5 Types of Chemical Reactions Worksheet With Answers

Understanding chemical reactions is fundamental for anyone studying chemistry. Chemical reactions are the processes by which substances interact, change, and produce new compounds. To make sense of these complex interactions, categorizing them into types can greatly simplify learning. This worksheet will delve into five primary types of chemical reactions, providing examples, descriptions, and answers to ensure a comprehensive understanding.
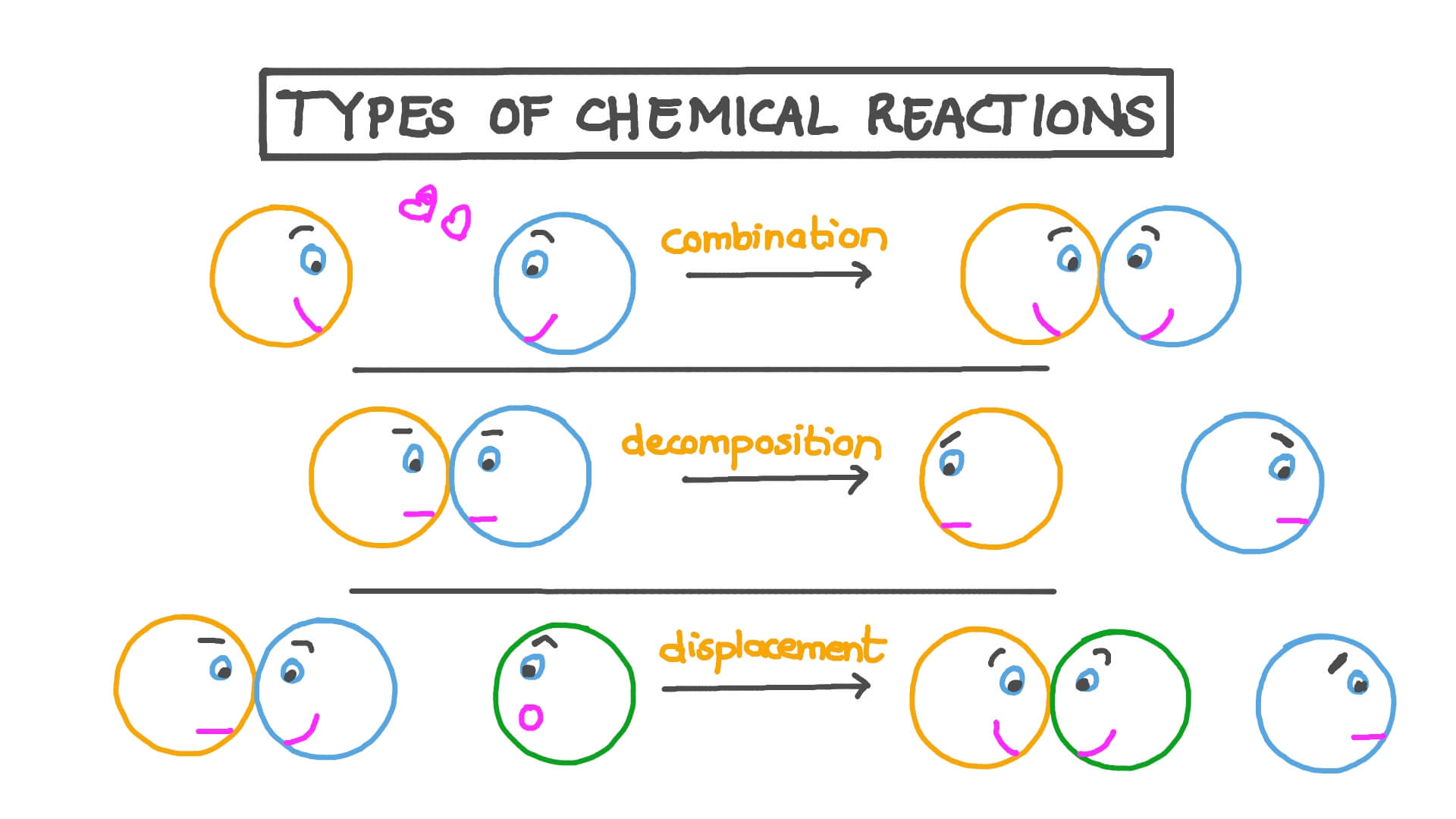
1. Synthesis Reactions

A synthesis reaction, often referred to as a combination reaction, occurs when two or more simpler substances combine to form a more complex compound. Here is the general formula:
[A + B \rightarrow AB]
- Example: The formation of water from hydrogen and oxygen: \[ 2H_{2}(g) + O_{2}(g) \rightarrow 2H_{2}O(l) \]
⚗️ Note: Synthesis reactions can involve elements, compounds, or a combination of both.
2. Decomposition Reactions

Decomposition reactions are the opposite of synthesis. They involve a complex substance breaking down into simpler substances. The general formula is:
[AB \rightarrow A + B]
- Example: The electrolysis of water: \[2H_{2}O(l) \rightarrow 2H_{2}(g) + O_{2}(g)\]
⚗️ Note: These reactions often require energy in the form of heat, light, or electricity.
3. Single Displacement Reactions

A single displacement reaction, also known as a single replacement reaction, happens when one element takes the place of another in a compound. The general formula looks like this:
[A + BC \rightarrow AC + B]
- Example: Zinc displacing copper in a copper sulphate solution: \[Zn(s) + CuSO_4(aq) \rightarrow ZnSO_4(aq) + Cu(s)\]
4. Double Displacement Reactions

In a double displacement reaction, two compounds exchange ions or elements with each other. Here's the typical form:
[AB + CD \rightarrow AD + CB]
- Example: Barium chloride with sodium sulphate: \[BaCl_2(aq) + Na_2SO_4(aq) \rightarrow BaSO_4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)\]
⚗️ Note: These reactions often occur in aqueous solutions and might lead to the formation of a precipitate or gas.
5. Combustion Reactions

Combustion reactions generally involve burning substances in oxygen, producing heat and light. Here's a typical reaction:
[Fuel + O{2} \rightarrow CO{2} + H_{2}O]
- Example: Combustion of methane: \[CH_4(g) + 2O_2(g) \rightarrow CO_2(g) + 2H_2O(g)\]
In summary, each type of chemical reaction provides a framework to understand how chemicals interact under various conditions. Synthesis reactions demonstrate the formation of compounds from simpler substances; decomposition shows the breakdown of complex molecules; displacement reactions highlight the competition between elements; double displacement reactions illustrate ionic exchanges; and combustion reactions reveal the exothermic process of rapid oxidation. By understanding these five core reactions, one gains insight into the vast and complex world of chemical changes.
What is the difference between a synthesis and a decomposition reaction?

+
A synthesis reaction involves the combination of simpler substances to form a more complex compound, whereas a decomposition reaction breaks down a single compound into two or more simpler substances.
Can a reaction be both endothermic and exothermic?
+
Yes, a reaction can be both endothermic and exothermic at different stages. However, the net energy change will classify it as either endothermic (absorbing heat) or exothermic (releasing heat).
How can one determine if a reaction is likely to be a combustion reaction?

+
If a substance is being reacted with oxygen and produces CO2 and H2O as main products along with energy release, it’s most likely a combustion reaction.
Why do single displacement reactions occur?

+
These reactions occur due to the varying reactivity of elements. An element will displace another in a compound if it is more reactive than the element it is displacing.
What role does energy play in chemical reactions?

+
Energy is critical in chemical reactions. It can be absorbed (endothermic) to break bonds or released (exothermic) when new bonds form. Energy also influences the speed and feasibility of reactions.



