Climate vs Weather: Simplified Worksheet for All Ages
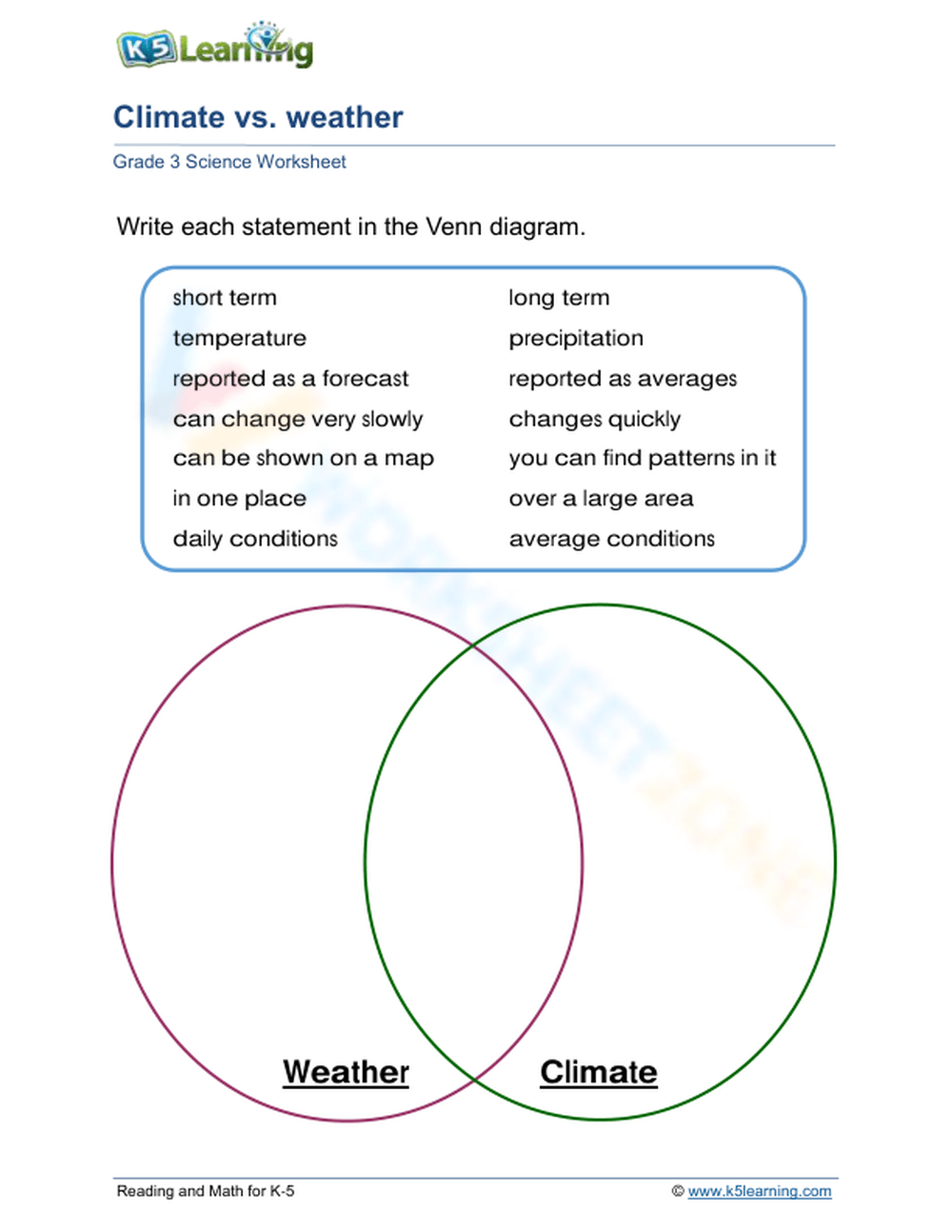
The concepts of climate and weather often get confused, but they are fundamentally different. Let's dive into what these terms mean, how they differ, and how they impact our environment and daily lives.
Understanding Weather

Weather refers to the atmospheric conditions at a specific time and place. Here are some of its key attributes:
- Short-term: It changes from day to day, sometimes even from hour to hour.
- Observable: You can see, feel, and measure the weather through elements like temperature, humidity, wind, precipitation, and air pressure.
To visualize weather changes, imagine looking out your window and noting:
- If it's sunny or overcast,
- How warm or cold it feels,
- Whether it's raining, snowing, or dry,
- How calm or windy the day is.
Understanding Climate

