Temperature Conversion Guide: Answers Included

The topic of temperature conversion can seem mundane, yet its significance becomes clear when we talk about travel, cooking, weather forecasting, scientific research, and numerous other applications. Whether you're a chef, a traveler, or just a curious mind, knowing how to convert between the different temperature scales can prove incredibly useful. This guide will walk you through the primary temperature scales – Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin – and provide you with detailed instructions on how to convert temperatures between these scales.
Understanding Temperature Scales

Celsius ©:
- Formally known as Centigrade, this scale is named after Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer.
- The freezing point of water is set at 0°C and the boiling point at 100°C at standard atmospheric pressure.
- Each degree Celsius is equal to one degree Kelvin.
Fahrenheit (F):
- Named after the German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit.
- The freezing point of water is 32°F, and the boiling point is 212°F at standard atmospheric pressure.
- Each degree Fahrenheit is smaller than a degree Celsius or Kelvin.
Kelvin (K):
- Used predominantly in scientific environments.
- The Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, which is approximately -273.15°C, where molecular motion theoretically stops.
- The size of one degree Kelvin is the same as one degree Celsius.
⚠️ Note: Remember, you can't have a negative temperature in Kelvin, as it represents absolute zero, the lowest possible temperature.
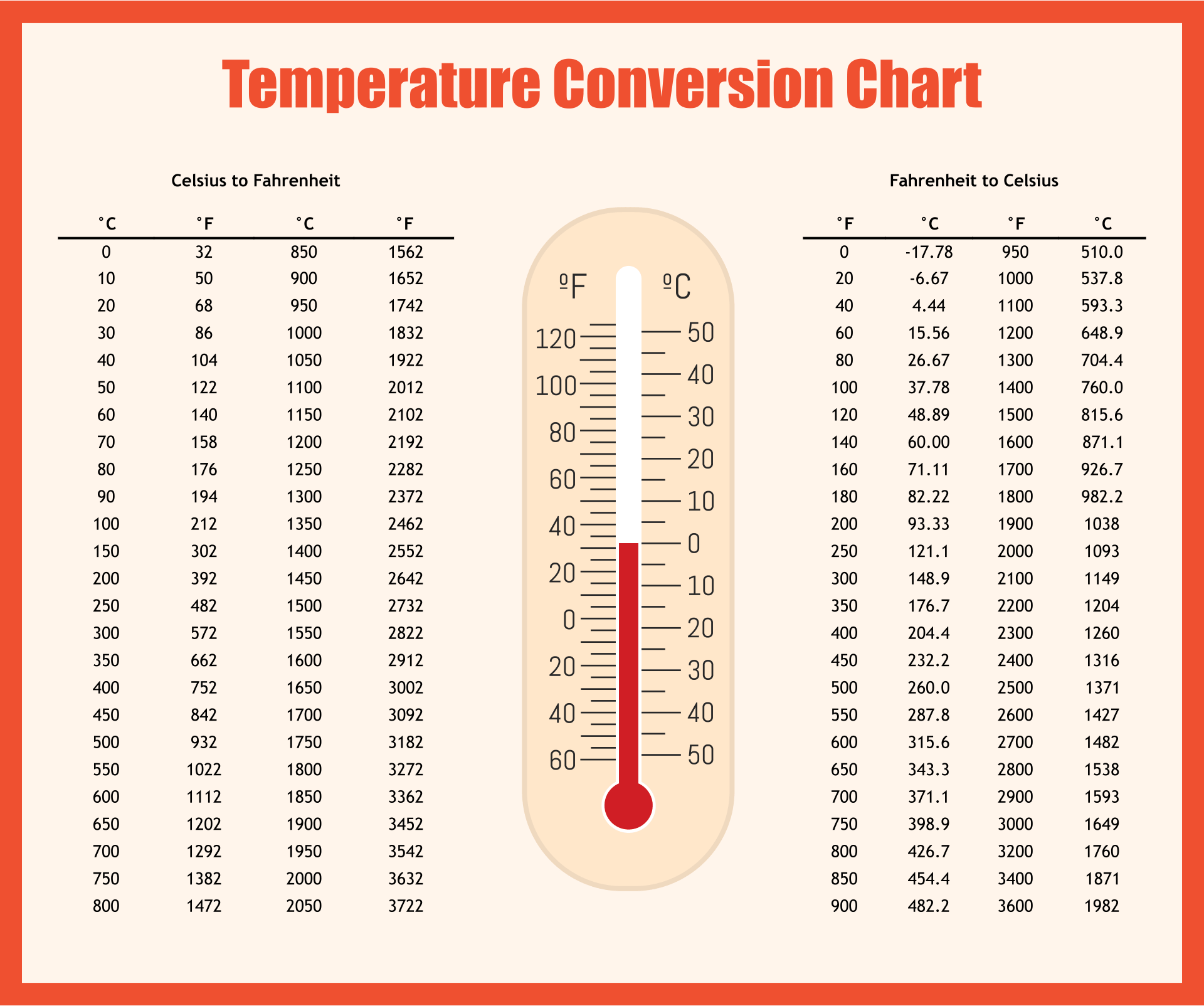
Converting Between Celsius and Fahrenheit
The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential, given their widespread use in different countries:
Celsius to Fahrenheit

