6 Types Force
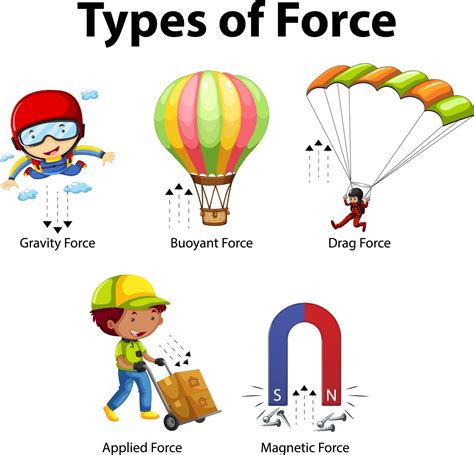
Understanding the 6 Types of Forces in Physics

In the realm of physics, forces are interactions that can cause an object to change its state of motion. These interactions can be classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics. The understanding of these forces is crucial for analyzing and predicting the behavior of objects in various physical contexts.
Types of Forces

There are primarily six types of forces, which are categorized based on their nature and the phenomena they are associated with. These include: - Frictional Force: This force opposes the motion of an object and is dependent on the nature of the surfaces in contact. It can be further divided into static friction, which prevents an object from moving, and kinetic friction, which slows down a moving object. - Normal Force: Also known as the ground reaction force, this is the force exerted by a surface on an object in contact with it, perpendicular to the surface. It is what keeps us on the ground and what prevents objects from falling through surfaces. - Tension Force: This force acts within strings, ropes, and cables when they are pulled tight by forces acting from opposite ends. The magnitude of tension force is the same throughout a massless, frictionless string. - Air Resistance Force: Also known as drag, this force opposes the motion of an object through a fluid (liquid or gas). The magnitude of air resistance depends on the velocity of the object, its cross-sectional area, and the density of the fluid it is moving through. - Gravitational Force: This is the attractive force between two masses. On Earth, it pulls objects towards the center of the planet, which we experience as weight. The strength of gravitational force depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between their centers. - Applied Force: This refers to any force that is applied to an object by another object or person. It can be used to accelerate an object, slow it down, or change its direction of motion. Applied forces can be in the form of pushes, pulls, or any other interaction that results in a force being exerted on an object.
Characteristics and Applications

Each type of force has its unique characteristics and applications. For example, frictional force is essential for walking and preventing objects from slipping, but it also generates heat and can lead to wear and tear. Understanding these forces is critical in engineering, where they are considered in the design of machines, vehicles, and structures to ensure stability, efficiency, and safety.
Interactions and Balance
Forces do not act in isolation; they interact with each other in complex ways. According to Newton’s third law of motion, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. This principle explains how forces are balanced and how objects maintain their state of motion unless acted upon by an external force. The balance of forces is a key concept in physics and engineering, used to analyze and predict the motion of objects under various conditions.
Examples and Illustrations

To better understand these forces, let’s consider some examples: - When you push a box across the floor, you are exerting an applied force. The floor exerts a normal force on the box, keeping it from sinking, and frictional force opposes the motion, trying to keep the box stationary. - A car moving at a constant speed on a straight road experiences a balance between the applied force (from the engine) and the opposing forces (mainly air resistance and rolling friction). - The gravitational force between the Earth and the Moon is what keeps the Moon in orbit around our planet.
📝 Note: Understanding the types of forces and how they interact is fundamental to solving problems in physics and engineering, allowing for the prediction of motion and the design of efficient systems.
Conclusion and Further Study
In conclusion, the six types of forces - frictional, normal, tension, air resistance, gravitational, and applied - form the foundation of understanding motion and interactions in the physical world. Each force plays a vital role in various phenomena, from the simplest everyday actions to complex engineering applications. Further study into these forces and their interactions can provide deeper insights into the natural world and help in the development of new technologies and solutions.
What is the primary factor that affects the magnitude of frictional force?
+
The primary factors that affect the magnitude of frictional force include the nature of the surfaces in contact and the force pressing these surfaces together, known as the normal force.
How does air resistance affect the motion of objects?
+
Air resistance, or drag, opposes the motion of an object through the air, slowing it down and converting some of its kinetic energy into heat. The effect of air resistance increases with the velocity of the object and its cross-sectional area.
What role does gravitational force play in the universe?

+
Gravitational force is responsible for the attraction between masses. It keeps planets in orbit around their stars, causes objects to fall towards the ground, and holds galaxies together. It is one of the four fundamental forces of nature and plays a crucial role in the structure and evolution of the universe.



