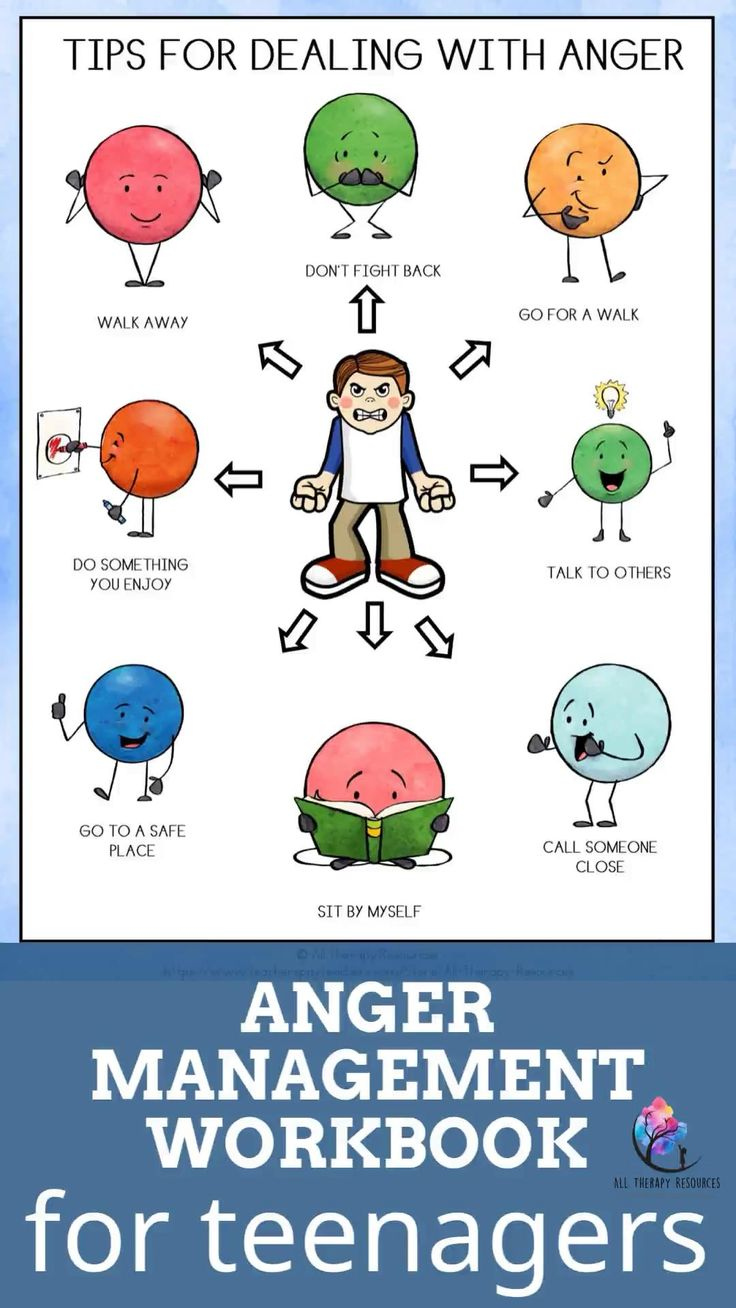
5 Key Answers on Early Human Origins in Africa

The question of human origins has long fascinated scientists, historians, and enthusiasts alike. When delving into the discussion of where humans come from, a central theme emerges: Africa is the cradle of our species. In this comprehensive guide, we'll uncover five key answers to some of the most pressing questions about early human origins in Africa, illustrating how our ancestral journey began in this diverse and rich continent.
The Out of Africa Hypothesis

At the heart of our understanding of human evolution is the Out of Africa hypothesis. This theory posits that modern humans, Homo sapiens, originated in Africa and eventually spread to other continents, replacing archaic human populations elsewhere.
- Timing: Approximately 200,000 years ago.
- Evidence: Genetic, fossil, and archaeological evidence supports this hypothesis, including:
- Mitochondrial DNA studies indicating a common African origin for all humans.
- The oldest Homo sapiens fossils found in East Africa.
- The absence of earlier human species traits in current populations outside of Africa.
The Role of Environment

Africa’s varied environments played a crucial role in the development and spread of early humans:
- Habitat Variability: From the lush savannahs to dense forests and arid deserts, these environments promoted adaptability in human physiology and behavior.
- Climate Fluctuations: Climatic changes forced humans to develop tools and strategies for survival, enhancing brain development.
Technological Advances

The technological leap known as the Middle Stone Age saw humans develop:
- Advanced Tools: Transition from simple flake tools to finely crafted points, scrapers, and blades, showing a significant cognitive leap.
- Fire Usage: Control and use of fire, which allowed for cooking, warmth, and protection, improving survival rates.
🔍 Note: The technological advances of this period indicate not just physical evolution but also cultural and social evolution, as groups of humans began to live together more effectively.
Genetic Diversity

Africa’s genetic landscape provides a window into our past:
- Greater Genetic Diversity: Due to the longer history of human presence, Africans possess the most genetic diversity among humans worldwide.
- Insights into Migrations: Genetic markers reveal patterns of migration, indicating multiple waves of emigration from Africa.
| Ethnic Group | Region | Estimated Time of Divergence |
|---|---|---|
| San People | Southern Africa | 130,000 years ago |
| Himba People | Namibia | 80,000-55,000 years ago |
| Nilotes | Eastern Africa | ~30,000 years ago |

Cultural Foundations

The roots of human culture can be traced back to:
- Artistic Expression: Early examples of art, like cave paintings in South Africa, show the beginnings of symbolic thought.
- Language Development: The emergence of complex vocal communication, crucial for the organization and transmission of knowledge.
In summary, Africa is not only the birthplace of humanity but also the stage for significant evolutionary events. The genetic, cultural, and technological advancements that occurred in Africa have shaped who we are today. These key answers illustrate the profound impact of this continent on human history, leaving us with an appreciation for our common origins and the interconnectedness of our species.
Why is Africa considered the cradle of human evolution?

+
Africa is considered the cradle of human evolution because fossil evidence, genetic studies, and the oldest known archaeological sites for modern humans are found there. The genetic diversity in African populations, coupled with the archaeological record, suggests that humans originated in Africa and then migrated elsewhere.
How did early humans adapt to different environments in Africa?
+
Early humans in Africa adapted to varied environments through the development of sophisticated tool use, control over fire, and the evolution of social structures that facilitated group living and survival. They also developed physical adaptations like sweat glands to help with temperature regulation.
What technological advances occurred during the Middle Stone Age?

+
The Middle Stone Age marked advances in tool-making, including the creation of more sophisticated tools like points and blades, as well as the widespread use of fire, which had profound implications for diet, social interaction, and technological innovation.
How does genetic diversity relate to human origins?

+
Genetic diversity provides clues about human origins by showing the length of time different populations have been separated from each other. Greater genetic diversity in Africa points to a longer evolutionary history there, supporting the idea that humans evolved in Africa and then spread to other regions.
Can we trace back to our exact place of origin?

+
While we can’t pinpoint an exact location where all humans originated, genetic and fossil evidence suggest an origin in East or Southern Africa. This region, encompassing places like Ethiopia, Kenya, and South Africa, is rich in findings that support human origins.