U.S. Navy Enlisted Ranks Explained
Understanding the U.S. Navy Enlisted Ranks
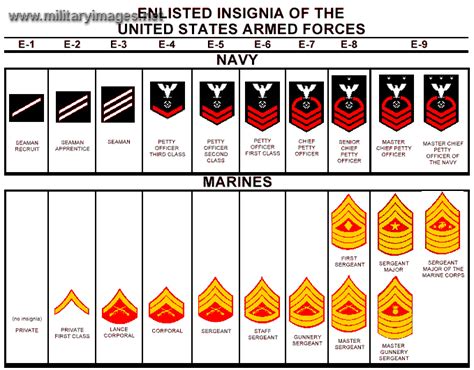
The United States Navy has a complex ranking system, with 13 enlisted ranks and various ratings that can be confusing for those not familiar with the military. In this article, we will break down the U.S. Navy enlisted ranks, explaining the roles, responsibilities, and requirements for each rank.
Junior Enlisted Ranks (E-1 to E-3)

The junior enlisted ranks in the U.S. Navy are entry-level positions that require little to no experience. These ranks are:
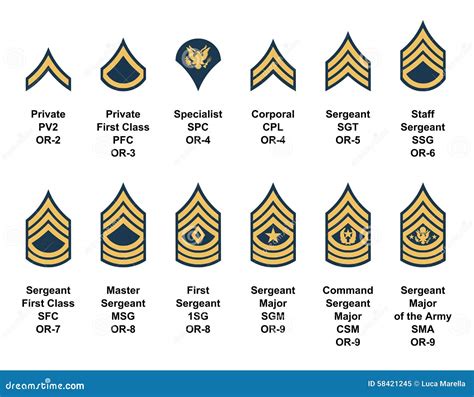
- Seaman Recruit (E-1): The lowest rank in the Navy, typically held by new recruits who have just joined the service.
- Seaman Apprentice (E-2): A rank that requires completion of basic training and is typically held by sailors who are still in their first year of service.
- Seaman (E-3): A rank that requires completion of a rating-specific training program and is typically held by sailors who have completed their first year of service.
Non-Commissioned Officer (NCO) Ranks (E-4 to E-6)

The non-commissioned officer (NCO) ranks in the U.S. Navy are leadership positions that require experience and technical expertise. These ranks are:
- Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): A rank that requires completion of a rating-specific training program and is typically held by sailors who have 2-4 years of experience.
- Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): A rank that requires completion of advanced training and is typically held by sailors who have 4-6 years of experience.
- Petty Officer First Class (E-6): A rank that requires completion of advanced training and is typically held by sailors who have 6-10 years of experience.
Senior Enlisted Ranks (E-7 to E-9)

The senior enlisted ranks in the U.S. Navy are senior leadership positions that require significant experience and technical expertise. These ranks are:
- Chief Petty Officer (E-7): A rank that requires completion of advanced training and is typically held by sailors who have 10-15 years of experience.
- Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): A rank that requires completion of advanced training and is typically held by sailors who have 15-20 years of experience.
- Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): The highest enlisted rank in the Navy, typically held by sailors who have 20+ years of experience.
Special Ratings and Designations

In addition to the standard enlisted ranks, the U.S. Navy also has special ratings and designations that require unique skills and training. These include:
- Aviation ratings: Ratings that require specialized training in aviation, such as aviation machinist’s mate or aviation electronics technician.
- Submarine ratings: Ratings that require specialized training in submarines, such as machinist’s mate or electronics technician.
- Special Warfare ratings: Ratings that require specialized training in special warfare, such as Navy SEAL or Special Warfare Combatant-Craft Crewman.
💡 Note: The requirements for each rank can vary depending on the rating and the individual's experience and qualifications.
Ranking System Comparison

Here is a comparison of the U.S. Navy enlisted ranks to other military branches:
| U.S. Navy | U.S. Army | U.S. Air Force | U.S. Marine Corps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seaman Recruit (E-1) | Private (E-1) | Airman Basic (E-1) | Private (E-1) |
| Seaman Apprentice (E-2) | Private Second Class (E-2) | Airman (E-2) | Private First Class (E-2) |
| Seaman (E-3) | Private First Class (E-3) | Airman First Class (E-3) | Lance Corporal (E-3) |
| Petty Officer Third Class (E-4) | Corporal (E-4) | Senior Airman (E-4) | Corporal (E-4) |
| Petty Officer Second Class (E-5) | Sergeant (E-5) | Staff Sergeant (E-5) | Sergeant (E-5) |
| Petty Officer First Class (E-6) | Staff Sergeant (E-6) | Technical Sergeant (E-6) | Staff Sergeant (E-6) |
| Chief Petty Officer (E-7) | Sergeant First Class (E-7) | Master Sergeant (E-7) | Gunnery Sergeant (E-7) |
| Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8) | Master Sergeant (E-8) | Senior Master Sergeant (E-8) | Master Sergeant (E-8) |
| Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9) | Sergeant Major (E-9) | Chief Master Sergeant (E-9) | Master Gunnery Sergeant (E-9) |

📚 Note: The ranking system can vary between branches, and some ranks may have different requirements or designations.
As we conclude, the U.S. Navy enlisted ranks are a complex system that requires dedication, hard work, and technical expertise. Understanding the roles, responsibilities, and requirements for each rank can help individuals navigate their careers in the Navy.
To wrap up, the U.S. Navy enlisted ranks are divided into junior, non-commissioned officer, and senior enlisted ranks. Each rank has its own set of requirements and responsibilities, and understanding these can help individuals advance in their careers. Additionally, the ranking system can vary between branches, and some ranks may have different requirements or designations.
By understanding the U.S. Navy enlisted ranks, individuals can better navigate their careers and achieve their goals in the military.
What is the lowest rank in the U.S. Navy?

+
The lowest rank in the U.S. Navy is Seaman Recruit (E-1).
What is the highest enlisted rank in the U.S. Navy?
+
The highest enlisted rank in the U.S. Navy is Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).
How many enlisted ranks are there in the U.S. Navy?

+
There are 13 enlisted ranks in the U.S. Navy, ranging from Seaman Recruit (E-1) to Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9).