Climate, on the other hand, describes the average weather conditions for a much longer period, typically over decades or longer:
- Long-term: It's the weather pattern you expect in a region based on historical data.
- Patterns: Climate includes elements like average temperature, rainfall, humidity, wind, and seasonal variations.
Here are some ways to think about climate:
- Do you expect winters to be snowy in your area?
- Is your region known for hot summers or mild ones?
- Does it tend to rain heavily during certain months?
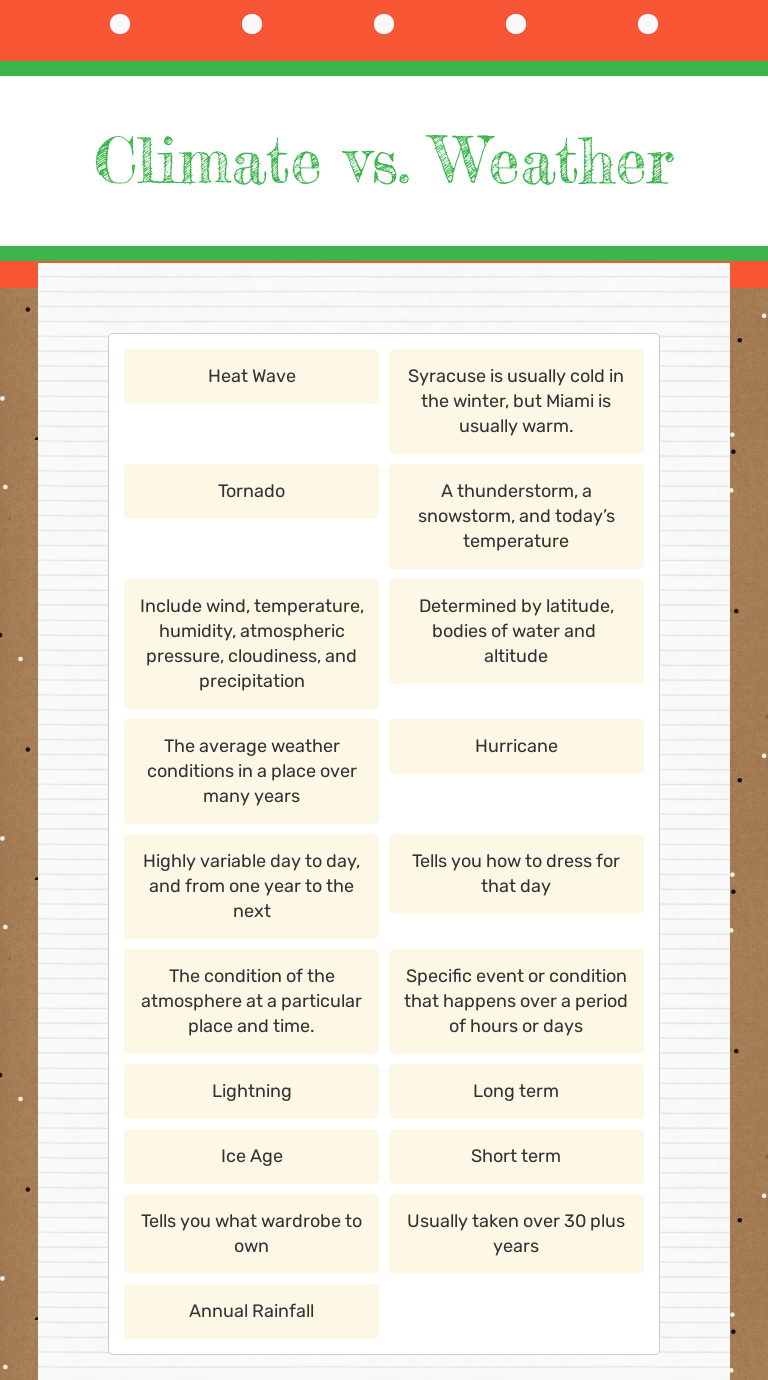
Differences Between Weather and Climate

| Attribute | Weather | Climate |
|---|---|---|
| Time Scale | Hours to Days | Years to Decades |
| Changeability | Can change rapidly | Changes slowly over time |
| Measurement | Immediate conditions | Averages over long periods |
| Influence | Local, transient events | Global, consistent patterns |

How Climate Impacts Weather
While weather can change abruptly, the underlying climate of a region influences the weather patterns:
- In a tropical climate, you might expect wet and dry seasons, leading to regular rainy weather.
- Regions with desert climate will more often have hot, dry weather.
- Coastal areas often experience more temperate weather due to the moderating effects of the sea.
Climate and Weather in Our Lives

Understanding both climate and weather is crucial for:
- Agriculture: Farmers need to know the long-term climate to plant crops and expect seasonal changes in weather to manage their fields.
- Travel: Knowing the climate helps plan trips, while current weather forecasts ensure safe travel conditions.
- Infrastructure: Cities plan their buildings and infrastructure considering both weather extremes and long-term climatic trends.
📝 Note: Weather events like hurricanes or snowstorms are part of the short-term weather, but their frequency or intensity might be influenced by climate trends.
Understanding the distinction between climate and weather is not just an academic exercise; it has practical implications for planning, managing risks, and preparing for the future. Knowing the difference helps us:
- Better prepare for natural disasters by understanding both the expected weather and the shifting climate.
- Plan sustainable urban and rural development that takes into account long-term climatic changes.
- Engage in meaningful climate change discussions, distinguishing between transient weather events and persistent climate shifts.
Can weather influence climate change?
+
While individual weather events don’t directly change the climate, the aggregation of weather data over long periods helps us understand climate trends. Extreme weather events might become more frequent or intense due to climate change.
How do we measure climate?

+
Climate is measured through extensive datasets over long periods, using parameters like temperature, precipitation, humidity, and wind patterns, usually collected from weather stations, satellites, and historical records.
What role does the greenhouse effect play in climate?

+
The greenhouse effect is essential for keeping our planet warm. However, human activities increasing greenhouse gases enhance this effect, leading to climate change by trapping more heat in the atmosphere.
How does climate affect ecosystems?

+
Climate shapes ecosystems by determining what species can live where, affecting migration, breeding cycles, and even leading to changes in biodiversity due to shifting climate zones.
What can individuals do to mitigate climate change?

+
Reducing personal carbon footprints, advocating for climate action, and supporting green technologies can make a difference. Actions like reducing travel emissions, conserving energy, and supporting reforestation efforts are key steps.