Transfer of Thermal Energy Worksheet Answer Key Revealed
In the realm of educational resources for physics, chemistry, and various other sciences, worksheet answer keys play an indispensable role. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the Transfer of Thermal Energy Worksheet Answer Key, offering educators and students alike a detailed understanding of the core concepts surrounding thermal energy transfer.
What is Thermal Energy?


Thermal energy, often referred to as heat, is the energy present within a system due to the motion of particles. Understanding this concept involves recognizing:
- The internal kinetic energy of the particles within an object.
- How the transfer of thermal energy affects the state of matter.
- The different methods by which thermal energy is transferred: conduction, convection, and radiation.
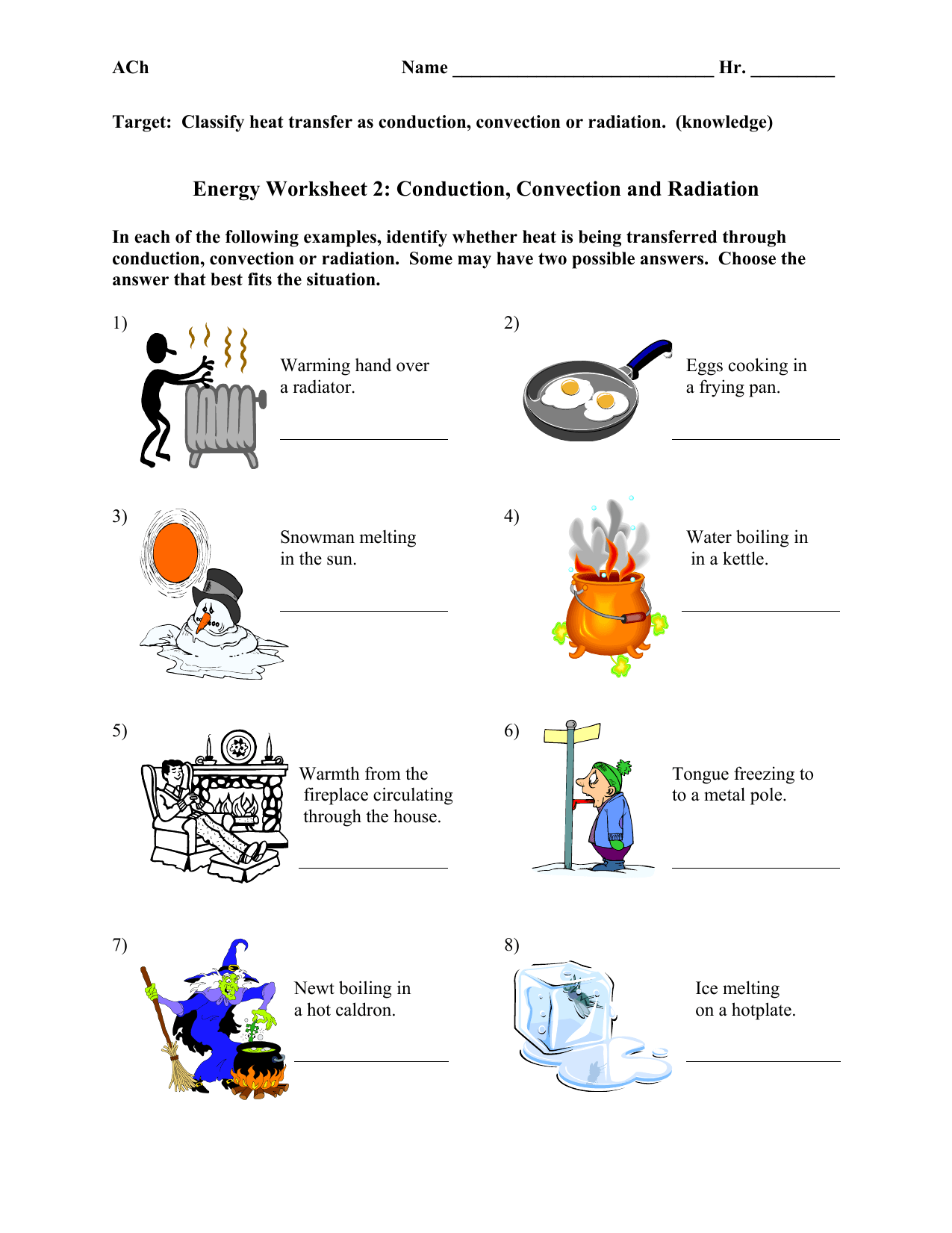
Conduction, Convection, and Radiation

| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Conduction | Transfer of heat through direct contact of particles. Examples include heating a metal spoon in hot tea. |
| Convection | Heat transfer through the movement of fluids (liquids and gases). Think of a pot of water heating on a stove. |
| Radiation | Heat transfer via electromagnetic waves, like the sun warming the Earth's surface. |

Answer Key: Understanding Each Question

Question 1: Conduction Example

In this question, students are often asked to identify an example of conduction. An answer might be:
A spoon heating up in a bowl of soup is an example of conduction, where heat from the soup is transferred to the spoon through direct contact.
Question 2: Convection Currents

Convection involves fluid movement, which is crucial in understanding phenomena like ocean currents or heating water in a pot. Here, students might be asked to explain:
The heat from the stove causes water at the bottom of the pot to become less dense, leading it to rise. This initiates a current where cooler water moves down to take its place, setting up a continuous loop.
Question 3: Radiation in Everyday Life

Radiation doesn’t require a medium for transfer. An example might be:
A person feeling the warmth of the sun on a cool day is experiencing thermal energy transfer through radiation.
Question 4: Mixed Scenarios

Some questions might present scenarios where multiple forms of energy transfer occur:
In a home, the heat from a fireplace:
- Conducts heat through the material of the fireplace.
- Radiates heat outwards into the room.
- Convects as the air circulates around the room.
Detailed Review and Notes

As you work through this worksheet, keep in mind:
💡 Note: Understanding the difference between the transfer methods can enhance comprehension of thermal dynamics.
📝 Note: Visual aids like diagrams can significantly aid in grasping these concepts.
Here are some key takeaways:
- Conduction requires direct contact and is most effective in solids.
- Convection involves fluid motion, making it more prevalent in liquids and gases.
- Radiation can travel through space, making it the primary method by which heat from the sun reaches Earth.
In summary, the transfer of thermal energy encompasses various phenomena, from the microscopic motions of particles to the macroscopic flow of fluids and the emission of electromagnetic waves. This worksheet and its answer key provide a structured way for students to engage with these concepts, ensuring a thorough understanding of the mechanisms and applications of thermal energy transfer.
What is the difference between heat and temperature?

+
Heat refers to the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another due to a temperature difference, while temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in an object.
Can thermal energy be transferred without mass movement?

+
Yes, through radiation, thermal energy can be transferred without mass movement. This is how the sun’s energy reaches Earth through the vacuum of space.
How can we insulate against heat loss?

+
Insulation can be achieved by:
- Using materials with low thermal conductivity (like wool or foam) to reduce conduction.
- Reducing air currents or convection through double glazing or insulation layers.
- Reflecting radiant heat with materials like aluminum foil.