The formula for converting from Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
Fahrenheit = (Celsius × 9⁄5) + 32Fahrenheit to Celsius
To convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius, use the following formula:
Celsius = (Fahrenheit - 32) × 5⁄9🔥 Note: 0°C is equivalent to 32°F, which can be a helpful reference point when converting temperatures.
Converting Between Celsius and Kelvin

Given that the difference between Celsius and Kelvin is merely an offset:
Celsius to Kelvin

Kelvin = Celsius + 273.15Kelvin to Celsius

Celsius = Kelvin - 273.15❄️ Note: Absolute zero in Kelvin (0 K) corresponds to -273.15°C.
Converting Between Fahrenheit and Kelvin

For those instances when you need to convert directly between Fahrenheit and Kelvin:
Fahrenheit to Kelvin

Kelvin = (Fahrenheit + 459.67) × 5⁄9Kelvin to Fahrenheit

Fahrenheit = (Kelvin × 9⁄5) - 459.67| Temperature Conversion | Formula |
|---|---|
| Celsius to Fahrenheit | F = (C × 9/5) + 32 |
| Fahrenheit to Celsius | C = (F - 32) × 5/9 |
| Celsius to Kelvin | K = C + 273.15 |
| Kelvin to Celsius | C = K - 273.15 |
| Fahrenheit to Kelvin | K = (F + 459.67) × 5/9 |
| Kelvin to Fahrenheit | F = (K × 9/5) - 459.67 |

Practical Examples of Temperature Conversion
Here are a few real-world scenarios to help you visualize temperature conversion in practice:
- Baking: If a recipe calls for 180°C, converting to Fahrenheit gives you 356°F, allowing you to adjust your oven settings accurately.
- Health: Normal human body temperature is around 37°C or 98.6°F, useful for understanding health readings.
- Weather: When planning a trip to a country using a different scale, converting temperature helps you pack appropriately.
👨🔬 Note: Even with digital tools for conversion, understanding the math behind it enhances your overall knowledge and can be handy during emergencies.
The mastery of temperature conversion not only bridges different scales but also different cultures, professions, and scientific disciplines. This knowledge allows for better communication, accurate science, and everyday convenience. Whether you're dealing with weather reports from another country, setting your thermostat, or conducting experiments, the ability to swiftly convert between Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin is invaluable. By keeping these conversion formulas in mind and understanding the practical applications, you're now equipped to handle any temperature-related challenge with confidence.
Why is there a need for different temperature scales?
+
Historically, different cultures and scientists developed temperature scales based on their observations and needs. Celsius is widely used in scientific communities and everyday life in most countries, while Fahrenheit remains prevalent in a few places like the United States due to historical reasons. Kelvin, used primarily in science, starts at absolute zero, providing a theoretical foundation for absolute temperature measurement.
Is it better to use Celsius or Fahrenheit?

+
It depends on context. Celsius is more straightforward for scientific and global communication, as it aligns with the metric system. Fahrenheit, however, has a finer granularity, which can be useful for measuring weather or body temperature with greater precision. There isn’t a “better” scale, but rather scales suited to different applications.
Can you use temperature conversion in everyday life?

+
Absolutely. From setting cooking temperatures to interpreting weather forecasts or understanding health conditions, temperature conversion is a practical skill. It’s particularly useful when dealing with international travel, scientific data, or engaging with content from different countries.