US Missile Defense: Protecting America from Threats

US Missile Defense: Protecting America from Threats

The United States has long been a leader in missile defense, recognizing the importance of protecting its citizens and allies from the threat of ballistic missiles. With the rise of rogue nations and terrorist organizations, the need for effective missile defense systems has never been more pressing. In this blog post, we’ll explore the history of US missile defense, its current systems, and future developments.
A Brief History of US Missile Defense

The concept of missile defense dates back to the 1950s, when the Soviet Union began developing intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). In response, the United States initiated its own missile defense program, with the aim of protecting against Soviet nuclear-armed ICBMs. Over the years, the US has developed various missile defense systems, including the Nike-Hercules, Safeguard, and Patriot.
Current US Missile Defense Systems

Today, the US operates a multi-layered missile defense system, comprising:
- Ground-Based Midcourse Defense (GMD): This system is designed to defend against long-range ICBMs. It consists of interceptors based in Alaska and California, which can engage and destroy incoming missiles in space.
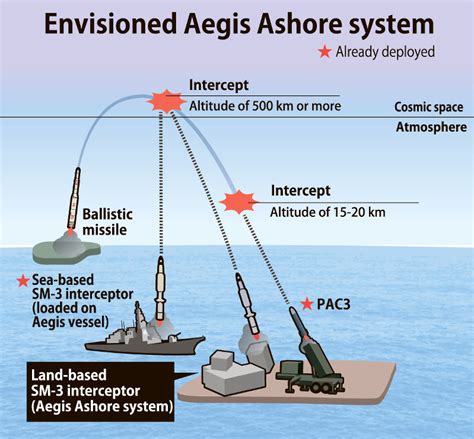
- Aegis Ballistic Missile Defense (BMD): Aegis BMD is a sea-based system that uses SM-3 interceptors to defend against short- to intermediate-range ballistic missiles. Aegis-equipped ships are deployed worldwide, providing protection for US and allied forces.
- Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD): THAAD is a land-based system that defends against short- to intermediate-range ballistic missiles. It has been deployed in South Korea and the UAE, with plans for future deployments in other regions.
How US Missile Defense Systems Work

US missile defense systems operate in several stages:
- Detection: Radars and sensors detect incoming missiles, tracking their trajectory and speed.
- Tracking: The system continuously updates the missile’s position, velocity, and trajectory.
- Interception: An interceptor missile is launched, guided by the tracking data.
- Kill vehicle: The interceptor’s kill vehicle separates, using its onboard sensors to guide itself to the target.
- Collision: The kill vehicle collides with the incoming missile, destroying it.
Future Developments in US Missile Defense

The US is continually updating and improving its missile defense systems, with several new developments on the horizon:
- Space-Based Sensors: The US plans to deploy a new generation of space-based sensors, providing enhanced detection and tracking capabilities.
- Hypersonic Missile Defense: The US is exploring technologies to counter hypersonic missiles, which can evade traditional missile defense systems.
- Directed Energy Systems: The US is researching directed energy systems, such as lasers, to potentially use against ballistic missiles.
🚀 Note: The development of new missile defense systems is an ongoing process, with new technologies and innovations being explored continuously.
Challenges and Controversies in US Missile Defense
While US missile defense systems have made significant progress, several challenges and controversies remain:
- Cost: Developing and maintaining missile defense systems is expensive, with costs running into billions of dollars.
- Effectiveness: Critics argue that current systems are not effective against advanced missile threats.
- International cooperation: The US has faced opposition from Russia and China, which view US missile defense systems as a threat to their national security.
Conclusion

US missile defense plays a critical role in protecting America and its allies from ballistic missile threats. While challenges and controversies remain, the US continues to invest in new technologies and innovations to stay ahead of emerging threats. As the global security landscape evolves, the importance of effective missile defense systems will only continue to grow.
What is the primary goal of US missile defense?

+
The primary goal of US missile defense is to protect the United States and its allies from ballistic missile threats.
What is the difference between GMD and Aegis BMD?

+
GMD is a ground-based system designed to defend against long-range ICBMs, while Aegis BMD is a sea-based system that defends against short- to intermediate-range ballistic missiles.
What is the role of THAAD in US missile defense?

+
THAAD is a land-based system that defends against short- to intermediate-range ballistic missiles, providing protection for US and allied forces.
Related Terms:
- U S missile defense system
- u s missile defense system name
- Air defense System
- Ballistic missile defense system
- U S Missile Defense Agency
- Aegis ballistic Missile Defense System



