Symbiosis Types Worksheet Answer Key Revealed

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the different types of symbiosis, a fascinating look into how different species live together for mutual benefit, one benefiting while the other is harmed, or where one partner lives at the expense of another. Today, we'll explore these intricate relationships through the lens of a Symbiosis Types Worksheet Answer Key, detailing the key concepts, examples, and their implications in nature.
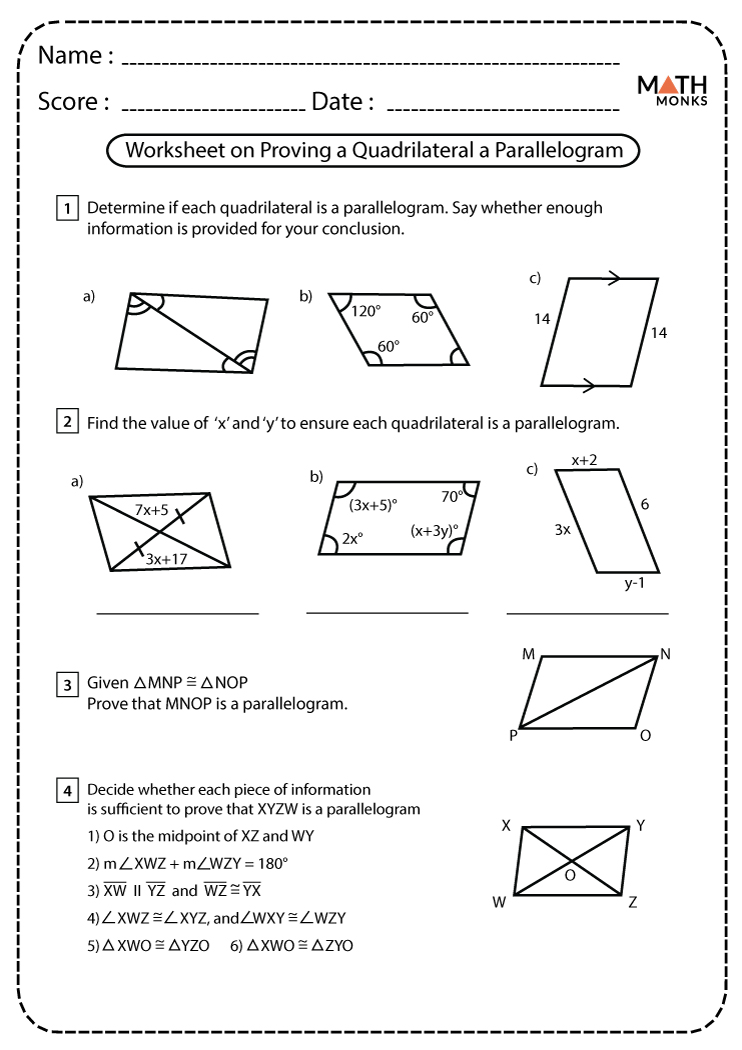
What is Symbiosis?

Symbiosis is a term that describes close, long-term biological interactions between different species. These relationships are categorized based on the impact on the species involved:
- Mutualism: Both species benefit.
- Commensalism: One species benefits, the other remains unaffected.
- Parasitism: One species benefits at the other's expense.
Each type of interaction has its own ecological significance, contributing to biodiversity, species evolution, and ecosystem health.

Exploring Types of Symbiosis

Mutualism

Mutualism is where both participating organisms benefit from the relationship. This type of symbiosis is often thought of as a ‘win-win’ situation. Here are some detailed examples:
- Flowers and Bees: Bees collect nectar, which provides them with food, while inadvertently pollinating the flowers, aiding in plant reproduction.
- Cleaner Fish: Cleaner fish feed on parasites found on larger fish, thus keeping the larger fish clean and providing the cleaner fish with food.
The key here is that each organism is dependent on the other, creating a balanced ecological interaction.
🔍 Note: Mutualistic relationships can be seen in action across various ecosystems, showcasing the intricate balance of nature.
Commensalism

In commensalism, one organism benefits while the other neither benefits nor is harmed. This type of symbiosis might not seem as dramatic, but it’s prevalent in nature:
- Epiphytic Plants: These plants grow on other plants (like trees) for physical support but do not take nutrients from the host plant. They benefit from the elevated position to gain more sunlight and rain while the host plant remains unaffected.
- Barnacles on Whales: Barnacles often attach to whales or turtles, gaining a moving home that exposes them to food in the water, while the host is neither helped nor harmed by their presence.
Commensalism might seem less impactful, but it showcases how species can coexist without causing harm.
Parasitism

Parasitism involves one organism (the parasite) living off another (the host), typically to the host’s detriment. Here are well-known examples:
- Tapeworms: These parasites live in the intestines of animals, absorbing nutrients, which can lead to malnutrition in the host.
- Parasitoid Wasps: Certain wasps lay their eggs inside other insects. The larvae then feed on the host, eventually killing it.
Parasitism raises fascinating questions about survival strategies and the balance between species in ecosystems.
⚠️ Note: Parasitism doesn’t always lead to the death of the host. Some parasites are careful not to kill their host to ensure their own survival.
Worksheet Examples Explained

| Type | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mutualism | Lichens | Combination of fungi and algae or cyanobacteria. Fungi provide structure and protection, while the photosynthetic partner provides nutrients. |
| Commensalism | Remora Fish | Remora fish attach to sharks for transport, feeding on scraps of food from the shark’s meal without affecting the shark. |
| Parasitism | Heartworms in Dogs | Heartworms live in the heart and lungs of dogs, taking nutrients and weakening the host’s health. |

Through these examples, we can understand how symbiosis is not just a theoretical concept but a tangible phenomenon in natural ecosystems.
Summing up our journey through the different types of symbiosis, we've covered mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism, providing insights into the delicate balance of ecological relationships. These relationships not only underline the complexity of life but also highlight the adaptability and interconnectedness of species within their environments. Understanding symbiosis helps us appreciate the intricate web of life where survival strategies are finely tuned to minimize harm and maximize mutual benefit.
What are some other examples of mutualism in nature?

+
Other examples include the relationship between ants and aphids (ants protect aphids from predators in exchange for honeydew), and the partnership between anemones and clownfish (anemones provide protection for clownfish, which helps clean them).
Can humans benefit from studying symbiosis?

+
Yes, understanding symbiotic relationships can enhance agricultural practices, medicine, and ecological conservation by learning how species can benefit from each other. This knowledge can lead to breakthroughs in pest control, vaccine development, and ecosystem management.
How do parasitic relationships affect ecosystems?

+
Parasites play a crucial role in regulating host populations, which can prevent overpopulation, drive evolutionary change, and maintain biodiversity. However, when parasites become too numerous or pathogenic, they can disrupt ecosystems by causing declines in host species.