarios like population growth, compound interest, or even the exponential growth of technology.
- Group Work: Discussing problems with peers can offer new perspectives and reinforce your understanding.
In wrapping up our exploration of exponents, it’s clear that this concept is not just about writing out repeated multiplication; it’s about understanding the elegance and power of mathematical notation. Mastery of exponents lays a strong foundation for algebraic concepts and beyond, equipping students with skills necessary for future studies in math and science. Through persistent practice and a deep dive into the underlying principles, exponents become not just a tool for solving problems but a window into the beauty and logic of mathematics.
Why are exponents important in mathematics?
+
Exponents allow us to express large numbers and repeated multiplication efficiently, simplifying complex calculations and making advanced mathematical topics like algebra, logarithms, and calculus more accessible.
How can I remember the rules of exponents?

+
Practice is key. Use mnemonic devices, visual aids, and repeated problem-solving to solidify these rules in your memory. Remember, understanding the underlying concepts helps with retention.
What’s the best way to practice exponents?

+
Start with worksheets that progressively increase in difficulty. Combine practice with understanding through visual aids, real-life applications, and group study sessions for a well-rounded learning experience.
How can I use exponents in real life?

+
Exponents appear in fields like science, finance, and technology. For instance, they’re used to calculate compound interest, represent exponential growth or decay, and simplify large numbers in scientific notation.
Are there any tools or apps to help with exponents practice?

+
Many educational apps offer math practice, including exponent exercises. Look for apps with step-by-step solutions, video tutorials, and interactive quizzes to make learning dynamic and engaging.