5 Essential Transcription and Translation Worksheets with Answers

Introduction to Transcription and Translation Worksheets

Understanding transcription and translation is fundamental for students studying biology or molecular biology. These processes are the essence of gene expression, converting the information encoded in DNA into functional proteins. Here, we've compiled five essential transcription and translation worksheets with answers to enhance learning and comprehension of these intricate molecular processes.
Worksheet 1: Basics of Transcription

Let's dive into the first worksheet which explores the basics of transcription:
- Understanding RNA Polymerase: Students will identify the key enzyme involved in the process.
- Promoter Sequence: Explain how the transcription initiation site is recognized.
- Steps of Transcription: Outline initiation, elongation, and termination.

| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription? | To synthesize an RNA molecule complementary to a template DNA strand. |
| What are the stages of transcription? | Initiation, Elongation, Termination |

Worksheet 2: Codons and Anticodons
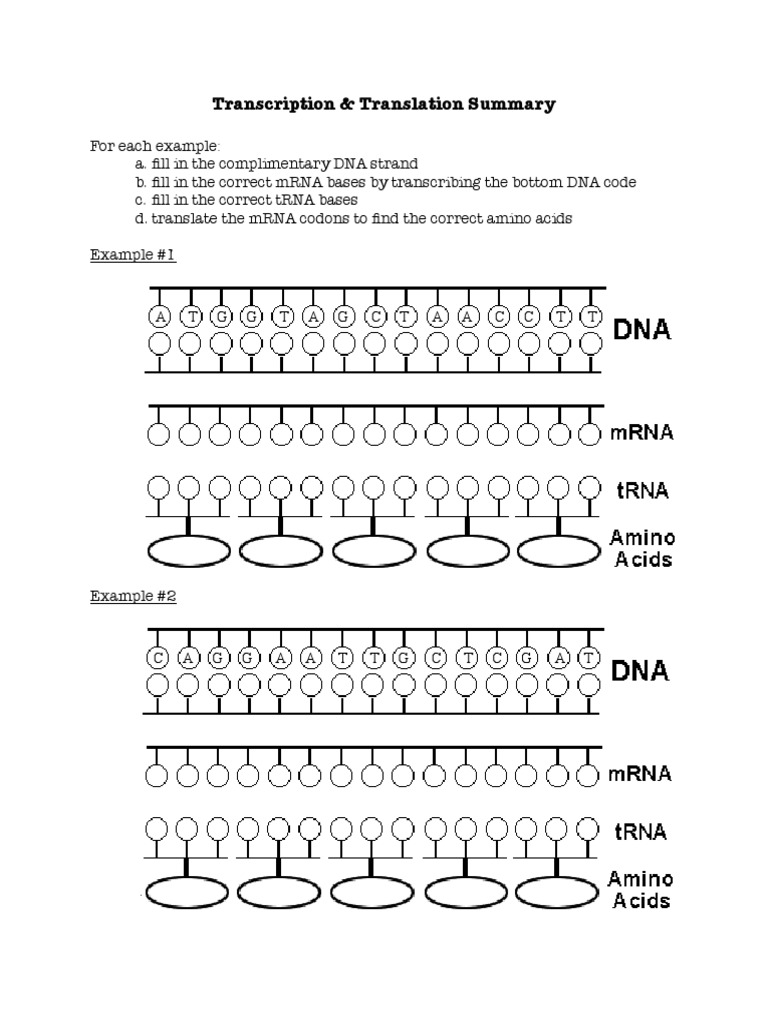
This worksheet focuses on codons and anticodons, vital for understanding translation:
- Codon Recognition: Students will learn about codons and how they are read by the ribosome.
- Anticodon: Understand the matching between tRNA anticodons and mRNA codons.
- Amino Acid Chart: Use of the codon table to determine amino acids from mRNA codons.

Worksheet 3: Translation Process

The third worksheet focuses on the detailed steps of translation:
- Initiation: Detail the steps from the binding of the small ribosomal subunit to the start codon.
- Elongation: Outline the cycle of amino acid addition to the growing polypeptide chain.
- Termination: Describe how translation ends with the recognition of a stop codon.
🧬 Note: Understanding translation requires knowledge of mRNA, tRNA, ribosomes, and the genetic code.
Worksheet 4: Genetic Mutations and Impact on Protein Synthesis

This worksheet explores how mutations affect transcription and translation:
- Types of Mutations: Explain silent, missense, and nonsense mutations.
- Impact on Protein: Discuss how mutations can alter protein structure and function.
Worksheet 5: Advanced Genetic Regulation

The final worksheet delves into the more intricate aspects of gene regulation:
- Regulatory Elements: Introduce enhancers, silencers, and operons.
- Gene Expression Control: Explain how cells control when and how much of each gene's product is made.
📚 Note: Regulation mechanisms can involve transcription factors, DNA methylation, and histone modification, which influence the transcription rate.
In wrapping up, these worksheets provide a comprehensive understanding of the molecular processes involved in converting genetic information into functional proteins. They guide students from the basic mechanisms of transcription and translation to the impacts of genetic mutations and regulatory elements, fostering a deeper appreciation for the complexity and elegance of life at the molecular level. Whether for exam preparation or enhancing one's molecular biology knowledge, these worksheets with answers serve as invaluable tools for students and educators alike.
What is the difference between transcription and translation?

+
Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of mRNA. Translation, on the other hand, is the process by which the genetic code contained in mRNA is read by the ribosome to produce a chain of amino acids, forming proteins.
Why are codons and anticodons important?

+
Codons are sequences of three nucleotides in mRNA that specify an amino acid, whereas anticodons are complementary sequences on tRNA molecules that bind to these codons during translation. This precise matching ensures the accurate synthesis of proteins according to the DNA’s genetic code.
How do genetic mutations affect protein synthesis?

+
Genetic mutations can change the sequence of nucleotides in DNA, which might alter the mRNA and, consequently, the amino acid sequence during protein synthesis. This can result in altered protein function, ranging from negligible changes to severe diseases or conditions.