5 Key Answers for Economics Demand Worksheet

Understanding the dynamics of demand in economics can be a complex task, often requiring a deep dive into consumer behavior, market conditions, and economic principles. For students of economics or anyone with a keen interest in how markets work, grasping the fundamentals of demand can provide a strong foundation. Here, we'll explore five key answers for an economics demand worksheet, which covers essential concepts and scenarios frequently encountered in studies or real-life applications.
Economics Demand Worksheet Analysis
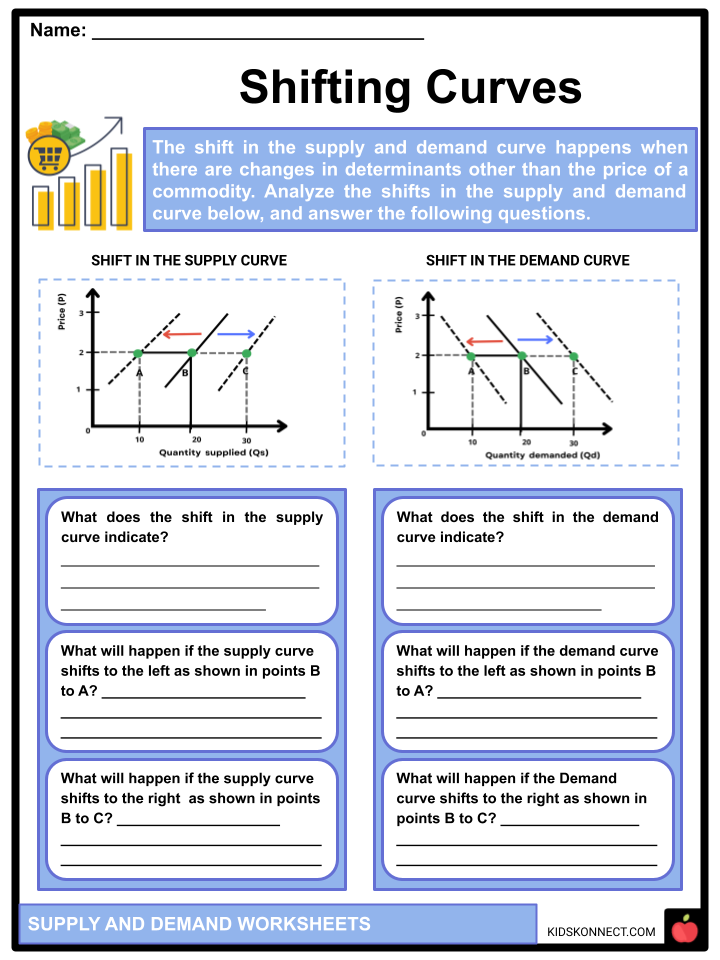
1. Understanding the Law of Demand

One of the most basic principles in economics is the Law of Demand, which states that, ceteris paribus (all else being equal), an increase in the price of a good or service will lead to a decrease in the quantity demanded of that good or service, and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be visualized on a demand curve, where:
- Y-axis shows the price.
- X-axis displays the quantity demanded.
Here, as price decreases, the quantity of the good that consumers are willing to buy increases, illustrating the consumer’s sensitivity to price changes.
2. Substitution and Income Effects

When prices change, there are two primary effects on consumers:
- Substitution Effect: As the price of a product rises, consumers will start to substitute it with cheaper alternatives. Conversely, if a product’s price falls, it becomes more appealing relative to substitutes.
- Income Effect: Price changes affect the consumer’s purchasing power. For instance, if the price of a good falls, consumers effectively have more money to spend, potentially increasing the quantity demanded of this good.
3. Factors Affecting Demand

Demand doesn’t solely depend on price. Other factors influence it as well:
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Consumer Income | Increased income can lead to higher demand for normal goods. |
| Tastes and Preferences | A shift in consumer preferences can increase or decrease demand. |
| Number of Buyers | More buyers generally increase total demand. |
| Expectations of Future Prices | Anticipation of price increases might boost current demand. |
| Changes in Price of Related Goods | Substitutes and complements affect demand dynamics. |
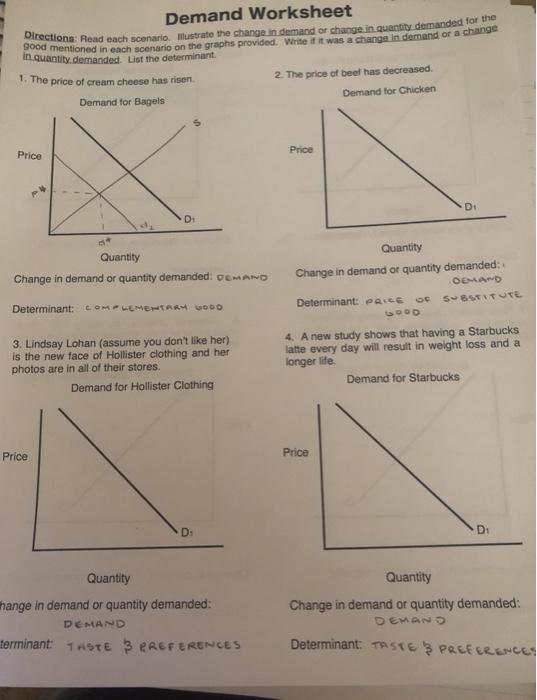
💡 Note: Keep in mind that these factors interact with each other, leading to complex demand scenarios in real markets.
4. Elasticity of Demand

Economic demand isn’t just about if people will buy something at a given price; it’s also about how much the quantity demanded changes when the price changes. This is where the concept of price elasticity of demand comes in:
- Elastic Demand: When the percentage change in quantity demanded is greater than the percentage change in price.
- Inelastic Demand: When the percentage change in quantity demanded is less than the percentage change in price.
Understanding elasticity helps businesses set prices and economists predict changes in consumer behavior.
5. Demand Shifters

Beyond the core factors, there are shifters of demand that can move the demand curve:
- Taxation: Increased taxes on goods can decrease demand.
- Advertising: Effective marketing can increase consumer demand.
- Income Distribution: How income is distributed affects the demand for different goods.
- Technology: Technological advancements can shift demand for both new products and existing ones (e.g., smartphones reducing demand for traditional cameras).
Wrapping up our exploration of demand concepts, it becomes clear that understanding demand is crucial for a comprehensive grasp of economic behavior. From the law of demand to the nuances of demand elasticity and the external forces that shift demand curves, these principles provide the tools for predicting and responding to market changes. The insights into consumer behavior, substitution and income effects, and the myriad factors influencing demand enable not only students but also business analysts and policymakers to make informed decisions.
What is the Law of Demand?

+
The Law of Demand states that, if all other factors remain constant, as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded will decrease, and vice versa.
What are the effects of a price change on demand?

+
The primary effects are the substitution effect, where consumers switch to alternative goods, and the income effect, where changes in price impact consumer purchasing power.
What does elasticity of demand mean?
+
Elasticity of demand measures how responsive the quantity demanded is to a change in price. It helps to understand whether demand for a product is sensitive or resistant to price changes.